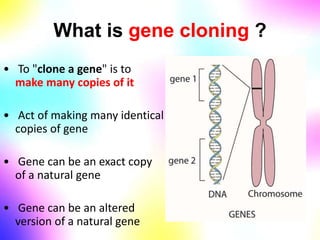
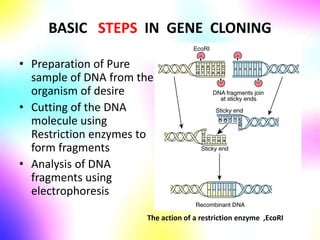
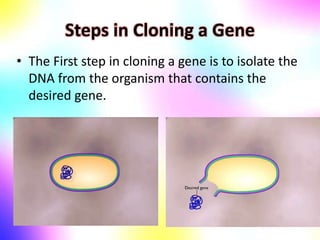
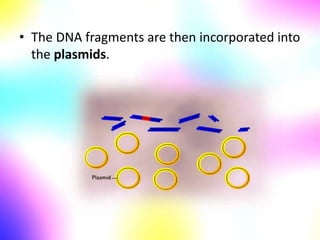
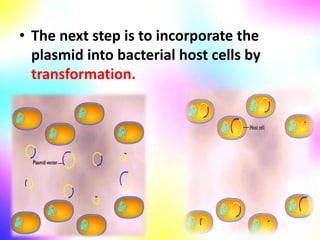
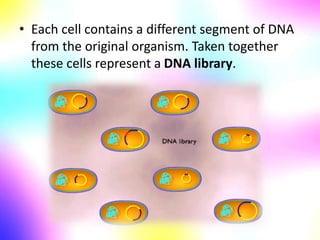
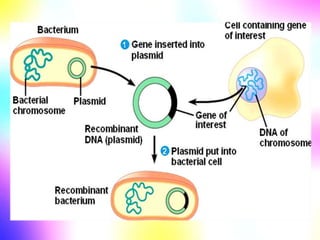
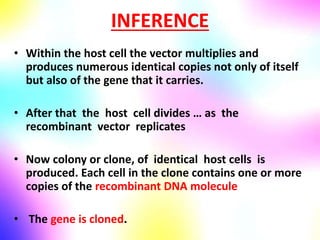
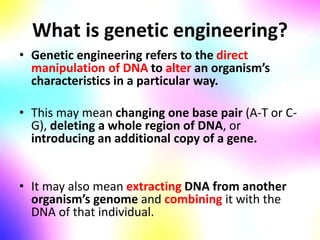
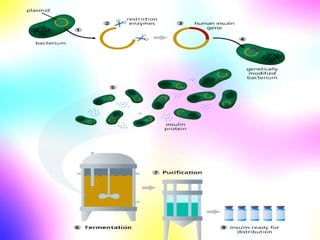
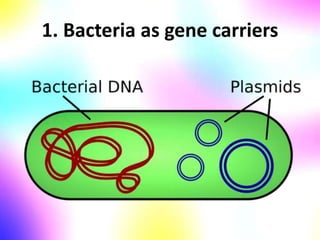
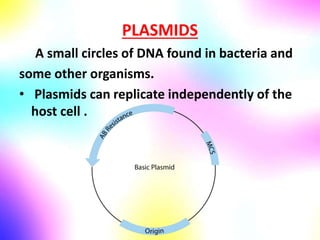
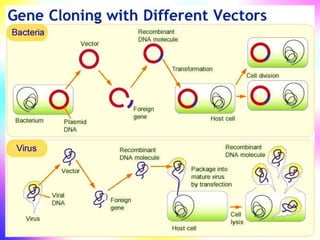
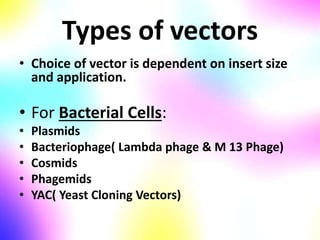
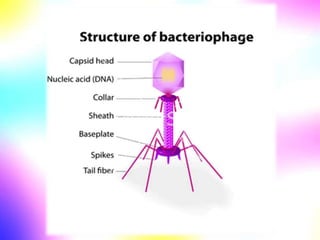
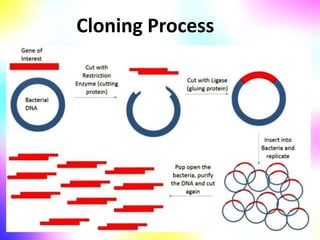
Gene cloning involves making many identical copies of a gene. The basic steps include isolating DNA from an organism, cutting the DNA into fragments using restriction enzymes, inserting the fragments into plasmids, and transforming the plasmids into bacterial cells. Each bacterial cell will contain copies of the gene of interest, allowing scientists to isolate and study that gene. Viruses and bacteria can act as vectors, or carriers, to transfer genes into cells. Plasmids and bacteriophages are commonly used vectors for cloning genes into bacterial cells.