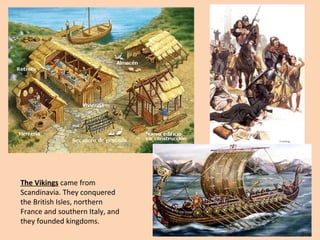
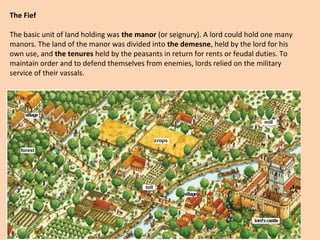
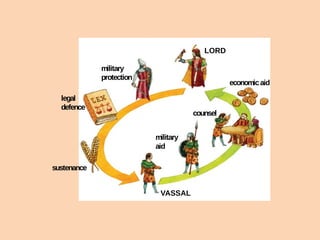
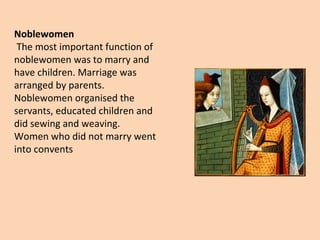
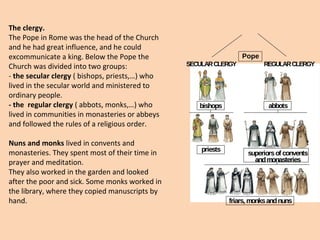
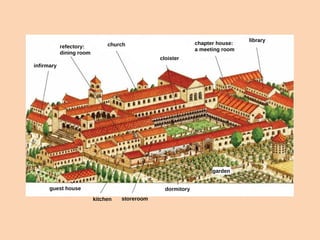
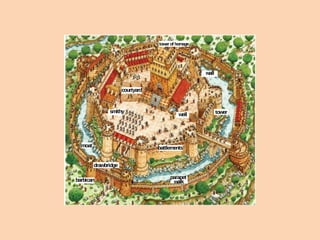
Feudal society was organized in a strict hierarchy. At the top was the king, followed by nobles who were granted land from the king, known as fiefs. Nobles gave parts of their fiefs to vassals, who pledged loyalty and service, such as providing knights. Peasants lived on the land and worked for the lord, either as freemen or serfs. Serfs had fewer rights and owed much of their work and crops as rent, while freemen had more freedom. Society was also divided into clergy like bishops and monks, and the laity like nobles and peasants. Knights trained from a young age to serve their lord through combat. Castles provided protection for lords and