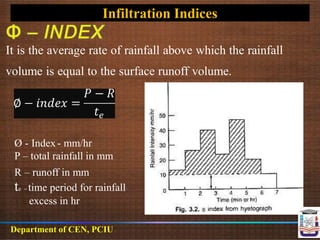
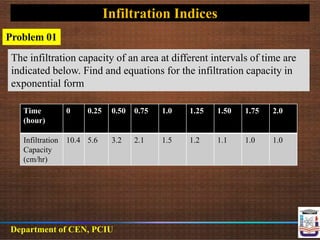
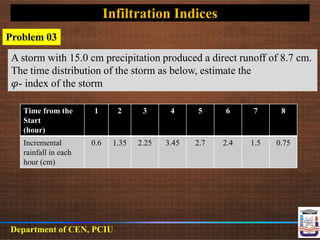
This document discusses infiltration rate and equations. It defines infiltration rate as the speed at which water enters soil and describes common methods to measure or calculate it over time. These include Horton's equation, Phillips equation, Kostiakov equation, and Holtan's equation. It also introduces the concepts of cumulative infiltration and infiltration capacity curves. Finally, it discusses infiltration indices like the phi index and W index, which provide average infiltration rates for estimating runoff from storms.





![b) Phillips equation :
Here a = Minimum infiltration capacity.
s = Initial infiltration capacity.
c) kostiakov equation:
c) holtans equation :
Here in above methods a & n are constants
depends on soil moisture & vegetable cover
F=[ A+(s/2) x t-0.5 ]
F= (a x t n)
F = ( afn
p + fc )
Infiltration Equations
Department of CEN, PCIU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7k0lva0eqfiwqrn9pu34-signature-a8a3b3f6e07baad56a7a82cebf821d833751ac5e3d734d29fa8c171d0424534e-poli-191226185150/85/L6-infiltrationr-rate-calculation-6-320.jpg)