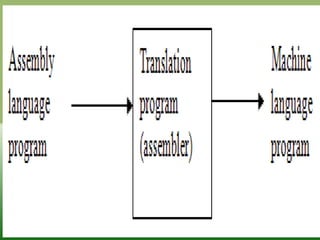
This document discusses assembly language. It defines assembly language as being one step up from machine language and originally created as a more user-friendly way to program. It describes the relationship between assembly language and machine code, explaining that assembly language uses mnemonics instead of operation codes and symbolic labels instead of offsets. It also lists some common types of assembly languages and discusses opcodes, operands, mnemonics, and the ASCII standard.