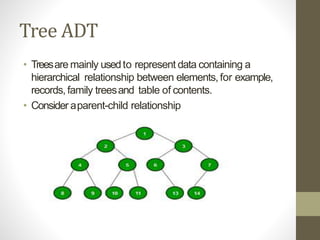
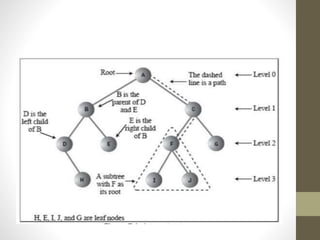
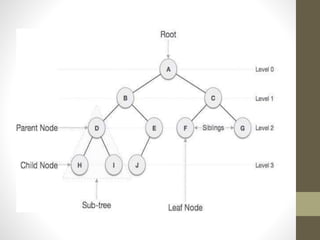
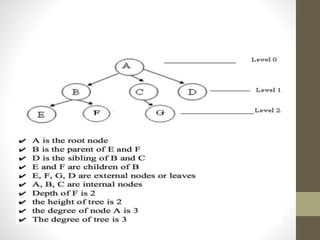
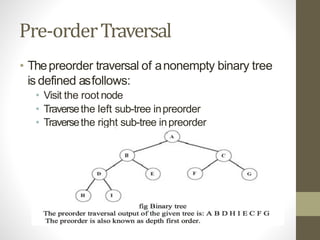
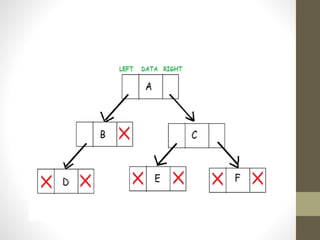
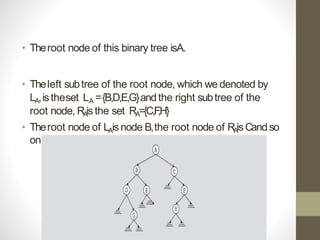
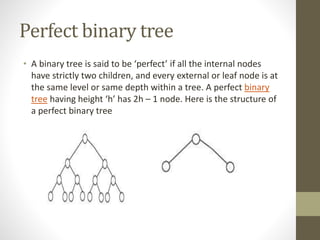
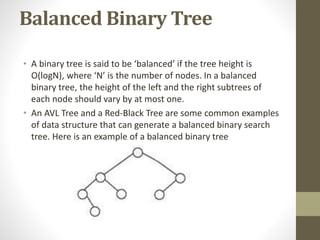
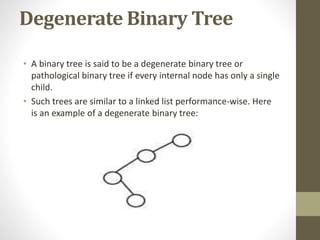
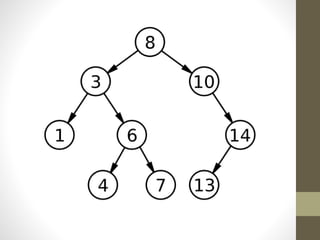
Trees are hierarchical data structures used to represent data with parent-child relationships. A tree has a root node with child nodes, and each non-root node has one parent. Trees allow fast search, insertion, and deletion similar to linked lists but can also maintain ordering like arrays. Binary trees restrict nodes to at most two children, enabling efficient search, storage of expressions, and routing algorithms. Binary search trees organize nodes to enable fast lookups based on key values.