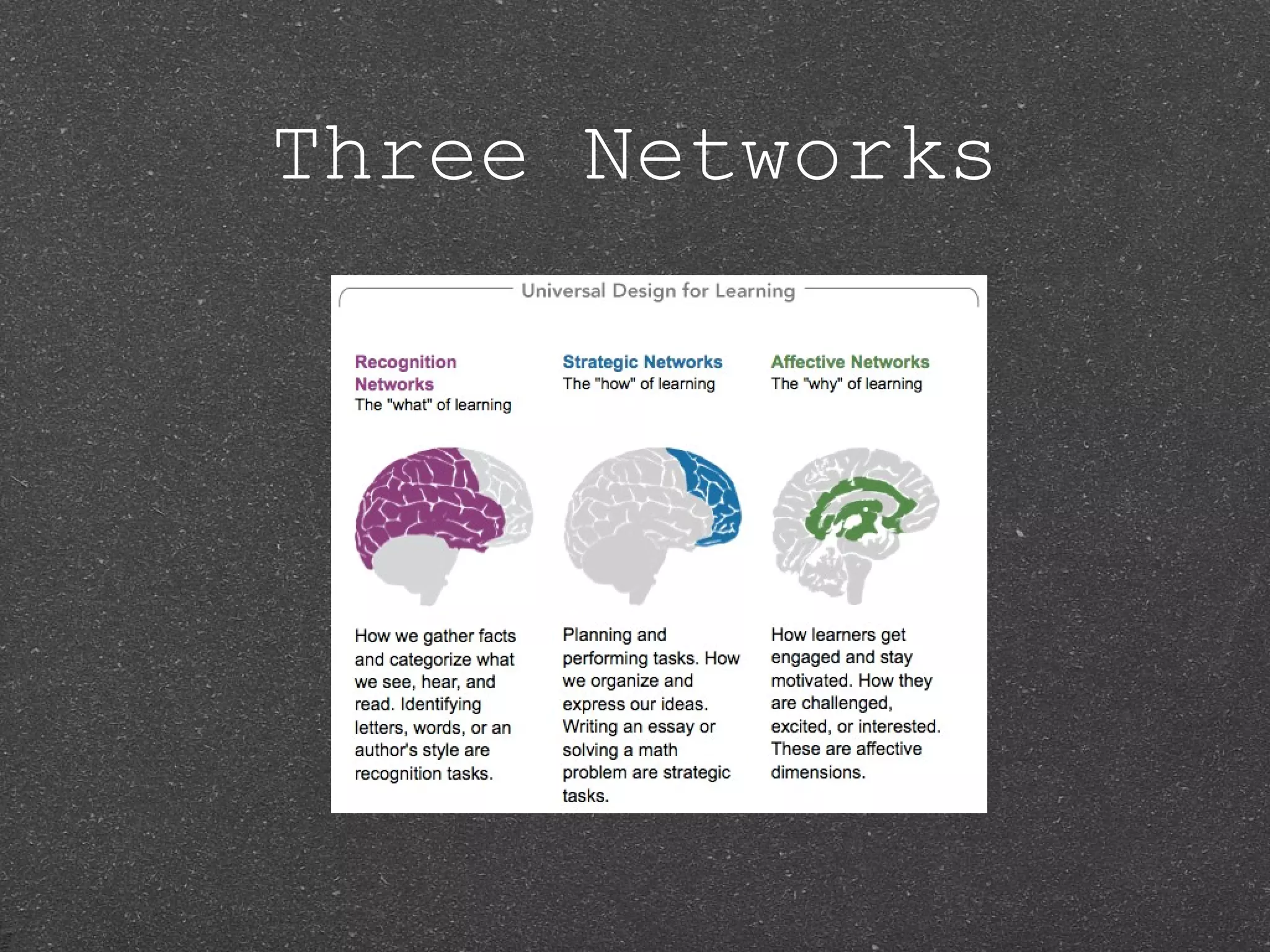
This document discusses Universal Design for Learning (UDL), which aims to make learning accessible to all students by providing multiple means of representation, engagement, and action/expression. UDL draws on principles of universal design applied to education. It encourages flexible approaches and materials to meet diverse learner needs. The document outlines the three UDL principles and brain research supporting its approach. It also provides examples of technology tools like the UDL Book Builder that can help implement UDL principles. Overall, UDL seeks to address learner diversity and make lessons more relevant through customizable, student-centered instructional methods and materials.