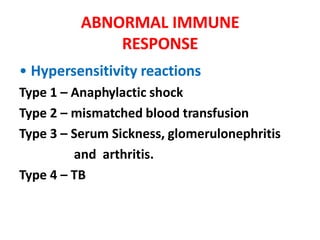
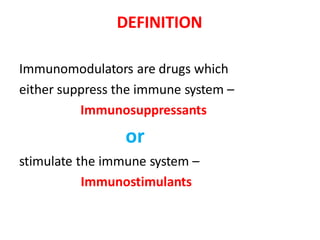
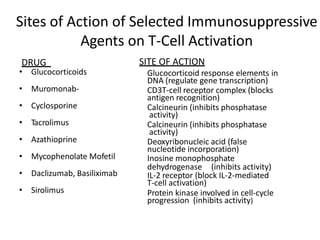
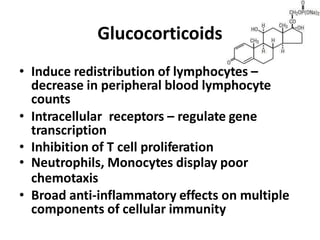
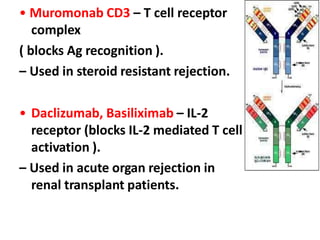
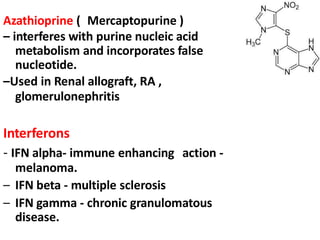
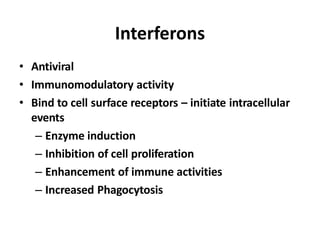
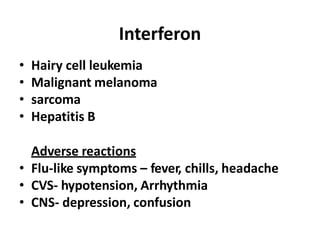
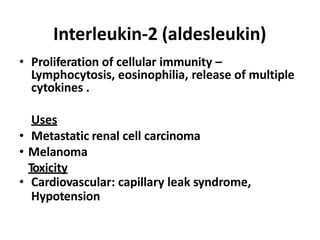
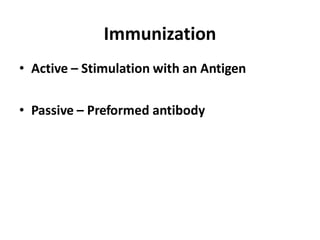
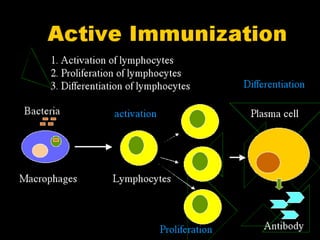
This document summarizes immunomodulators, which are drugs that suppress or stimulate the immune system. It describes the innate and adaptive immune response and how immunomodulators can act as immunosuppressants or immunostimulants. Key immunosuppressants discussed include glucocorticoids, calcineurin inhibitors, antiproliferatives, antibodies, and their mechanisms and uses for conditions like transplantation and autoimmune diseases. Immunostimulants covered include levamisole, thalidomide, BCG, interferons, interleukin-2, and immunization through vaccines and immune globulins.