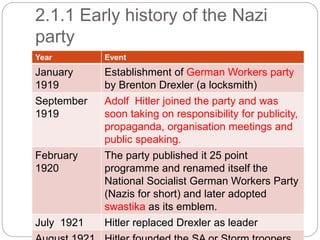
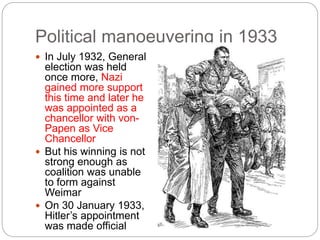
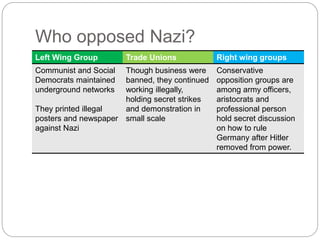
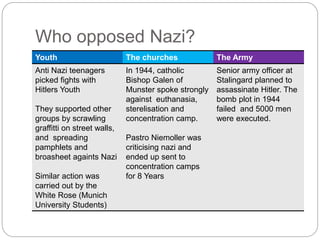
The document provides an overview of the rise of Nazism in Germany between 1919-1934. It discusses how the Nazi party was founded in 1919 with Hitler becoming its leader in 1921. The party promoted German nationalism, anti-Semitism and the superiority of the Aryan race. Despite failing in his Munich Putsch coup attempt in 1923, Hitler realized he needed to gain power legally. When the Great Depression hit Germany in 1930, the Nazis capitalized on the economic troubles and anti-government sentiment to become the second largest party by 1930. Hitler was appointed Chancellor in 1933 and quickly consolidated power by suspending civil liberties, banning other parties, and violently removing opposition like the SA leadership in the Night of the Long Knives in 1934.