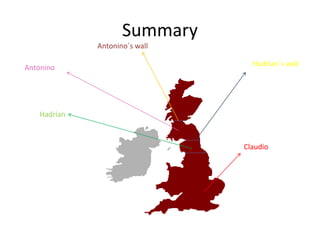
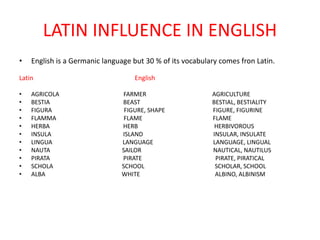
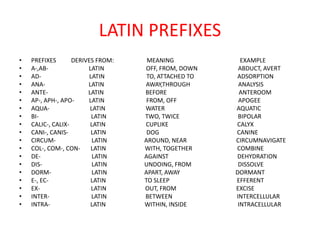
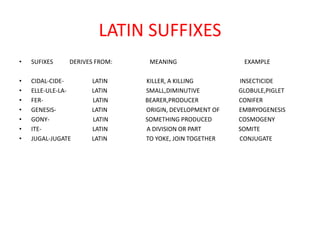
The Romans conquered Britain in the 1st century AD. They were led by emperors like Claudius and generals like Aulus Plautius. The Romans built many structures like Hadrian's Wall, roads, towns, and villas to establish control over Britain. They brought Latin influences that still remain in the English language today including vocabulary words and prefixes/suffixes derived from Latin. The Romans introduced urban planning, central heating, and public baths to Britain and integrated aspects of British Celtic culture with their own.