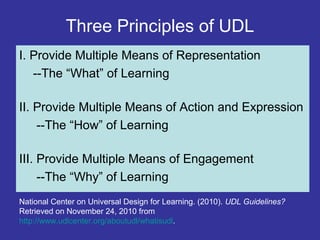
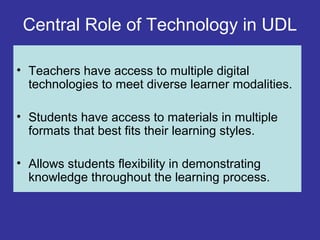
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) provides guidelines for creating flexible curricula to meet the needs of all learners by customizing instructional goals, methods, materials, and assessments. UDL originated in architecture to increase accessibility and was applied to education to reduce barriers for diverse learners. UDL principles include providing multiple means of representation, action and expression, and engagement. Technology plays a central role in UDL by allowing teachers to meet different learner modalities and students to access materials in different formats matching their learning styles.







![Implications for Learner
Differences for Instruction/Learning
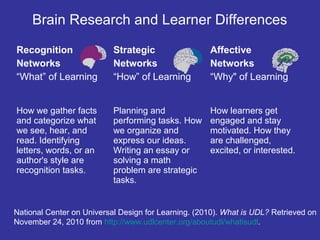
• The brain processes information differently to different
parts of the brain according to the type of task.
• Students are different in how they recognize and
organize information, and in how they engage with
information.
• Teachers should identify ways to address the strengths
and weaknesses of each students and provide
customized instruction to meet each student’s needs.
Laureate Education, Inc. (Executive Producer). (2009). Program 13. Universal
Learning by Design. [Motion Picture]. Reaching and Engaging All Learners
Through Technology. Baltimore: Dr. David Rose.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/app4lowej-101125150755-phpapp01/85/App4-lowej-11-320.jpg)


![References
CAST Teaching Every Student. (2010). Tools and Activities. Retrieved November 24, 2010 from
http://www.cast.org/teachingeverystudent/tools/
Laureate Education, Inc. (Executive Producer). (2009). Program 13. Universal Learning by Design.
[Motion Picture]. Reaching and Engaging All Learners Through Technology. Baltimore: Dr. David
Rose.
National Center on Secondary Education and Transition. (2010).Universal Design: A strategy to
support students access to the general education curriculum. Retrieved on November 24 from
http://www.ncset.org/publications/viewdesc.asp?id=707
National Center on Universal Design for Learning. (2010). UDL Guidelines? Retrieved on November
24, 2010 from http://www.udlcenter.org/aboutudl/whatisudl
Baltimore: Dr. David Rose.
National Center on Universal Design for Learning. (2010). What is UDL? Retrieved on November 24,
2010 from http://www.udlcenter.org/aboutudl/whatisudl.
UDL National Universal Design for Learning Taskforce. (2010). Universal Design for Learning.
Retrieved on November 25, 2010 from http://www.advocacyinstitute.org/UDL/.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/app4lowej-101125150755-phpapp01/85/App4-lowej-15-320.jpg)