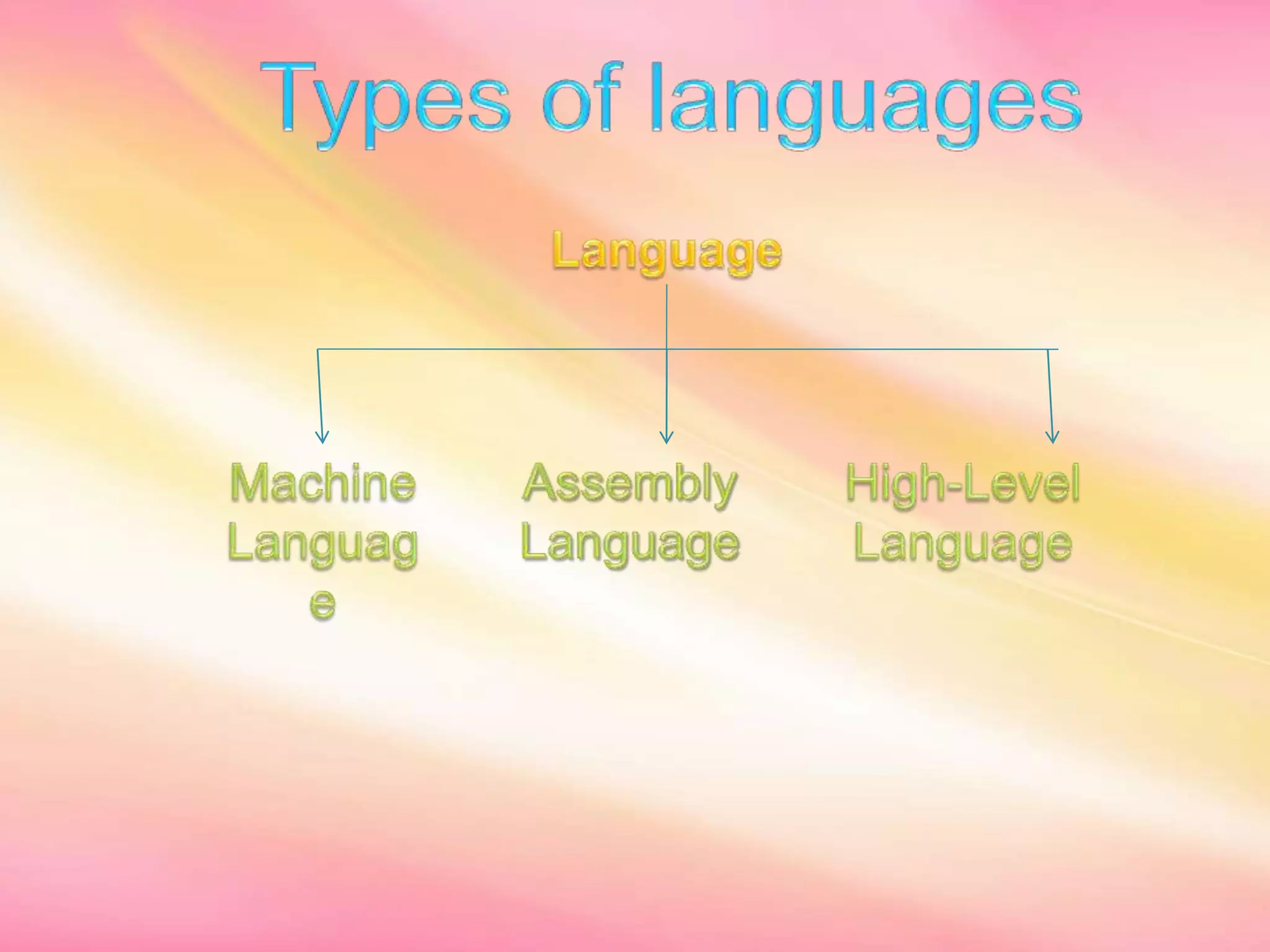
This document discusses different types of computer languages. It begins by defining a programming language as an artificial language used to communicate instructions to a computer. Originally, programs were written in binary code (1s and 0s), which is the native language of computers. Assembly language was then created using alphanumeric codes and mnemonics, making programming easier but still machine-dependent. High-level languages were later developed that use vocabulary closer to human languages, make programs more portable between machines, and are generally easier for humans to read, write and maintain. However, high-level languages must still be translated into machine language before execution.