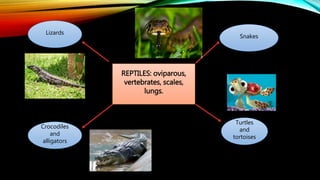
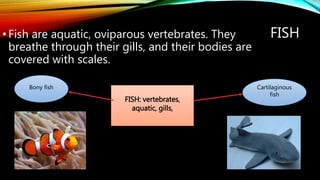
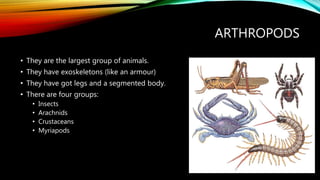
The document discusses different types of animals throughout the world. It covers vertebrate animals like mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish, as well as invertebrate animals like sponges, cnidarians, worms, molluscs, echinoderms and arthropods. For each group, it describes key characteristics like their nutrition, reproduction, physical features and habitats. The purpose is to educate about different animal classifications so students can choose one to research and describe its features.