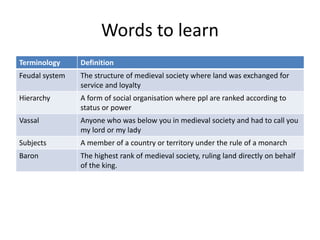
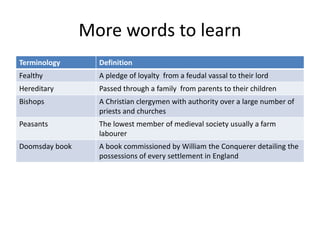
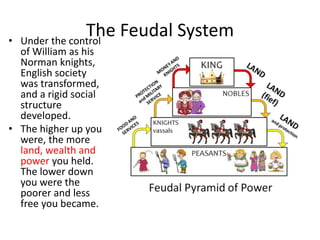
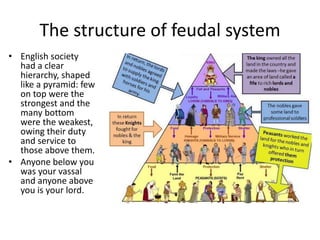
The feudal system in Norman England established a strict social hierarchy. The king was at the top and owned all the land, granting it to barons who fought for him. In return, barons gave land and protection to knights, who promised loyalty and military service. At the bottom were peasants, who lived and worked on the lands owned by lords above them. William the Conqueror commissioned the Domesday Book in 1086 to survey all land and property holdings in England to assess taxes, establishing a record so thorough it was likened to the biblical Day of Judgment.