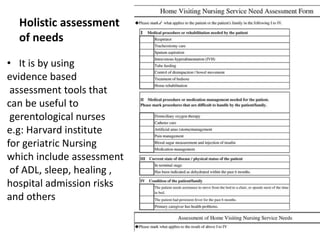
This document discusses a holistic model for gerontological nursing. It emphasizes caring for the whole person, including their physiological, psychological, social, and spiritual dimensions. A holistic assessment considers factors like activities of daily living, sleep, healing abilities, and hospital admission risks. Optimal health involves activities that promote well-being of body, mind, and spirit through connections with others and spiritual fulfillment. The nurse's role includes comprehensive care that addresses all needs, from physical to social and spiritual. Legal and ethical issues in gerontological nursing are also examined.