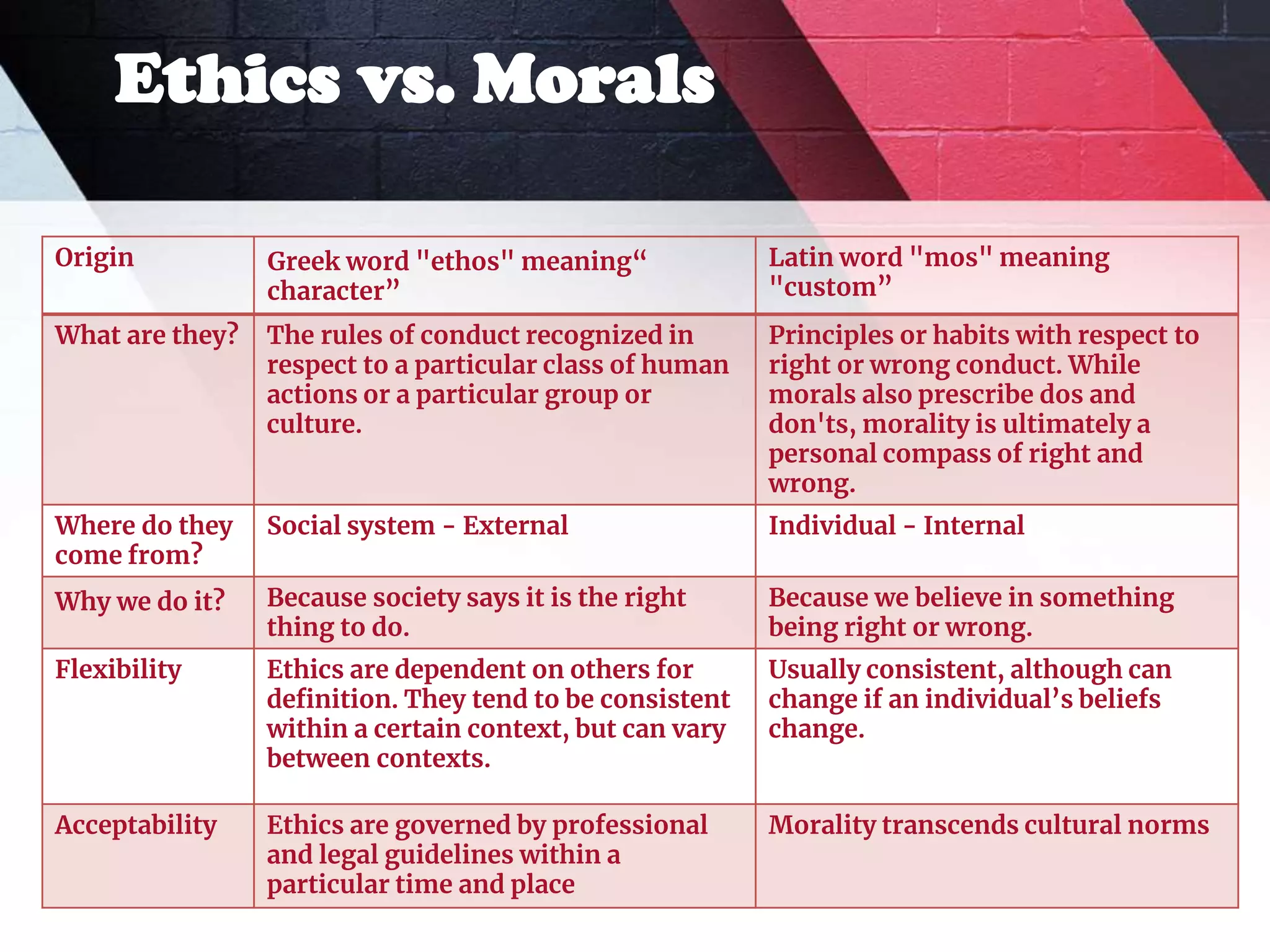
The document explores various concepts in ethics, including ethical theories such as absolutism, relativism, subjectivism, and situational ethics, as well as their practical applications in business ethics. It discusses the importance of ethics in organizational behavior, highlighting the distinction between ethics and morals, and the significance of ethical behavior for successful management. Additionally, it examines ethical dilemmas individuals may face in professional settings and the consequences of unethical practices.