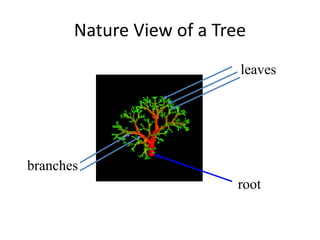
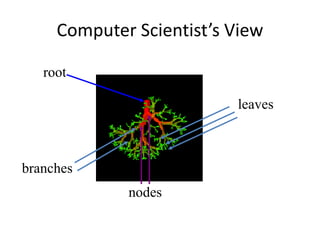
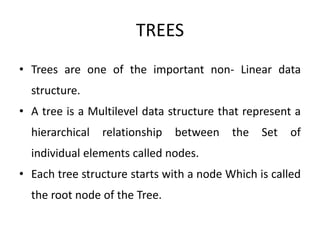
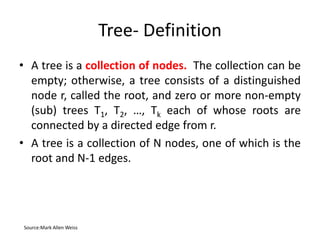
1. Trees are non-linear data structures that represent hierarchical relationships. They consist of nodes connected by edges, with one node designated as the root.
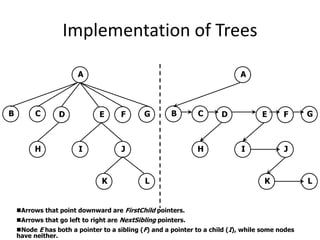
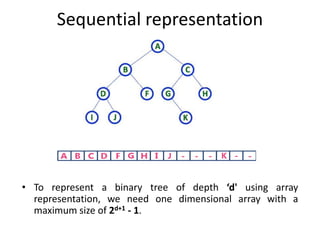
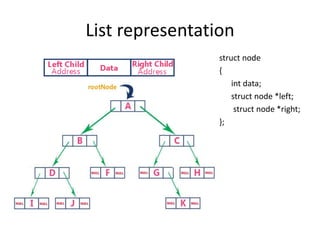
2. Trees can be represented using arrays or linked lists. Array representation requires knowing the height of the tree in advance, while linked lists do not waste memory but have slower access times.
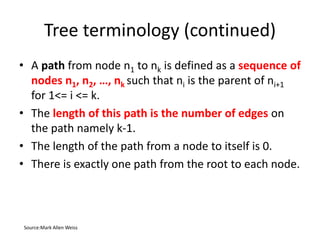
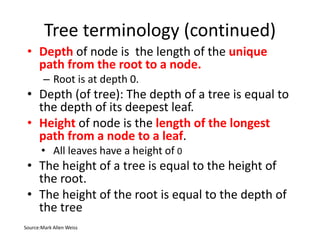
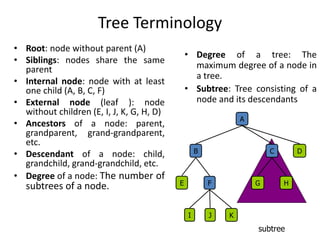
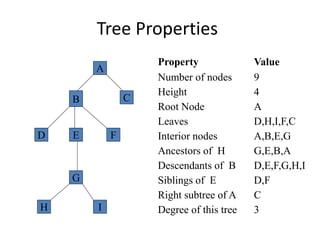
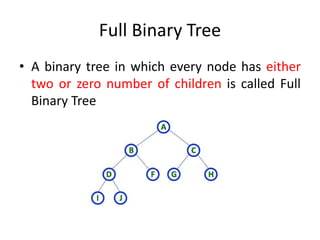
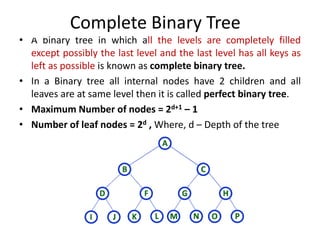
3. Common tree terminology includes root, leaf nodes, internal nodes, siblings, ancestors, descendants, depth, height, and subtrees. Binary trees restrict nodes to at most two children each.