Embed presentation






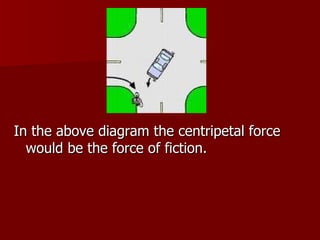














Uniform circular motion (UCM) describes the motion of an object moving at a constant speed in a circular path. Centripetal force is directed towards the center of curvature and causes the object to travel in a circular path. During UCM, centripetal force and centripetal acceleration are directed towards the center, while the velocity is tangential to the path. Examples show that the centripetal force can be the force of friction, normal force, tension, or gravity depending on the situation.




















