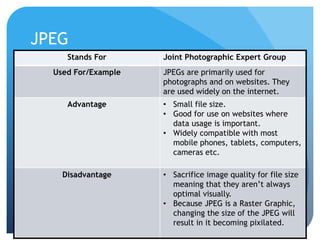
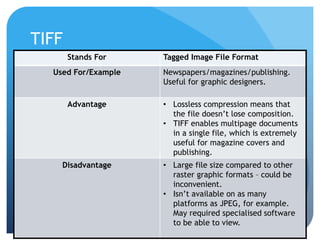
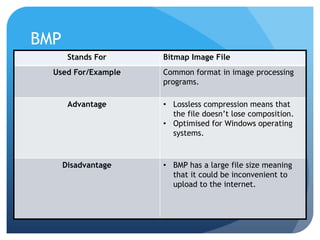
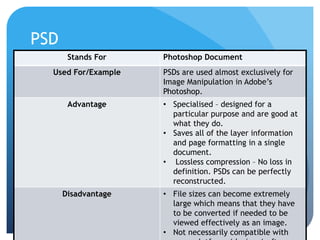
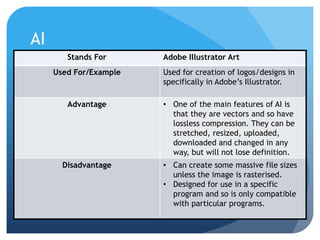
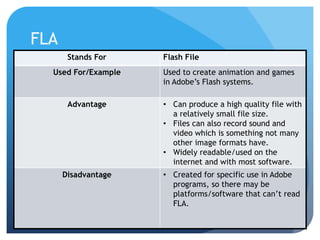
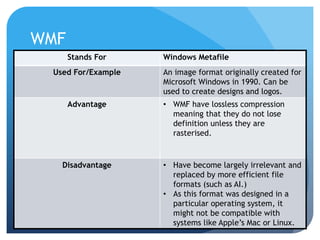
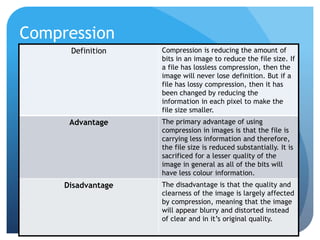
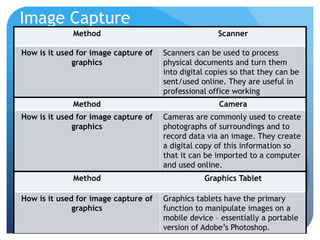
This document provides information on different types of digital graphics file formats including raster graphics like JPEG, TIFF, GIF and BMP as well as vector graphics like PSD, AI, FLA and WMF. It explains the key differences between raster and vector graphics, when each format type would be used, advantages and disadvantages of each format. It also discusses topics like compression, image capture methods, file optimizing, factors that influence file size, and best practices for file naming and asset management.