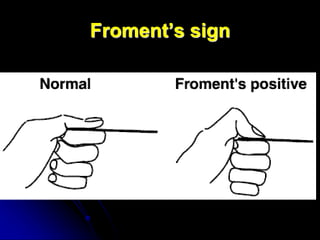
The ulnar nerve is formed from fibers from C8 and T1 that join the medial cord of the brachial plexus, with C7 fibers also joining. It travels through the axilla and arm, passing behind the medial epicondyle of the humerus through the cubital tunnel. In the forearm it lies between flexor muscles and becomes more superficial. At the wrist it passes through Guyon's canal before dividing into superficial and deep branches to innervate muscles and skin of the hand. Injuries can occur at the elbow, causing tardy ulnar palsy, or at the wrist, resulting in claw hand deformity from Guyon's canal syndrome.