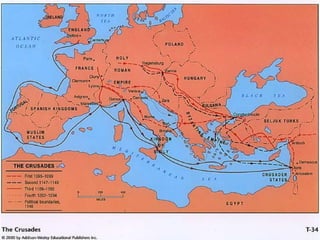
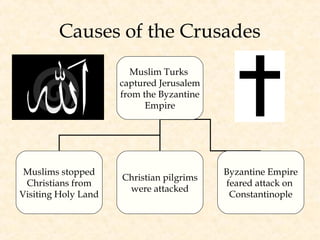
The Crusades were a series of wars between Christians and Muslims over control of Jerusalem and the Holy Land. The Muslims had captured Jerusalem, preventing Christian pilgrimages. Pope Urban II called for the defeat of the Turks and return of the Holy Land to Christianity. Thousands answered the call, including feudal lords, knights, and peasants. The First Crusade succeeded in capturing Jerusalem in 1099, though the Turks later retook much of the territory, leading to further Crusades over the next century with no lasting victories for the Christians.