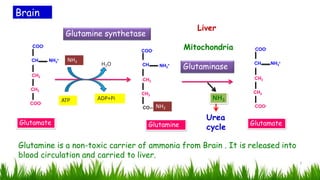
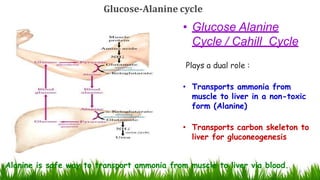
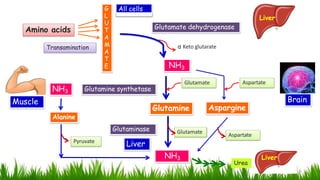
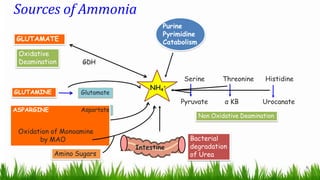
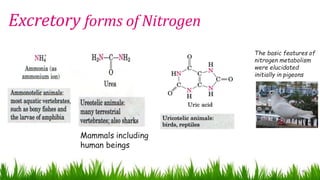
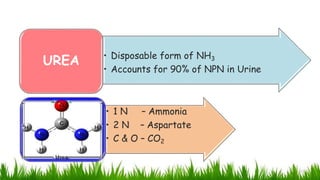
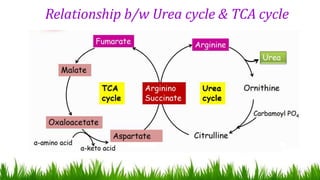
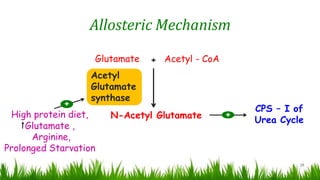
1) Ammonia is produced in tissues and transported to the liver where it is detoxified to urea in the urea cycle. The three main transport forms are glutamate, glutamine, and alanine.
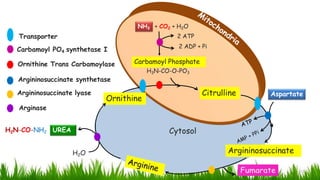
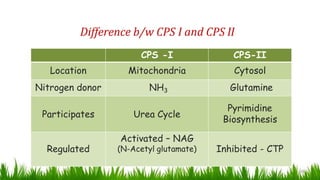
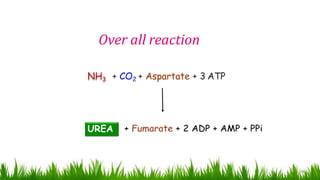
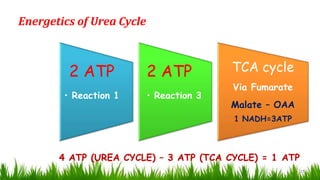
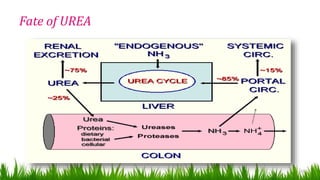
2) The urea cycle converts ammonia and carbon dioxide to urea using enzymes in the liver mitochondria and cytoplasm. This prevents ammonia toxicity.
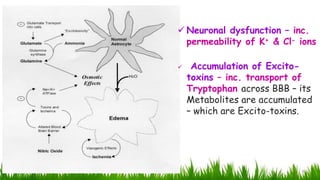
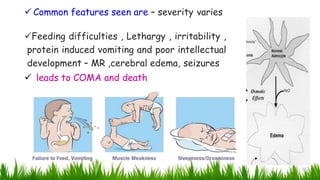
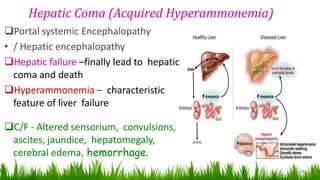
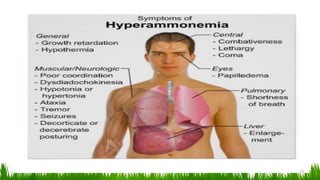
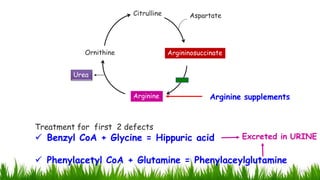
3) Genetic defects in urea cycle enzymes can cause hyperammonemia, leading to complications like cerebral edema, seizures, coma and death if not treated. Treatment aims to reduce ammonia levels and promote its excretion through alternate pathways.