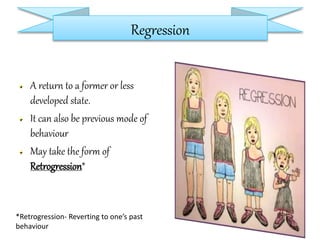
Frustration is a natural response to unachieved goals, resulting from feelings of deprivation or conflict related to goal-directed activities. It can lead to various behaviors such as aggression, regression, flight, and exploration, which are responses to the unmet expectations and efforts. To manage frustration, it is essential to understand the feelings involved and take constructive steps, including addressing physical and social effects associated with this emotional state.