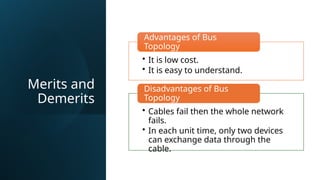
The document discusses data communication and various network topologies, explaining key concepts like transmission protocols, types of data flow (simplex, half duplex, full duplex), and network criteria for effectiveness (performance, reliability, security). It details four network topologies: bus, star, ring, and mesh, outlining their advantages and disadvantages. The bus topology connects all devices to a single cable, the star topology links devices to a central node, while the ring topology connects devices in a closed loop.