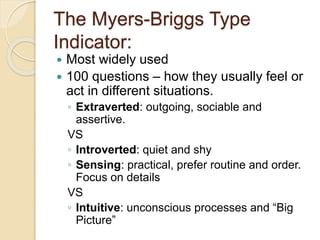
Personality refers to an individual's characteristic patterns of thought, emotion, and behavior. It arises from both genetic and environmental factors. Personality can be measured through self-report surveys and observer ratings to provide insight into hiring, job fit, and workplace behavior. Common personality traits include the "Big Five" dimensions of extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, emotional stability, and openness. Additional concepts are locus of control, self-esteem, self-monitoring, and the "Dark Triad" of Machiavellianism, narcissism, and psychopathy. The Myers-Briggs and Big Five models provide frameworks for understanding personality types and traits.