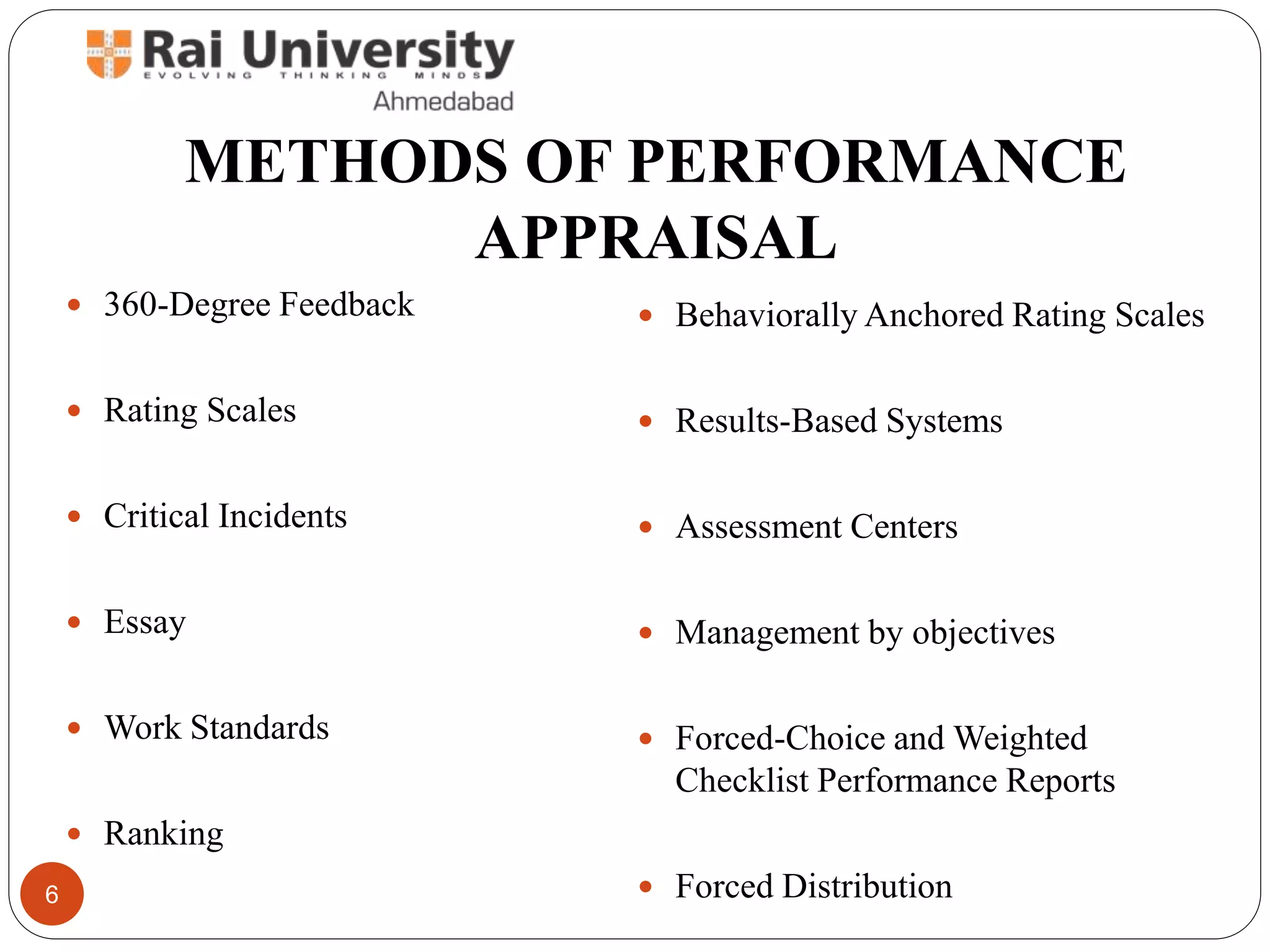
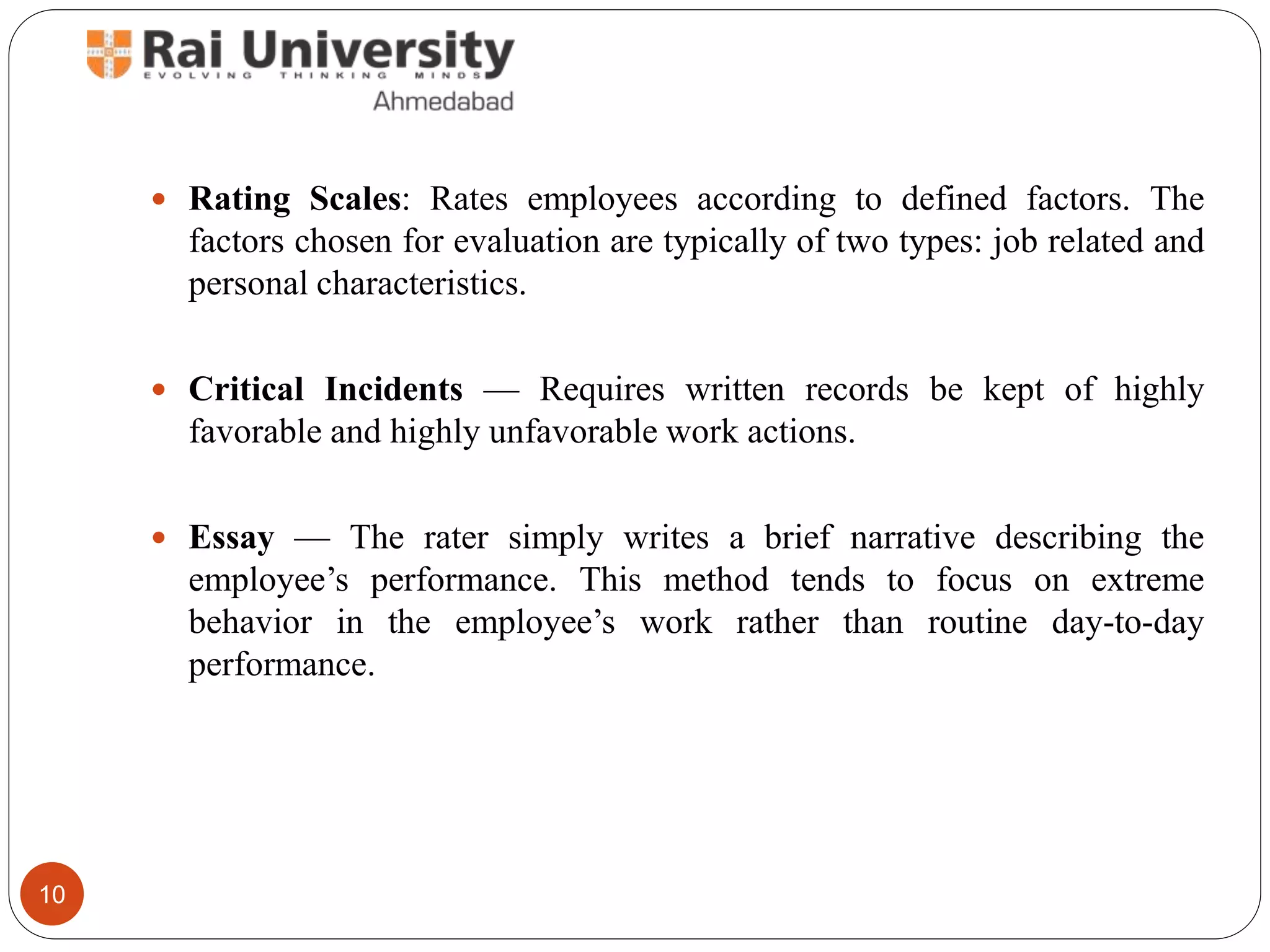
Performance appraisal is a system for reviewing individual or team job performance, aimed at enhancing organizational success through feedback, development, and personnel decisions. Various methods exist for performance appraisal, including 360-degree feedback, rating scales, and management by objectives, each with distinct advantages and challenges. Despite its benefits, performance appraisal can be hampered by biases and lack of objectivity.