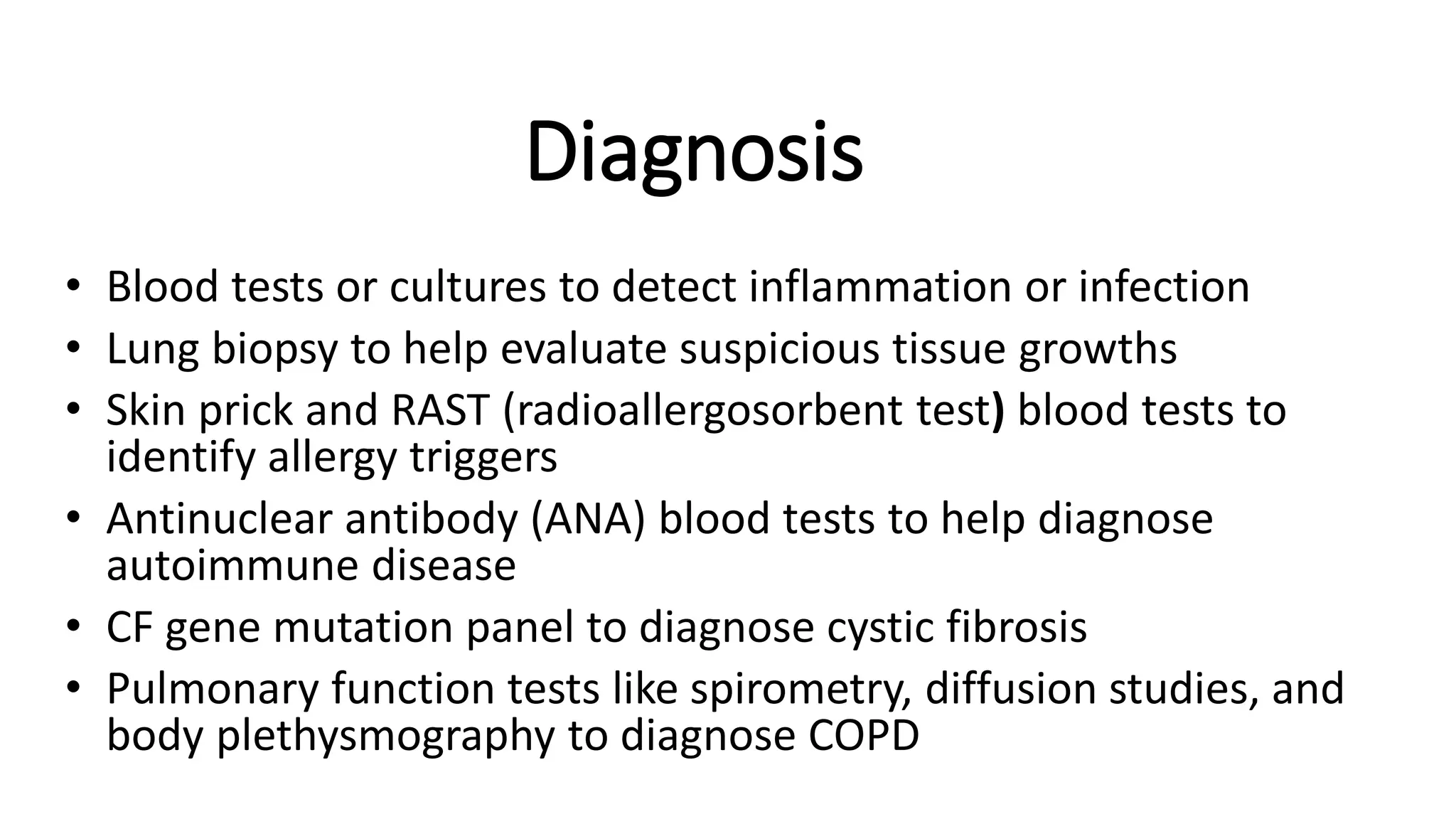
Reactive airway disease is a condition characterized by reversible airway narrowing caused by external triggers. It includes conditions like asthma and describes respiratory symptoms in infants too young for diagnostic testing. Common symptoms include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath and mucus in the airways. It is often caused by irritants like pet dander, pollen, smoke, or changes in weather. Diagnosis involves tests to check for infection or inflammation while treatment focuses on relieving symptoms through emergency oxygen, bronchodilators, epinephrine injections, or avoiding triggers.