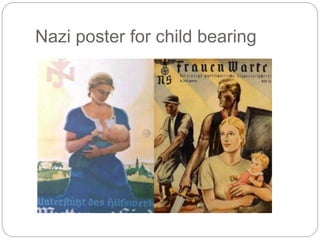
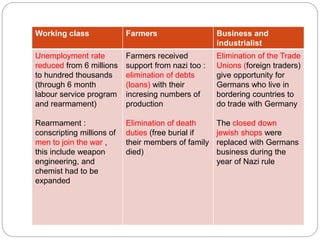
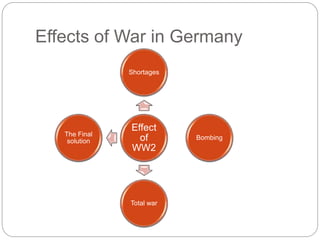
Nazi Germany implemented policies to control and indoctrinate the youth through schools and the Hitler Youth organization. Boys were given military training to serve as future soldiers, while girls were prepared for motherhood. The Nazi regime also pursued policies to increase the birth rate by encouraging marriage and childrearing while restricting women's roles. Most Germans benefited economically from reduced unemployment and support for farmers and businesses during Nazi rule. However, life deteriorated with the outbreak of World War 2 due to food and supply shortages, bombing of cities, and total mobilization of the economy for war. The Holocaust led to the mass murder of 6 million Jews in death camps across Nazi-occupied Europe.