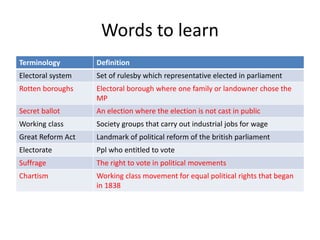
The old British electoral system was unfair, with only 400,000 of a population of 16 million able to vote in 1832. Rotten boroughs allowed landowners to choose MPs despite few or no residents. The Great Reform Act of 1832 expanded suffrage to more wealthy men and abolished rotten boroughs. However, the Chartist movement demanded further reforms, including universal male suffrage. Full male suffrage was achieved in 1884, while women obtained suffrage in the early 20th century due to activists like Emmeline Pankhurst.