Embed presentation
Downloaded 16 times


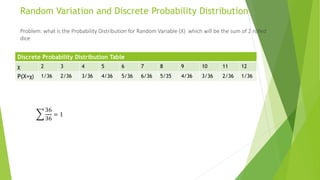
The document discusses random variables and discrete probability distributions, explaining that a random variable's value is determined by a random experiment. It illustrates how to construct a discrete probability distribution, such as the outcomes of flipping three coins or rolling two dice, showing that probabilities sum to one. Examples highlight how to derive probability tables for various random outcomes.


