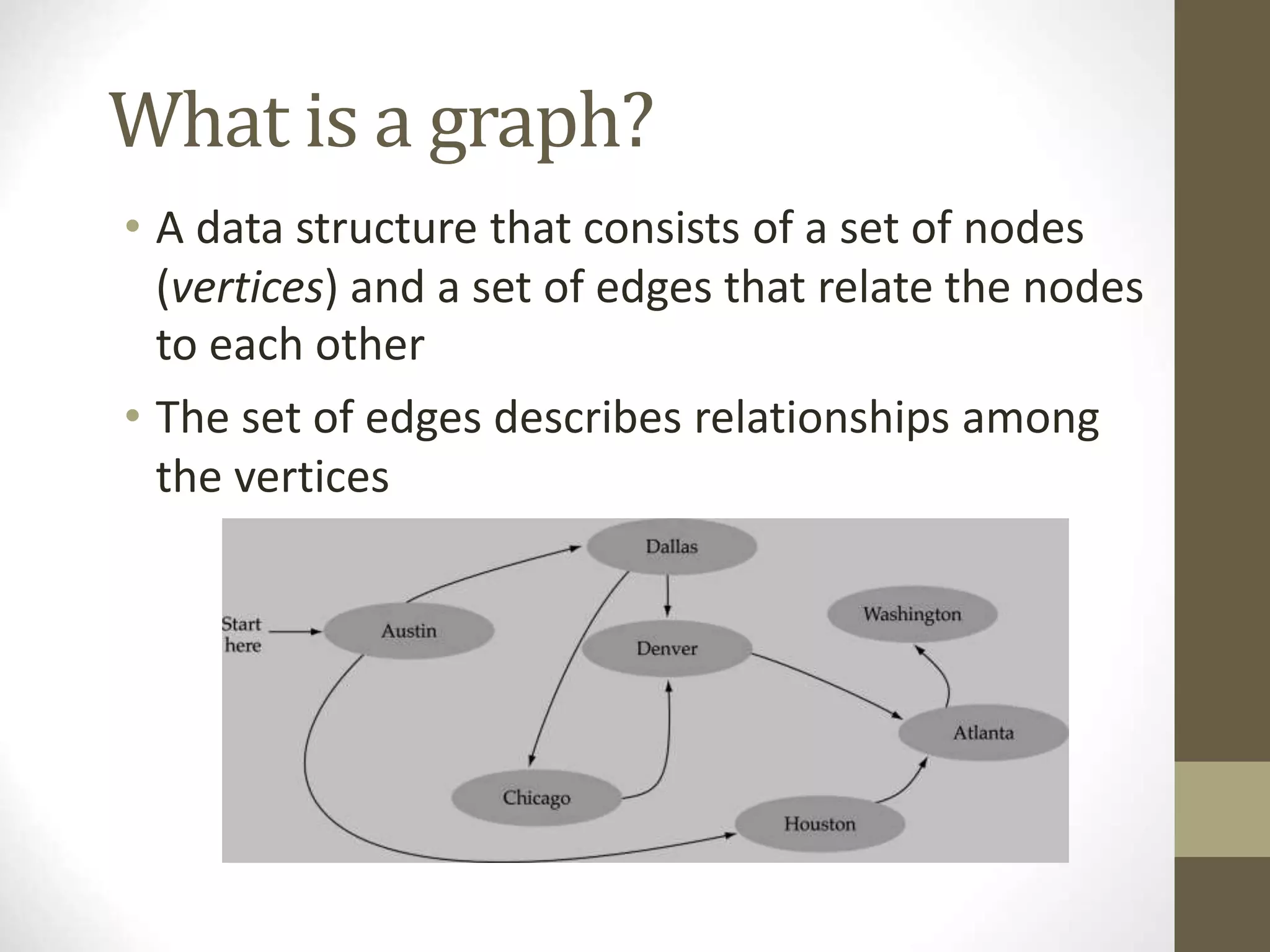
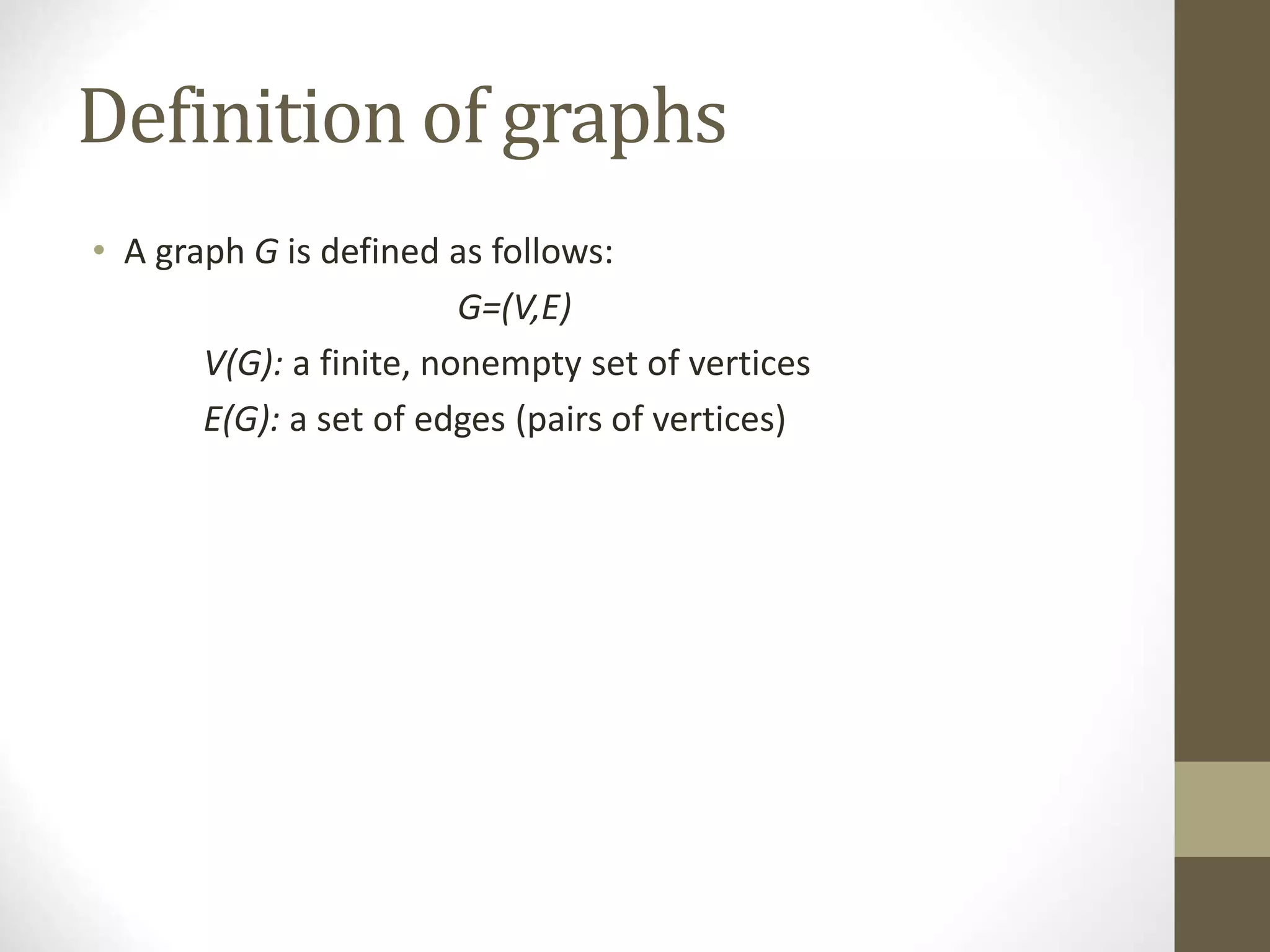
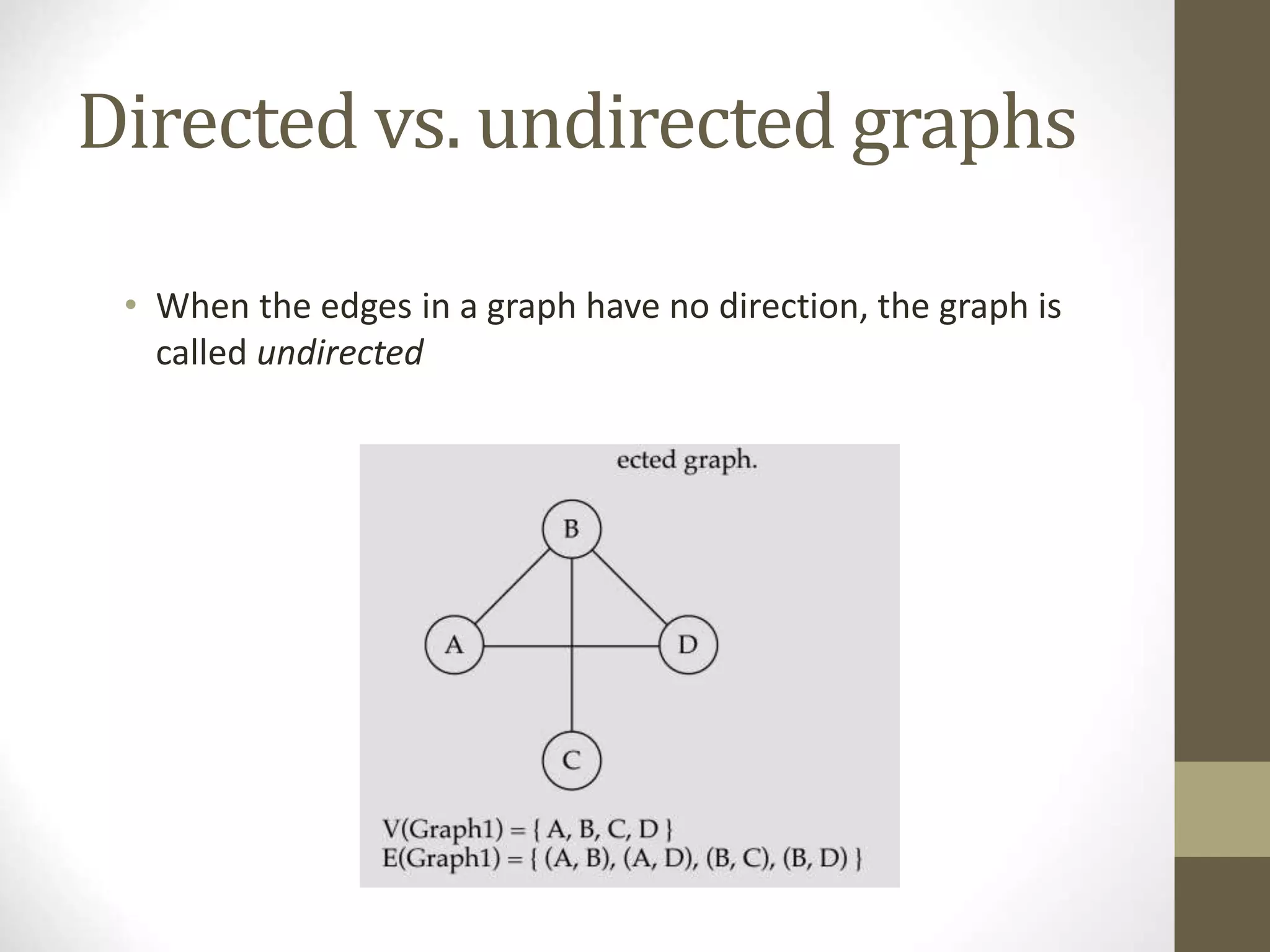
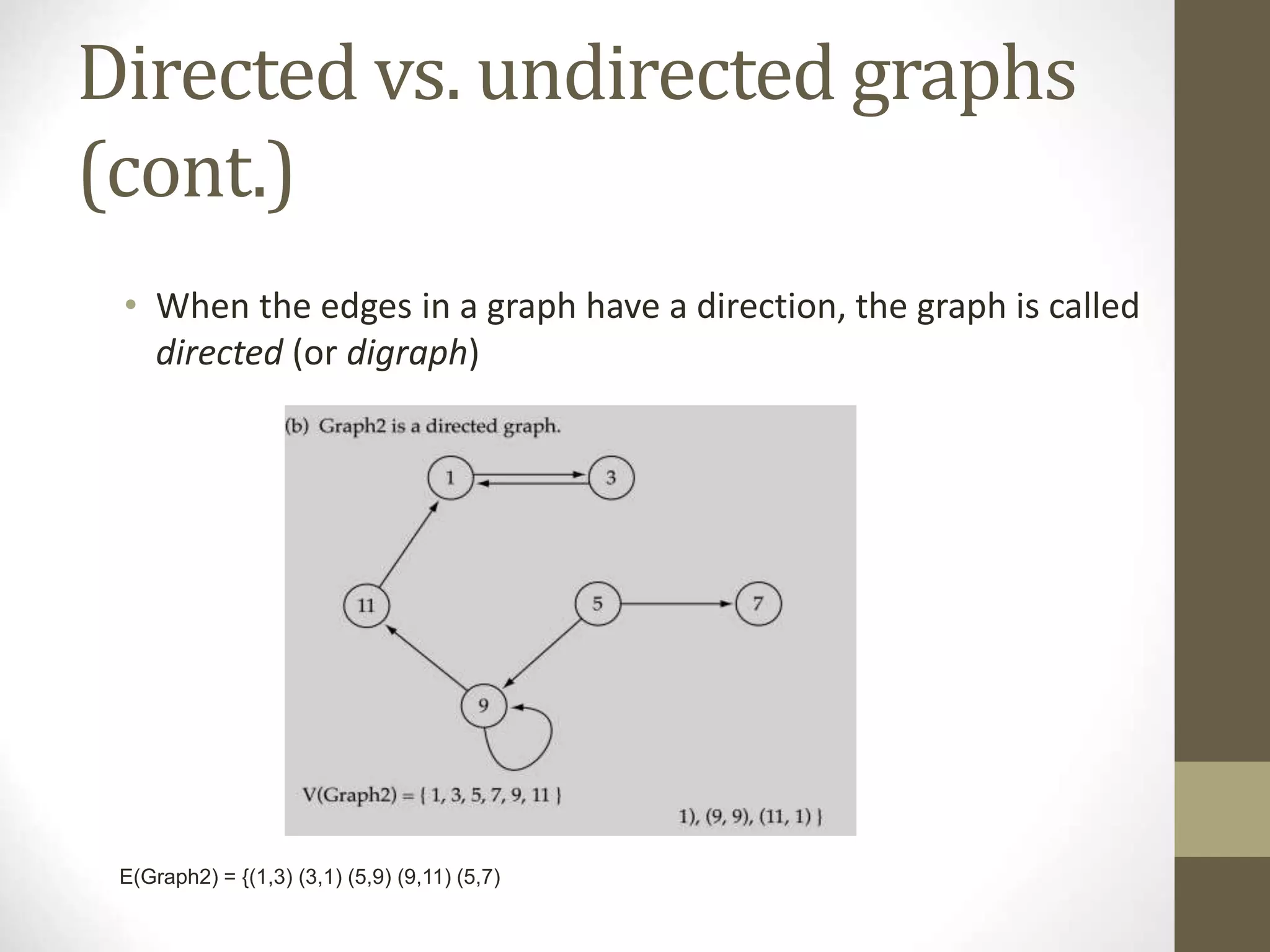
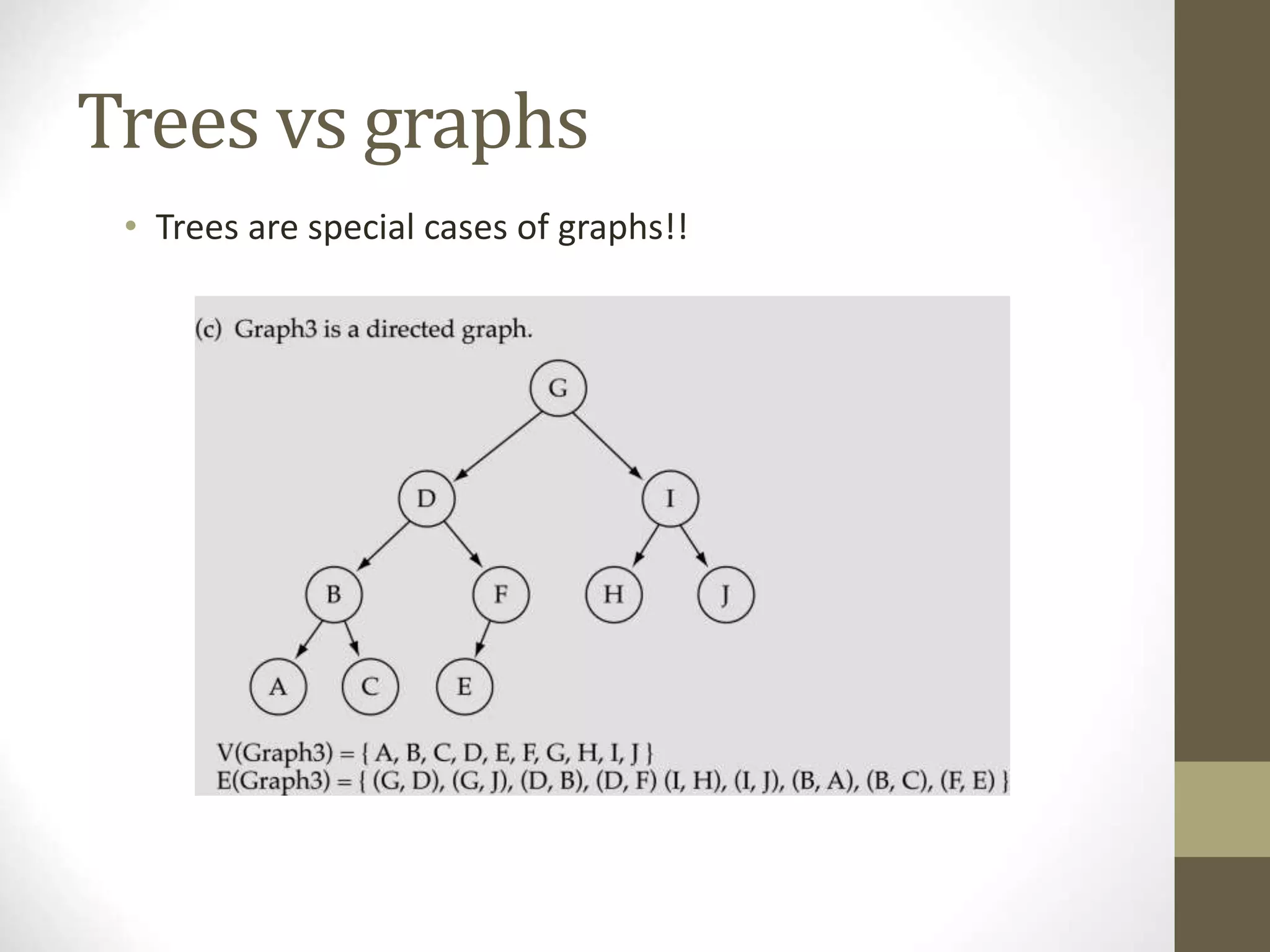
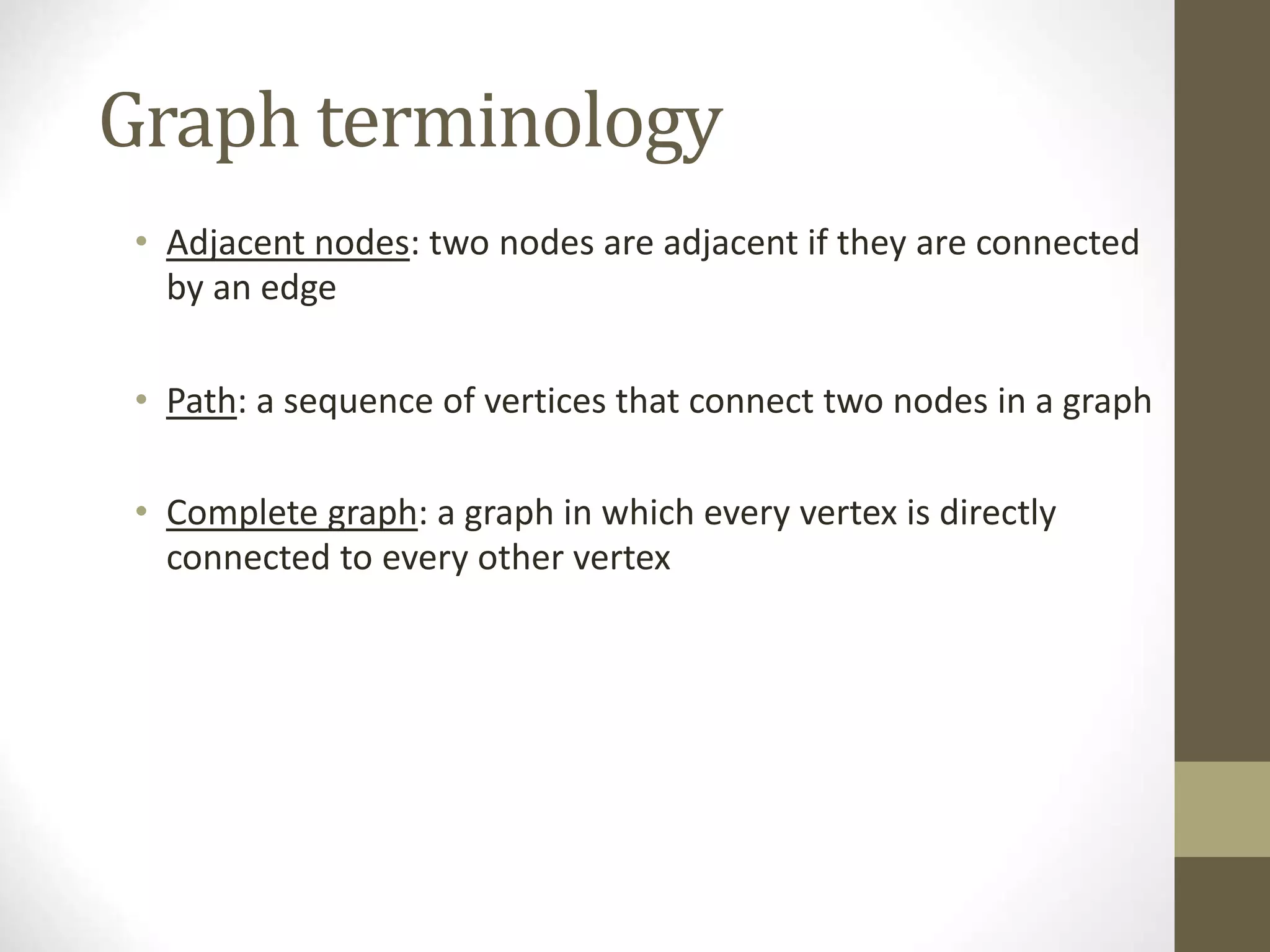
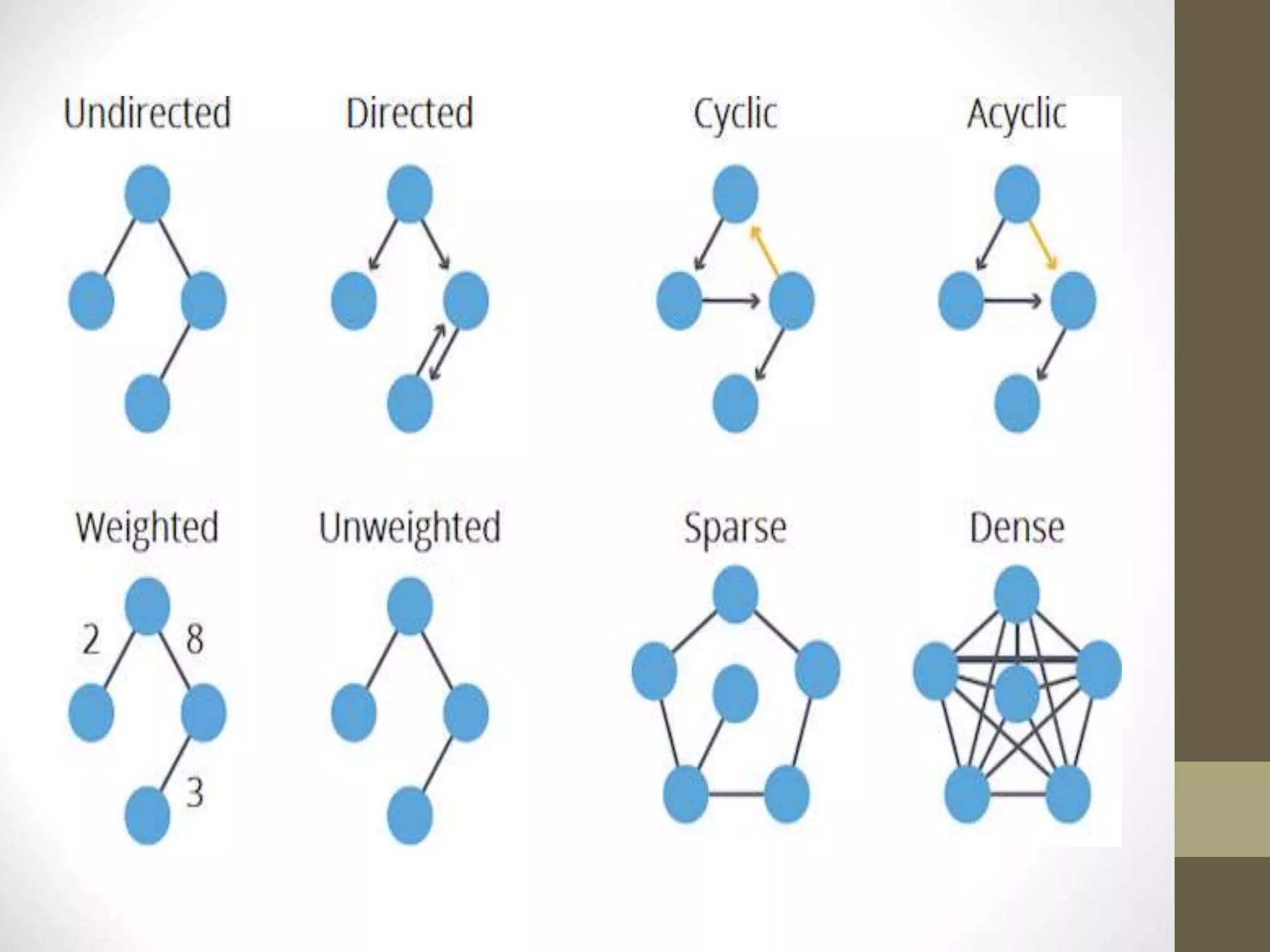
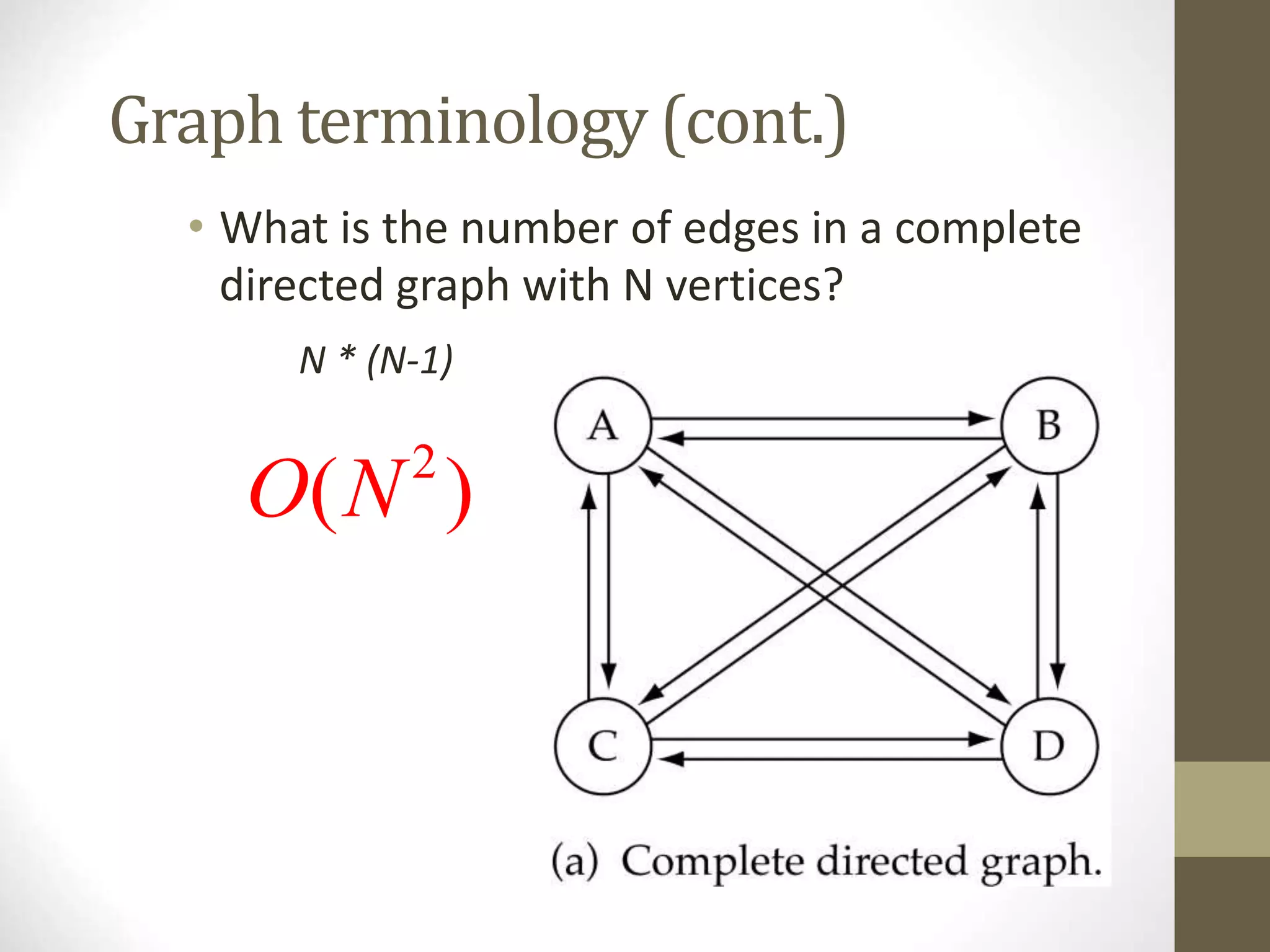
This document defines and explains various graph concepts:
- A graph consists of vertices and edges connecting the vertices. Graphs can be directed or undirected.
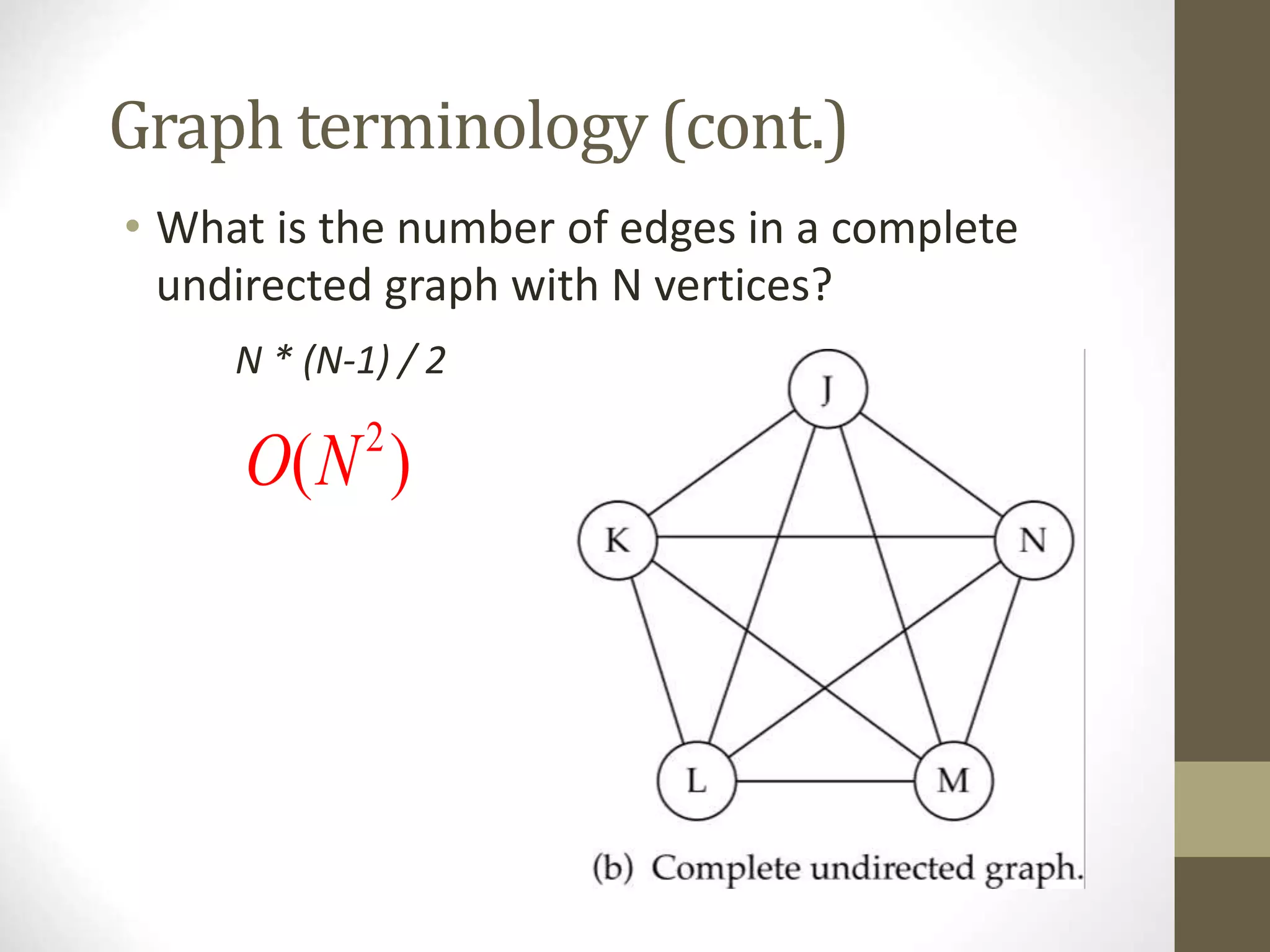
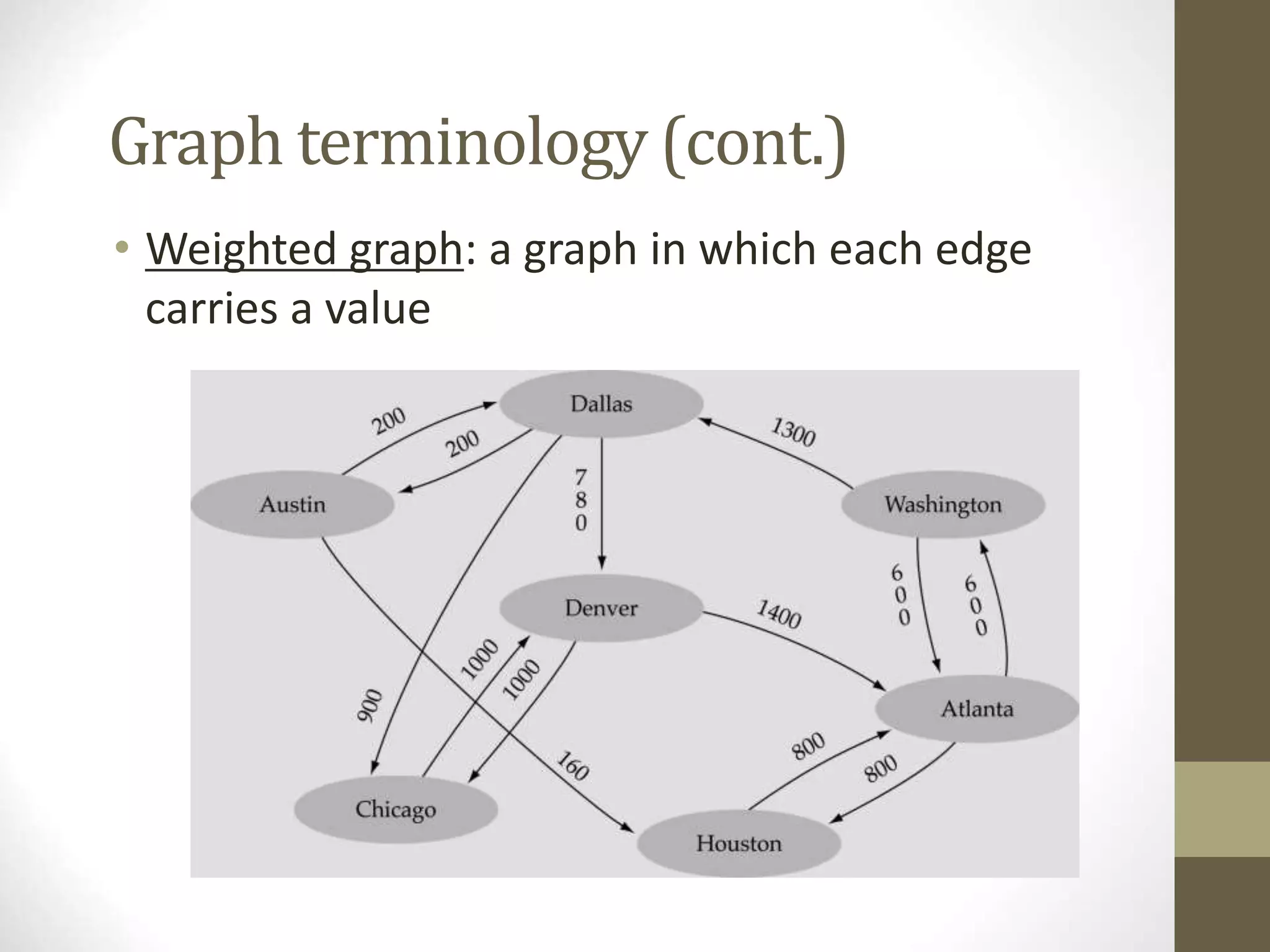
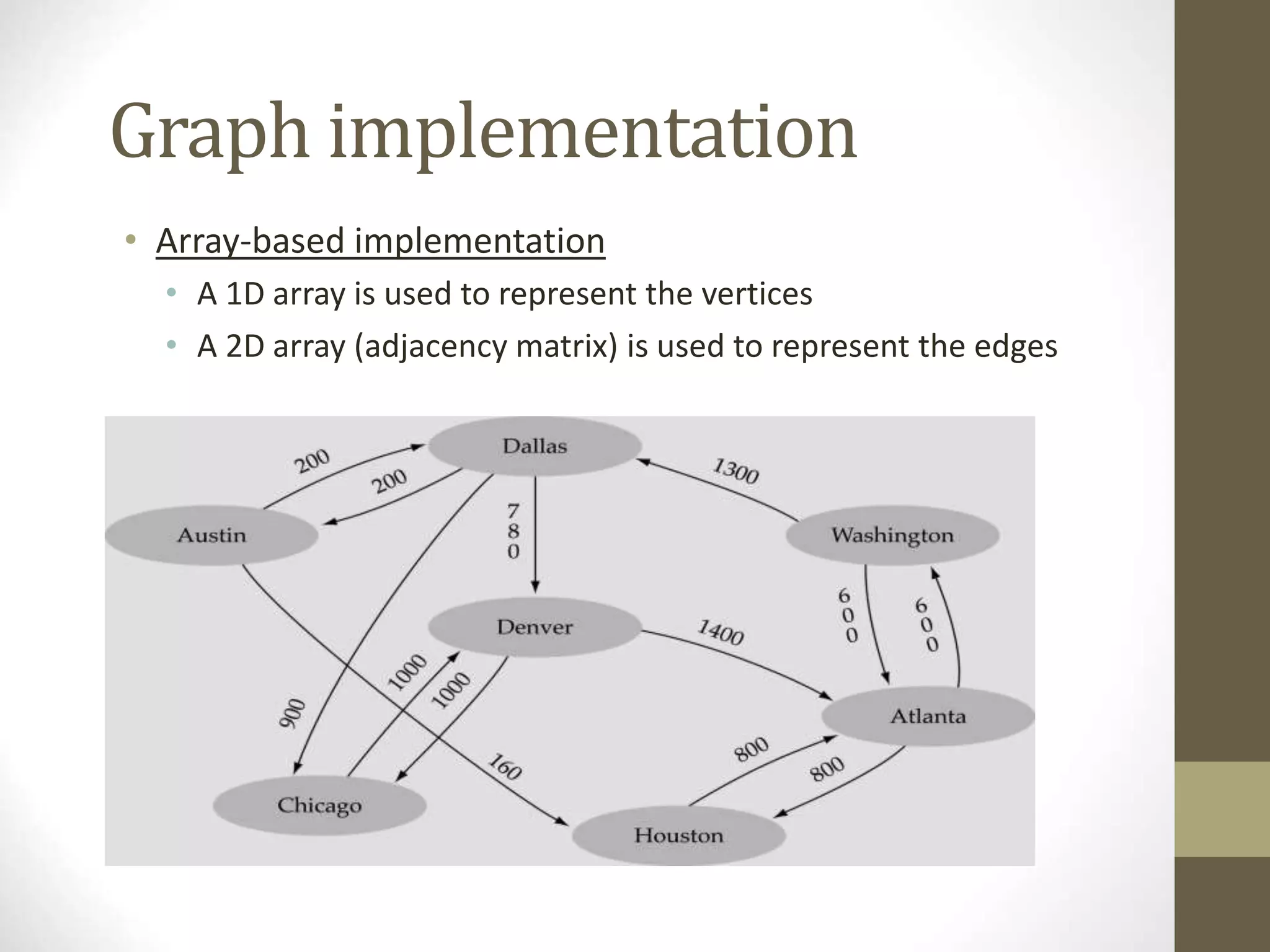
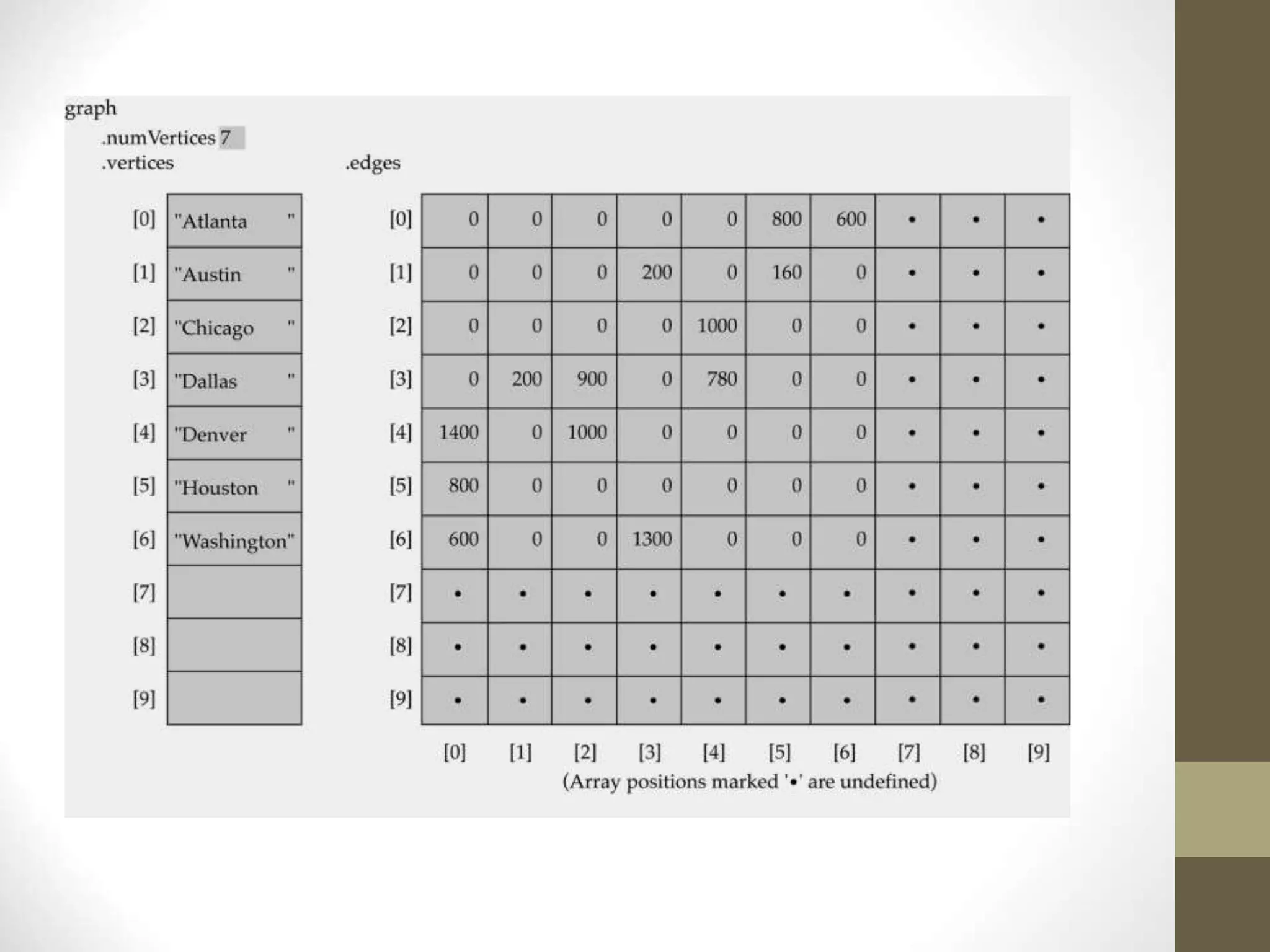
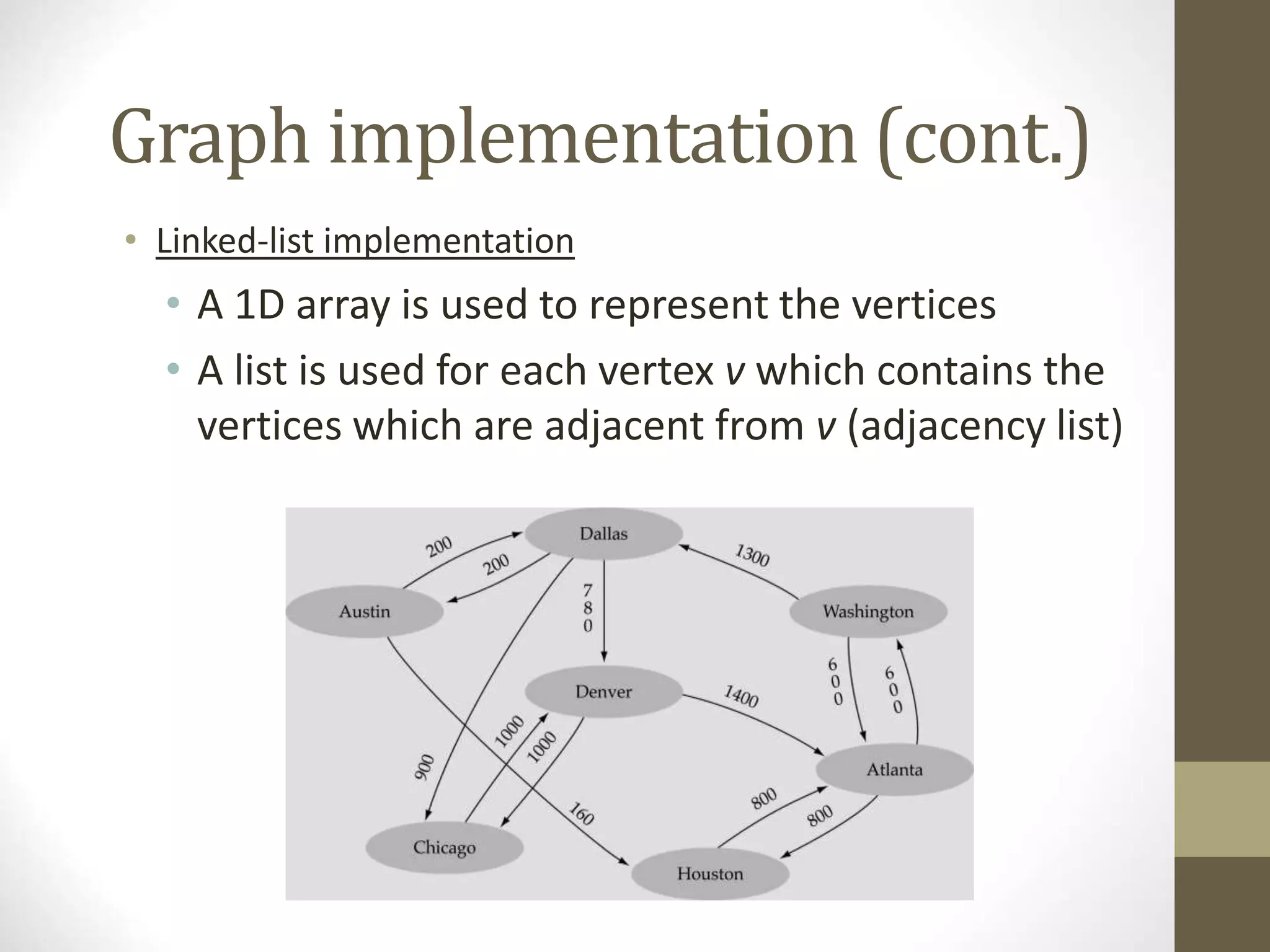
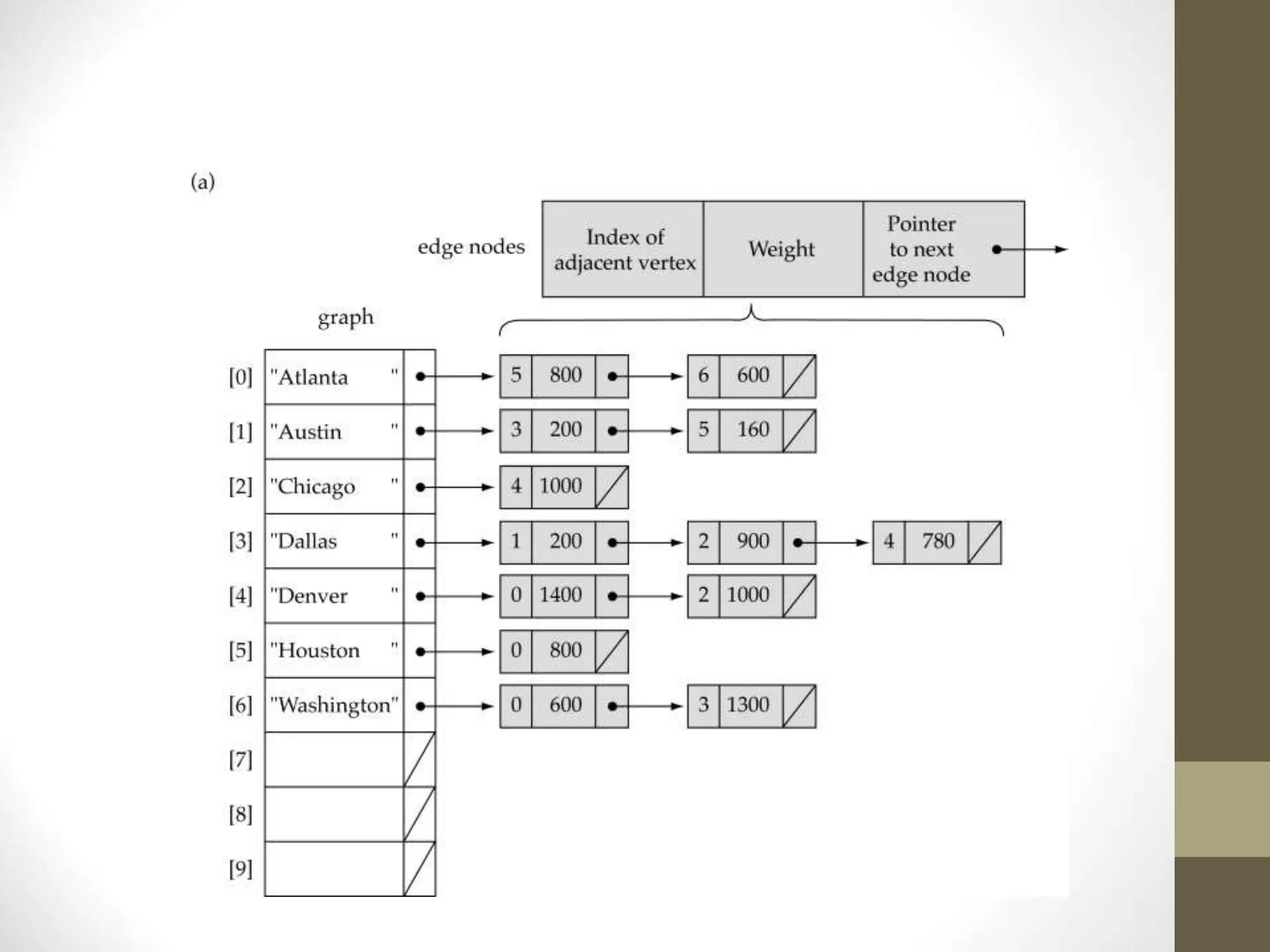
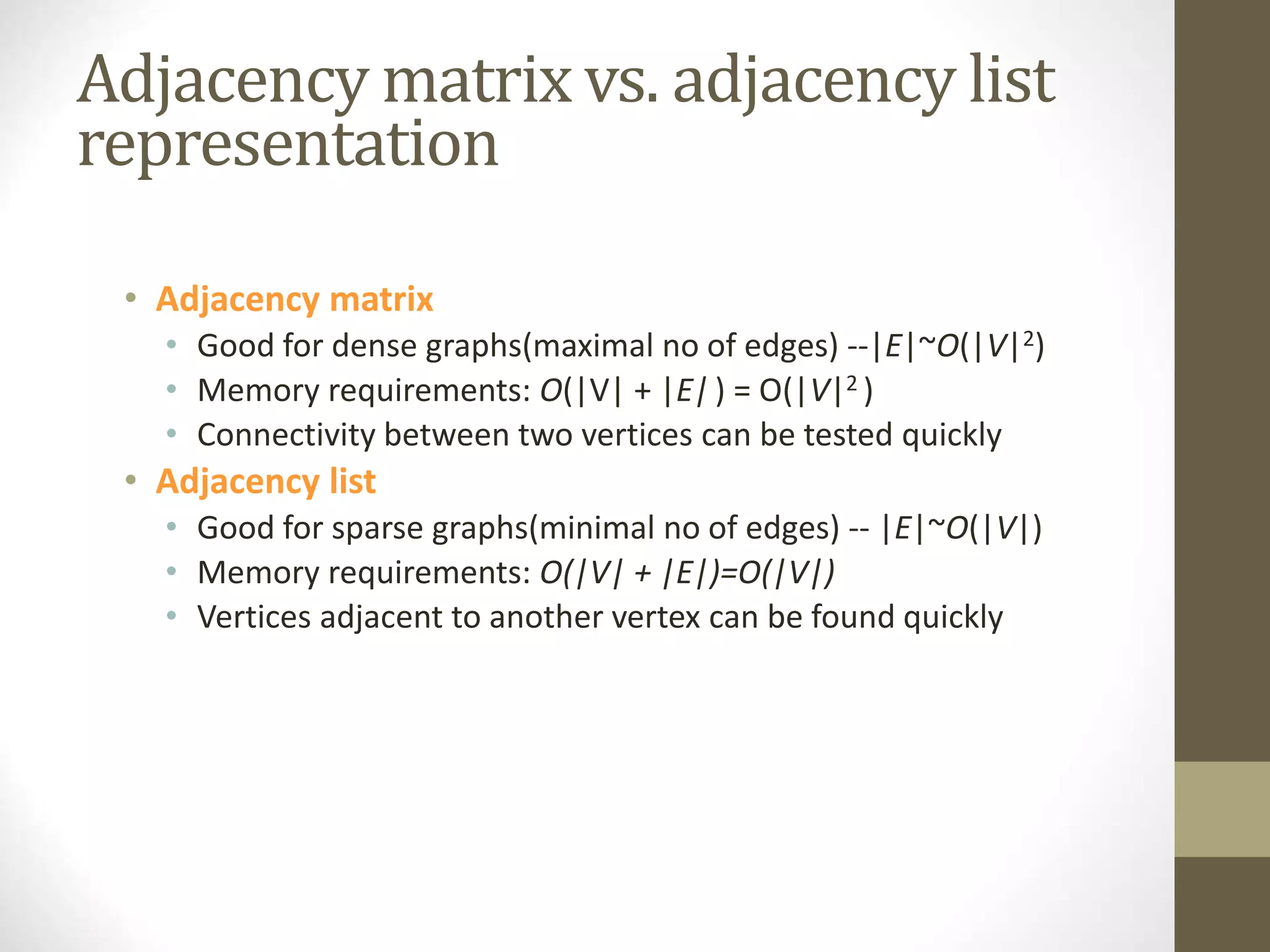
- Common graph terminology includes adjacent vertices, paths, complete graphs, weighted graphs, and representations using adjacency matrices and lists.
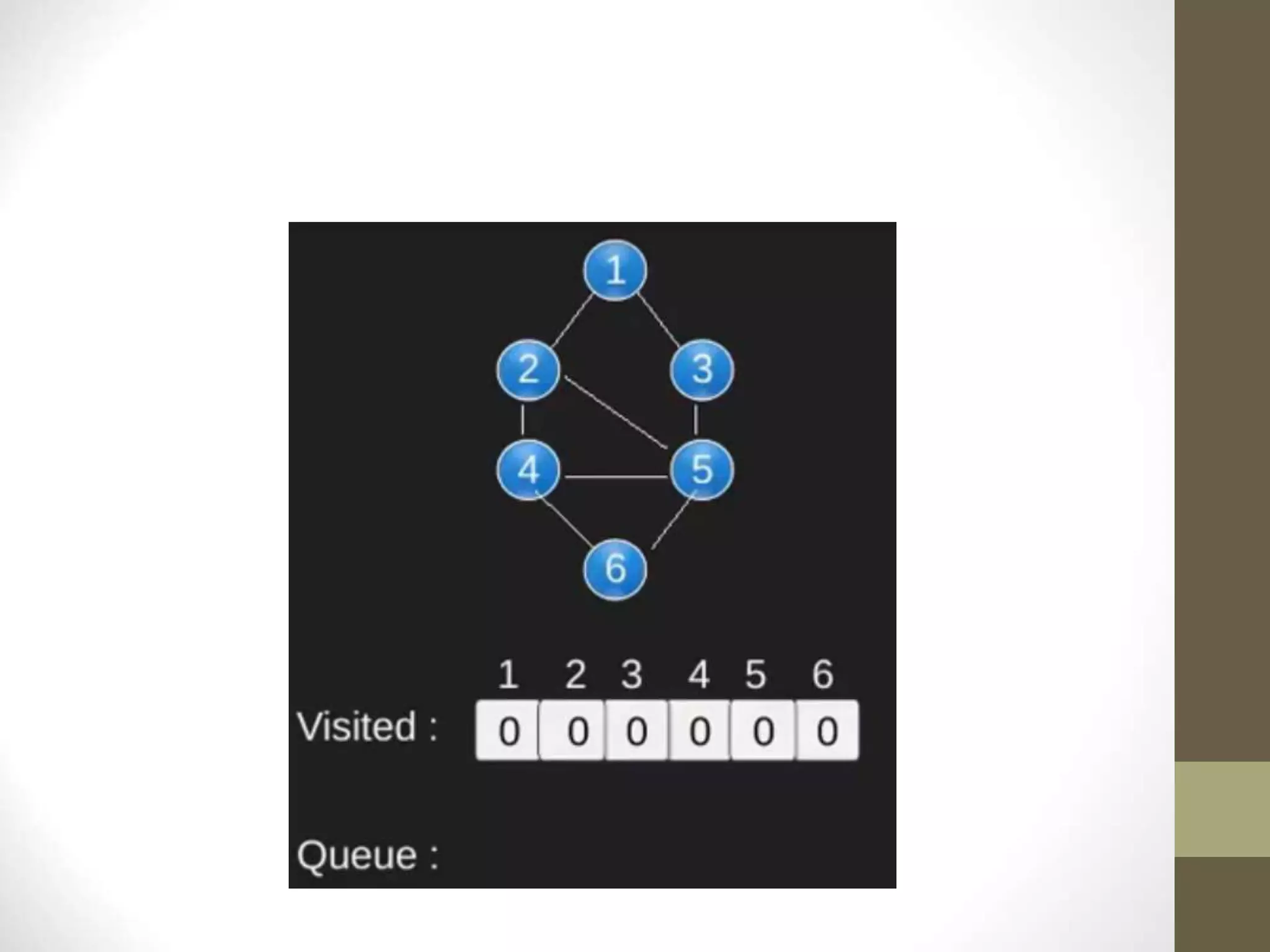
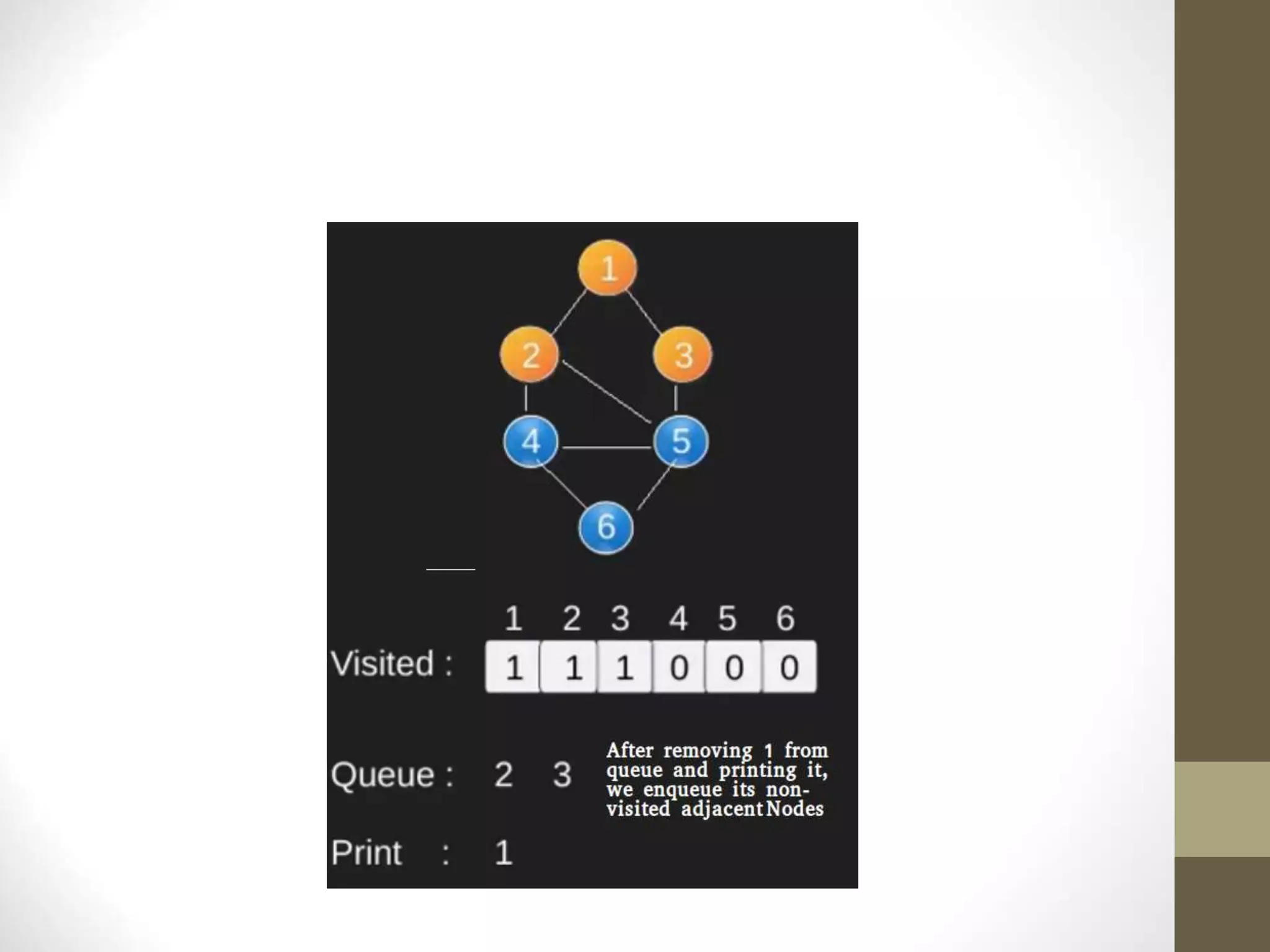
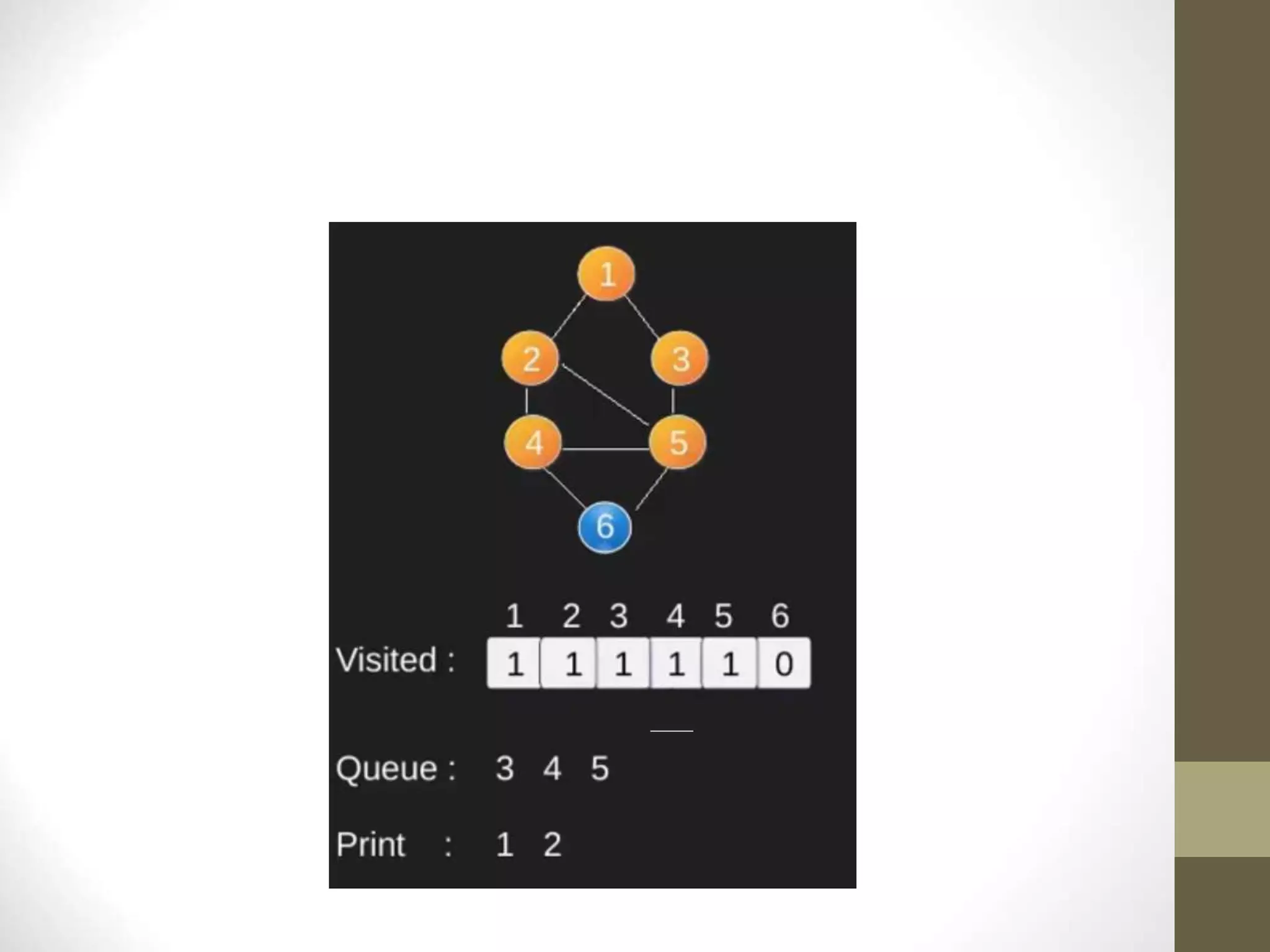
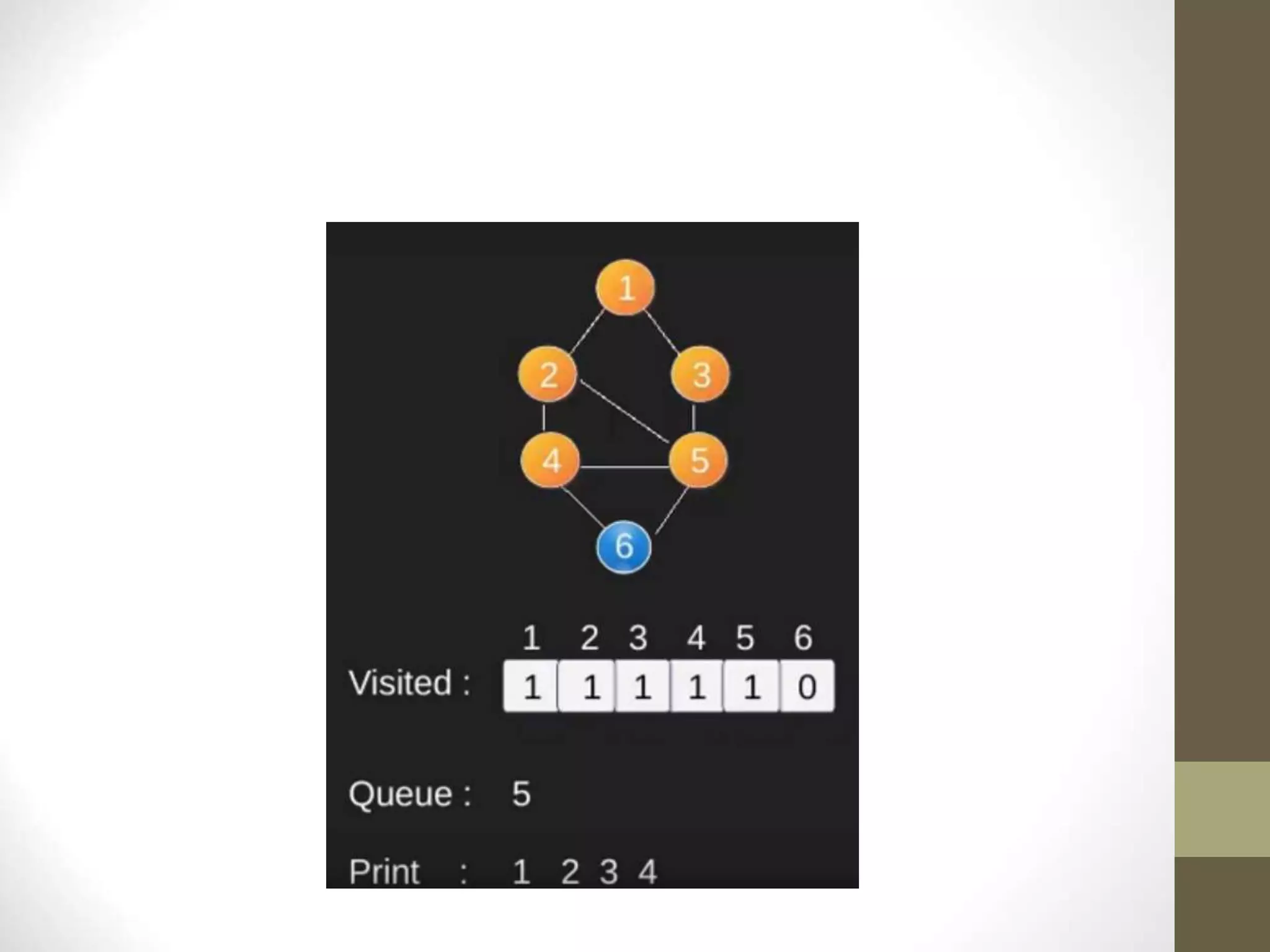
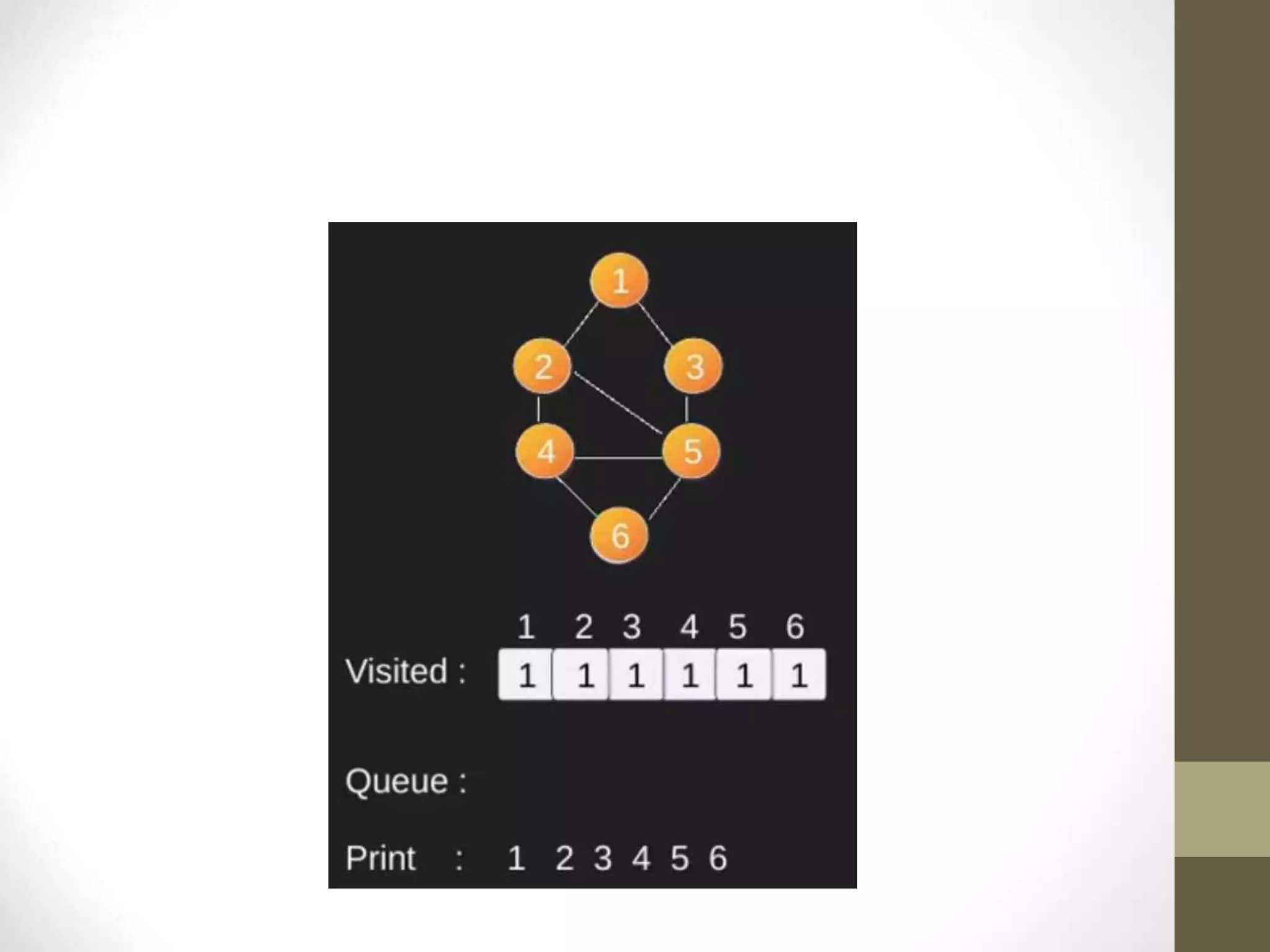
- Graph searching algorithms like depth-first search (DFS) and breadth-first search (BFS) are used to find paths between vertices.
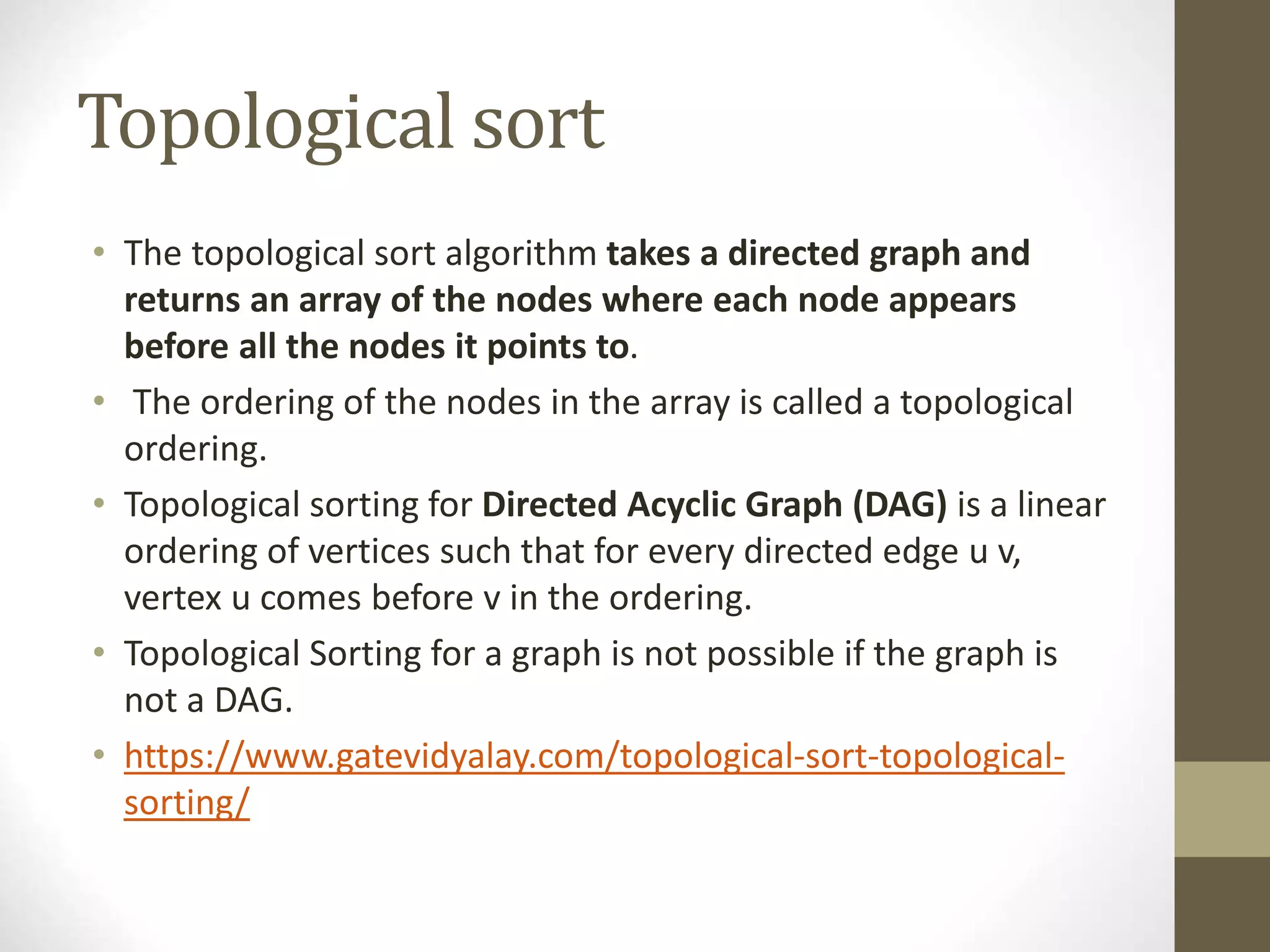
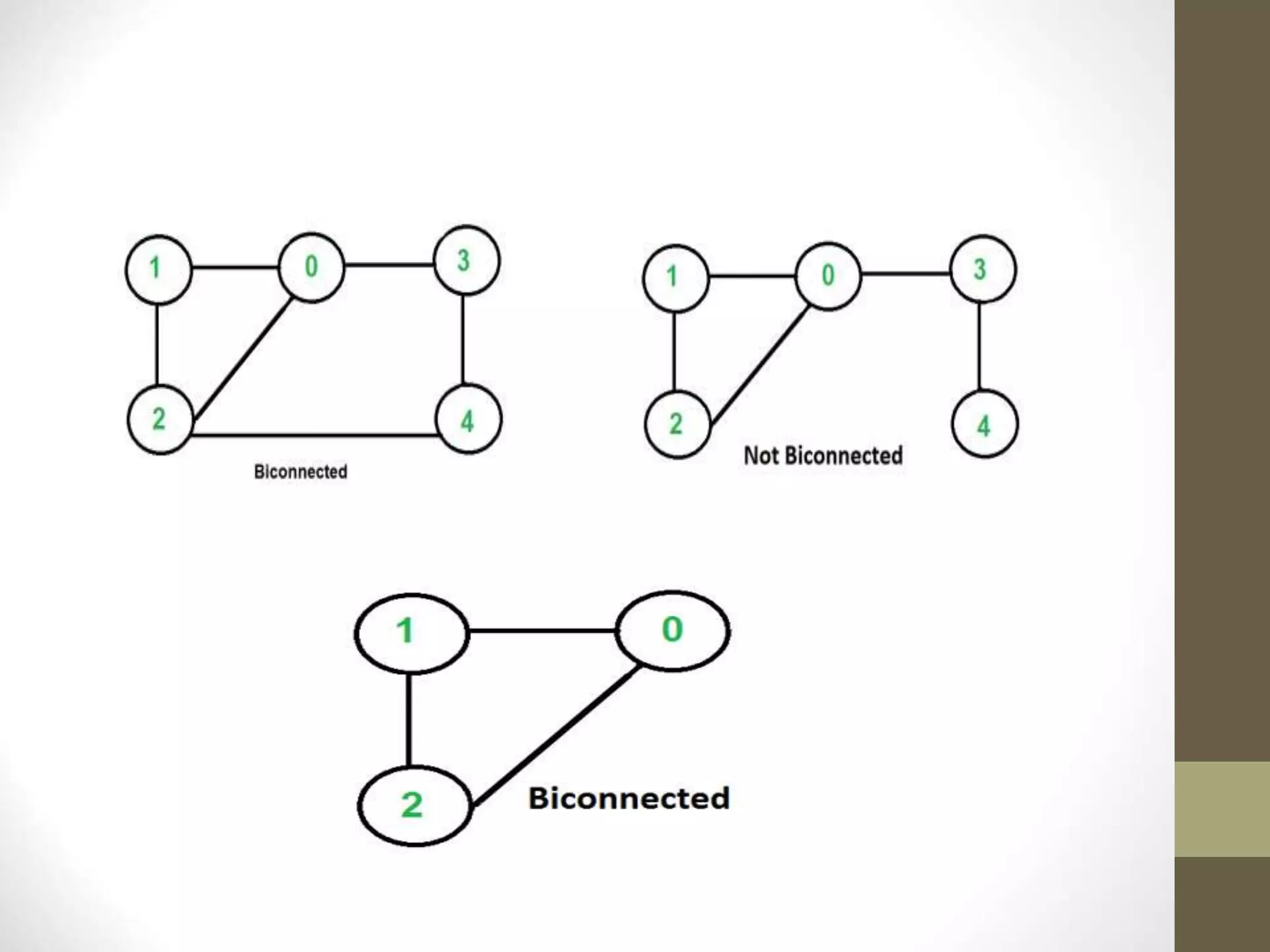
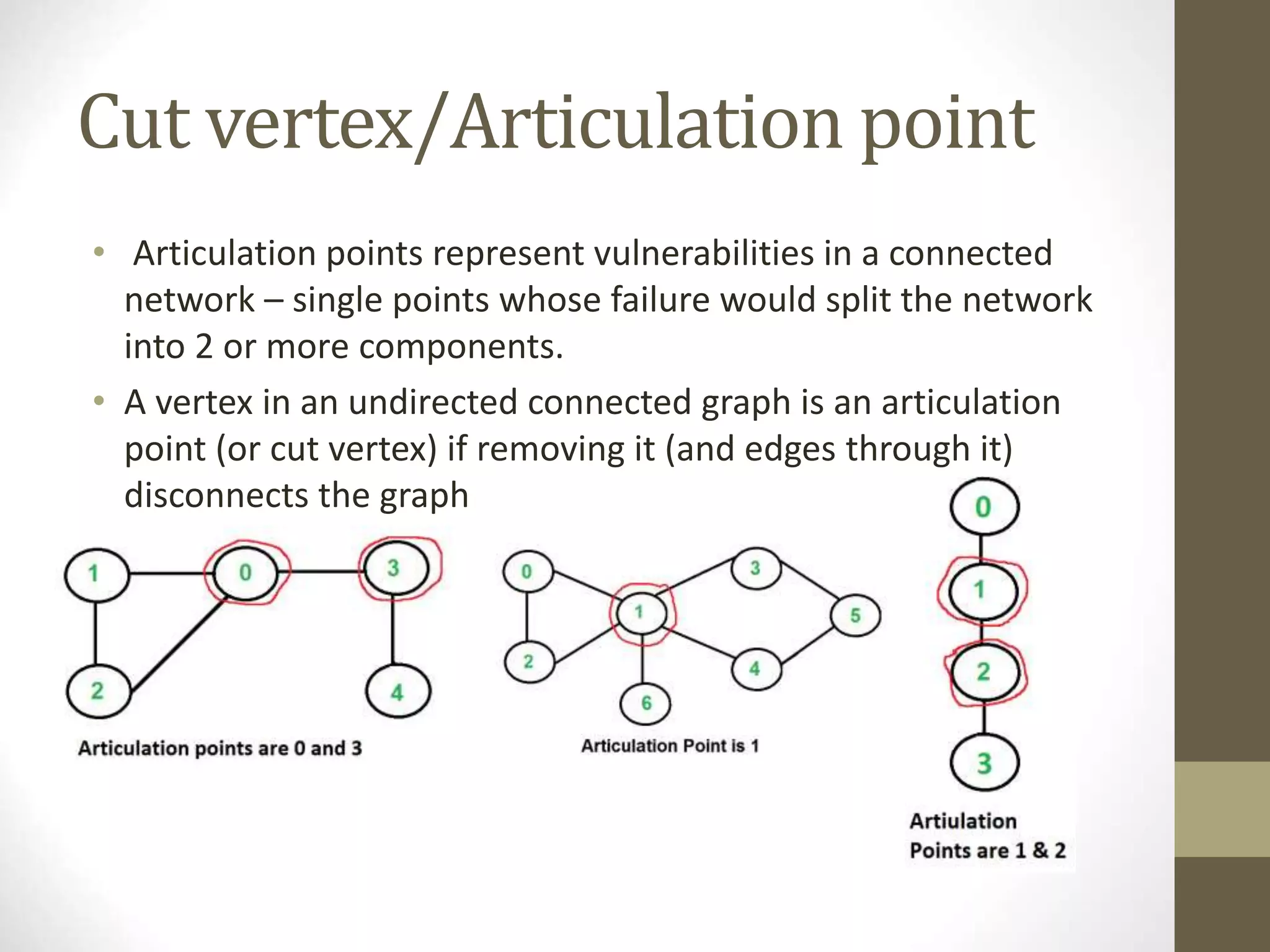
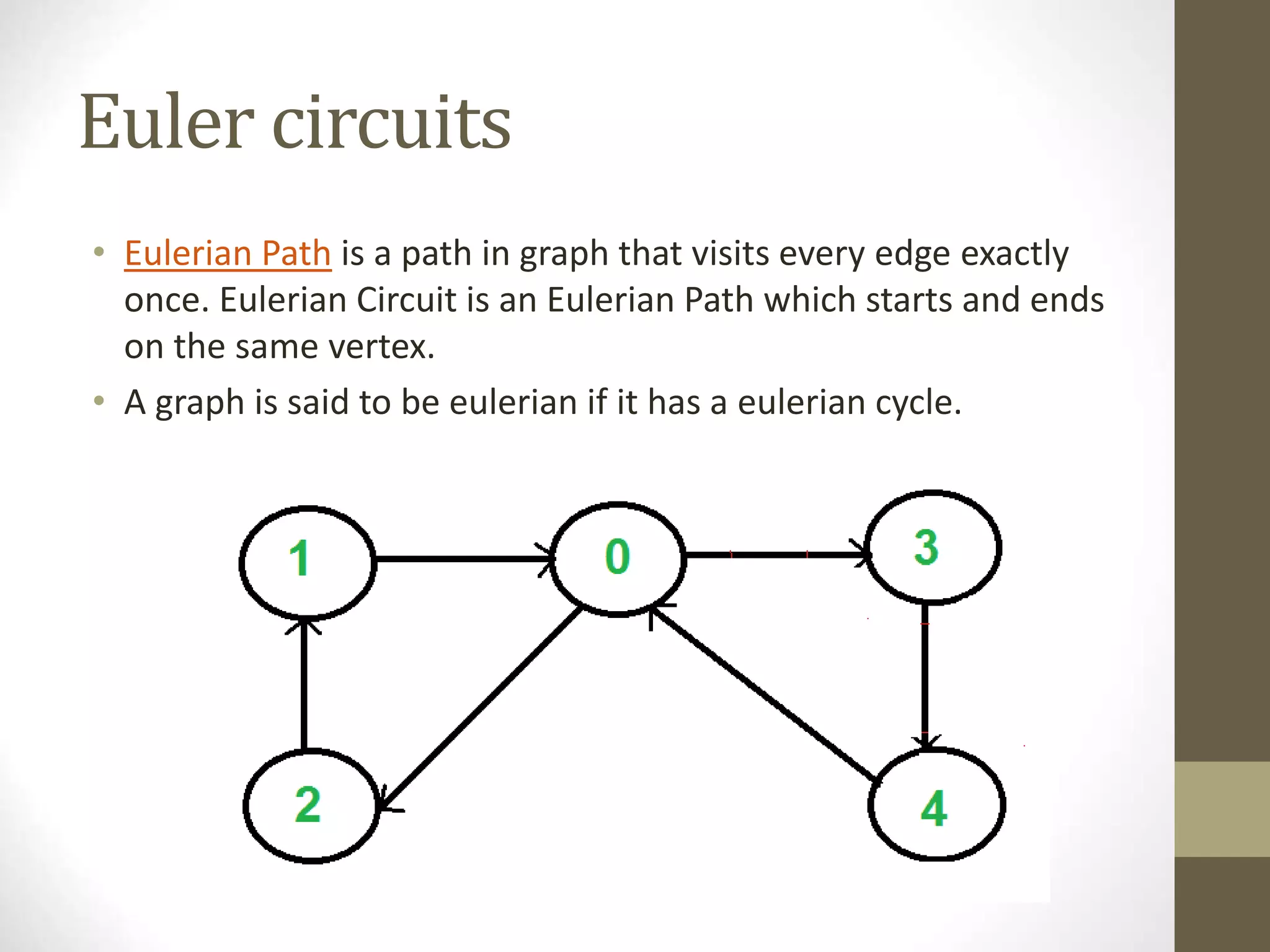
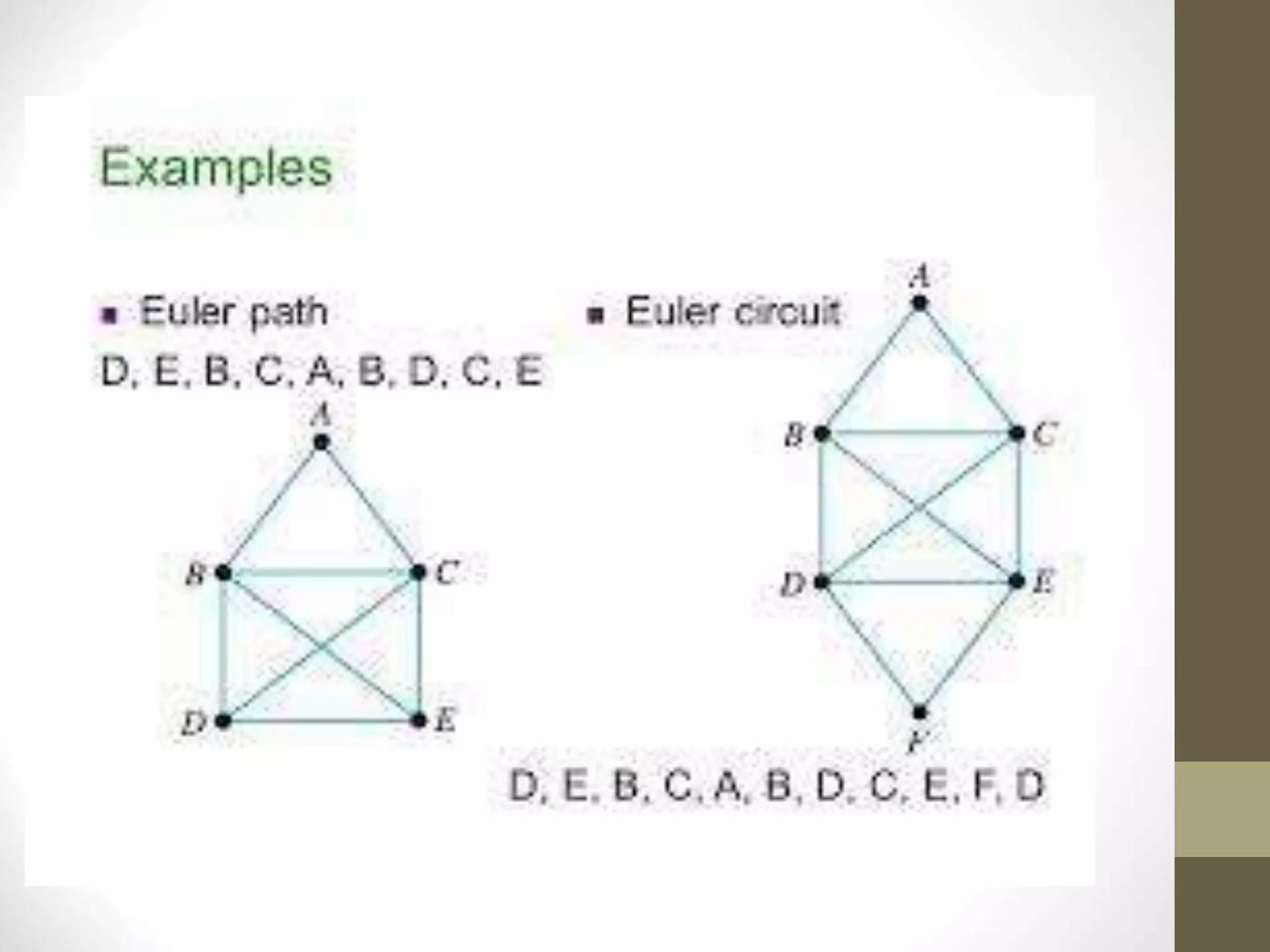
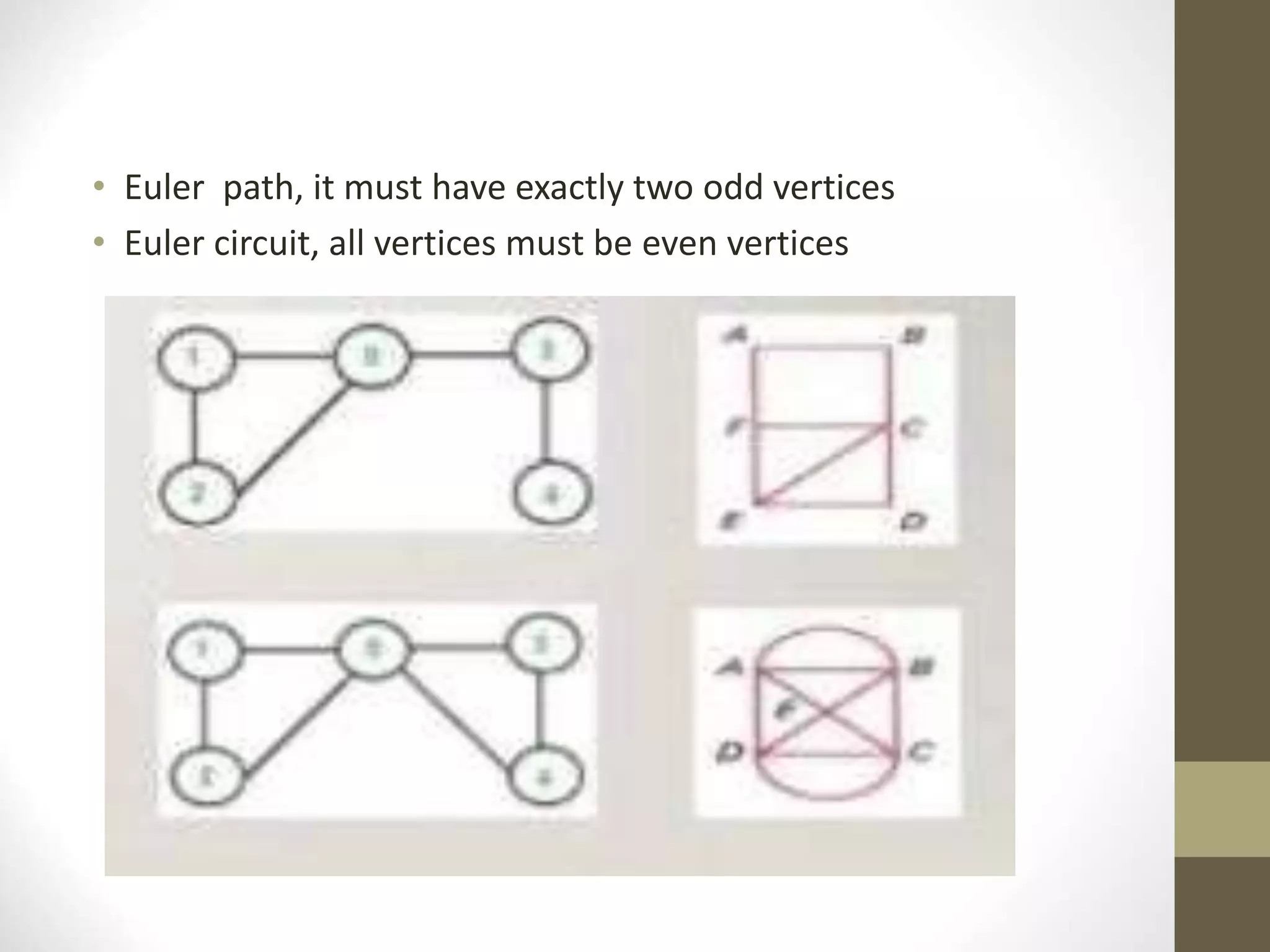
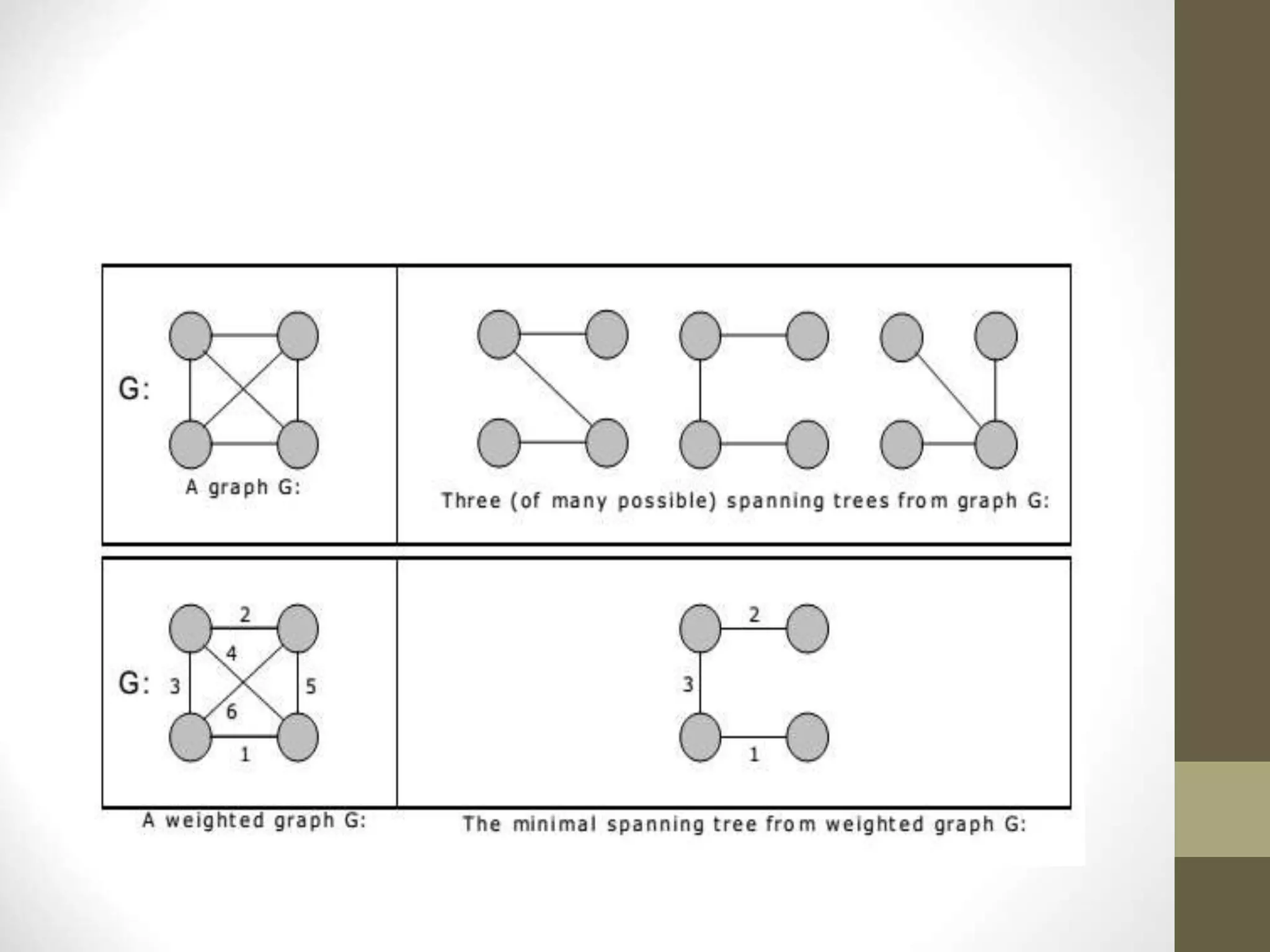
- Graphs have applications in areas like maps, networks, and computational systems. Other graph topics covered include topological sorting, biconnectivity, cut vertices, Euler circuits, and minimum spanning trees.