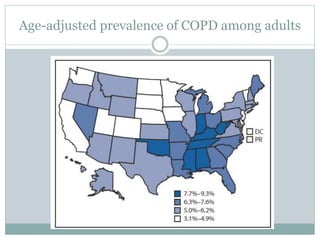
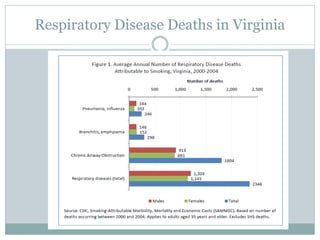
This document provides information about asthma and COPD. It defines asthma as a disorder causing airway swelling and narrowing leading to wheezing, shortness of breath, and coughing. Common asthma triggers include allergens like dust and pollen. There are four categories of asthma severity. Around 25 million Americans have asthma. COPD includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema and is often caused by smoking. It is underdiagnosed, with around 15 million Americans affected. Both conditions impose high health costs and reduce quality of life. Public health initiatives aim to improve diagnosis and management through education.