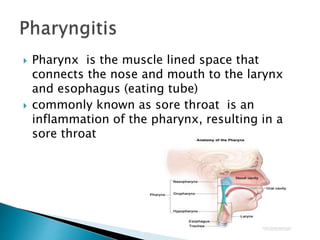
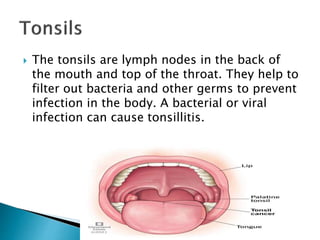
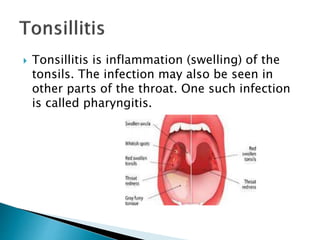
This document discusses upper respiratory disorders including sinusitis, pharyngitis, and tonsillitis. It defines each disorder and describes their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. Sinusitis is inflammation of the sinuses caused by bacterial/viral infection or allergies. Pharyngitis (sore throat) is commonly caused by viral infections. Tonsillitis is swelling of the tonsils due to bacterial/viral infection. Treatment involves antibiotics, antivirals, pain/fever medication, and surgery in severe cases. Nursing care focuses on medication administration, hygiene, comfort measures, and education.