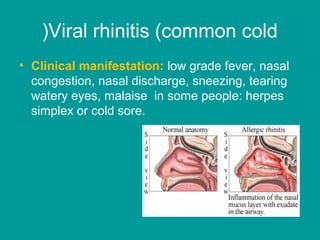
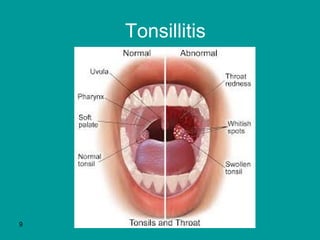
Here are the nursing diagnoses and interventions:
Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for infection related to fever and sore throat
Interventions:
1. Monitor vital signs every 4 hours to assess for worsening infection.
2. Administer antibiotics as prescribed to treat infection.
Nursing Diagnosis: Pain related to sore throat
Interventions:
1. Provide warm saline gargles every 2 hours for throat pain relief.
2. Administer pain medications such as acetaminophen as needed.