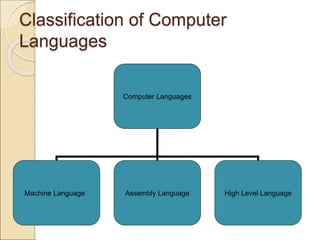
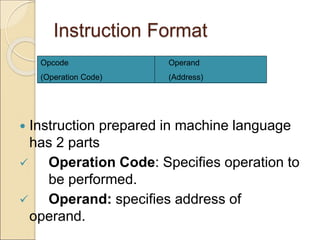
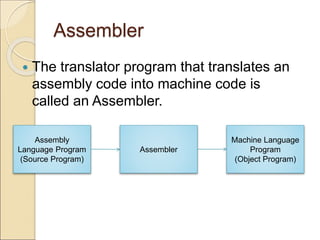
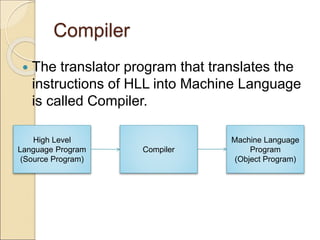
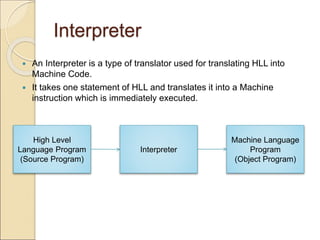
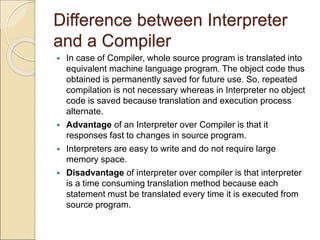
This document discusses different types of computer languages. It begins by defining natural language and computer language, noting that computer languages have a more limited vocabulary than natural languages. It then classifies computer languages into machine language, assembly language, and high-level languages. Machine language uses binary and has no translation, while assembly language substitutes mnemonics for machine codes. High-level languages are problem-oriented and translated into multiple machine codes. Assemblers translate assembly languages, compilers translate high-level languages, and interpreters translate high-level languages line-by-line before executing each one. High-level languages are more machine independent, easier to use and maintain than lower-level languages.