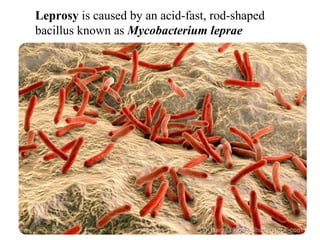
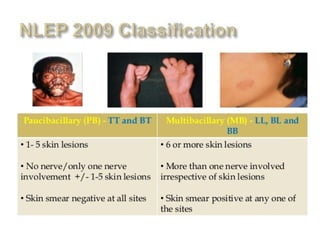
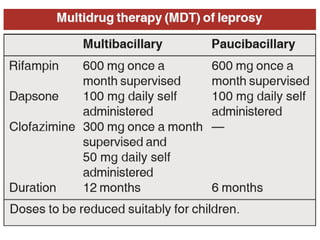
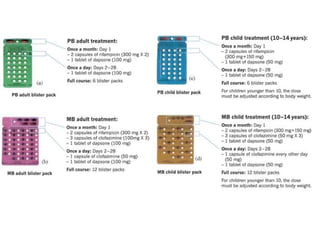
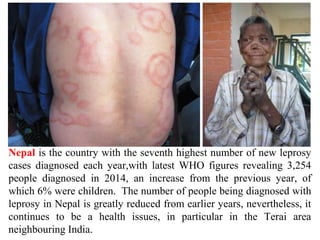
Leprosy is caused by Mycobacterium leprae and M. lepromatosis bacteria, which mainly affect the skin, mucus membranes, and nerves. It is classified based on the Ridley-Jopling system and can be paucibacillary or multibacillary. Leprosy is curable through multidrug therapy recommended by the WHO, which combines dapsone, rifampicin, and clofazimine. Nepal still has a significant number of new leprosy cases each year, particularly in the Terai region bordering India, though rates have decreased overall.