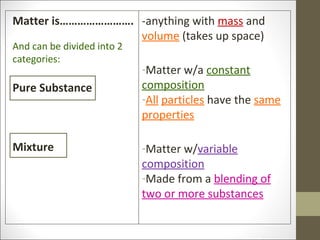
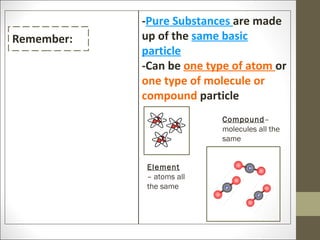
The document provides instructions for students on assignments and materials for an upcoming science class. It lists roles for group work including manager, materials manager, timer/designer, and oral presenter. It then provides a schedule of assignments and due dates including tests, power notes, and flashcards to review for a state science exam. Key topics to be covered are the classification of matter and the periodic table.