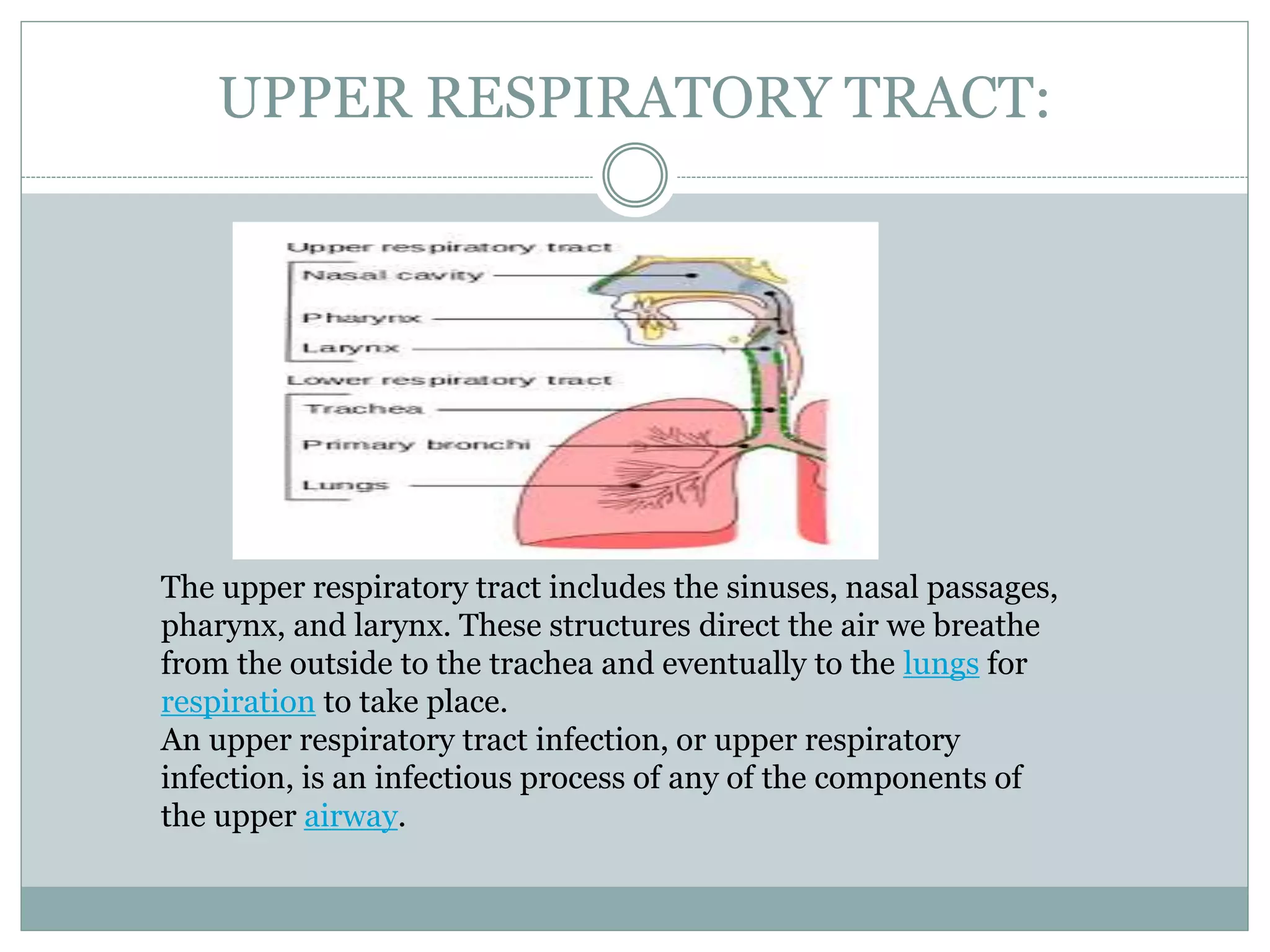
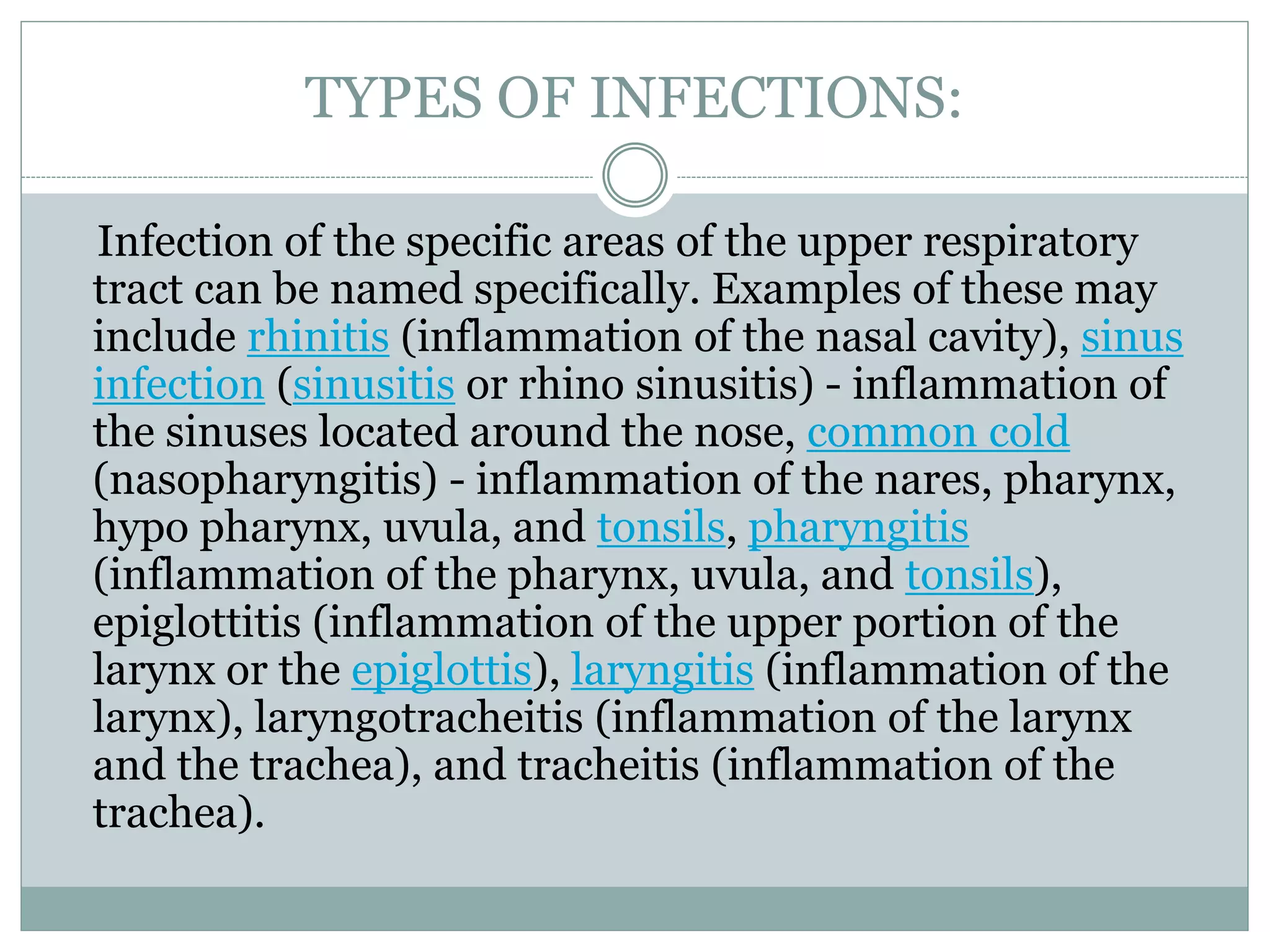
1. An upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) is an infection of the sinuses, nasal passages, pharynx, or larynx. Common symptoms include cough, sneezing, nasal congestion and discharge.
2. URTIs are usually caused by viruses like rhinoviruses, influenza, and respiratory syncytial virus. Bacteria like Streptococcus can also cause certain URTIs like strep throat.
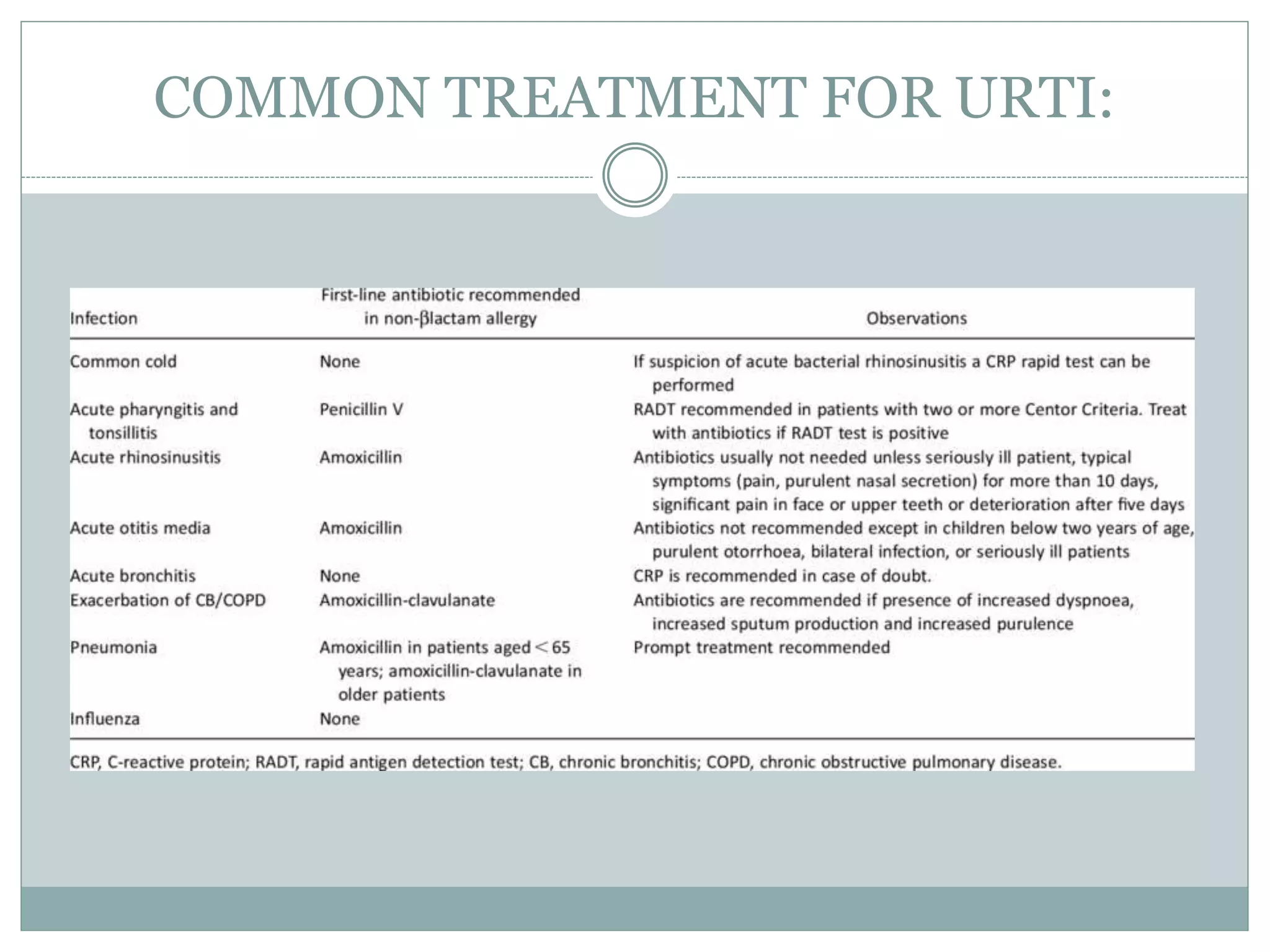
3. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms through rest, increasing fluid intake, and over-the-counter medications. Antibiotics are only effective for bacterial infections. Most URTIs resolve on their own within 1-2 weeks.