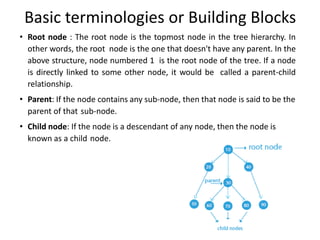
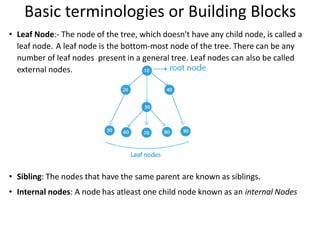
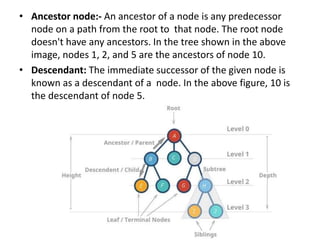
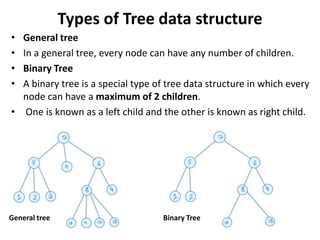
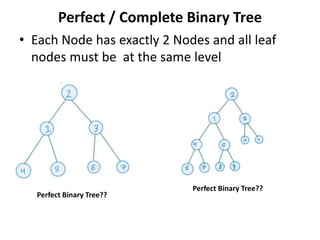
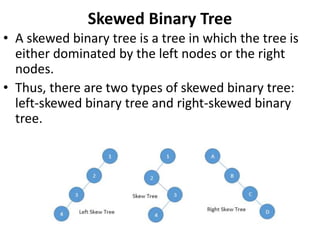
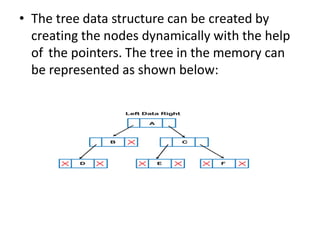
A tree is a hierarchical data structure consisting of nodes connected by edges. The topmost node is the root node. Nodes can have child nodes below them in the hierarchy. Leaf nodes have no children. Binary trees restrict nodes to have at most two children. Different types of binary trees include full, perfect, degenerate, and skewed binary trees based on how nodes are structured. Trees are useful data structures that can represent hierarchical relationships.