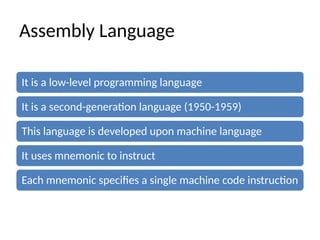
Assembly language is a low-level programming language that uses mnemonics to represent machine code instructions and is easier to understand than machine language. It has advantages such as simpler programming and error correction but is machine-dependent and requires an assembler. In comparison to machine language, assembly language is human-readable, modifiable, and has lower syntax error risks.