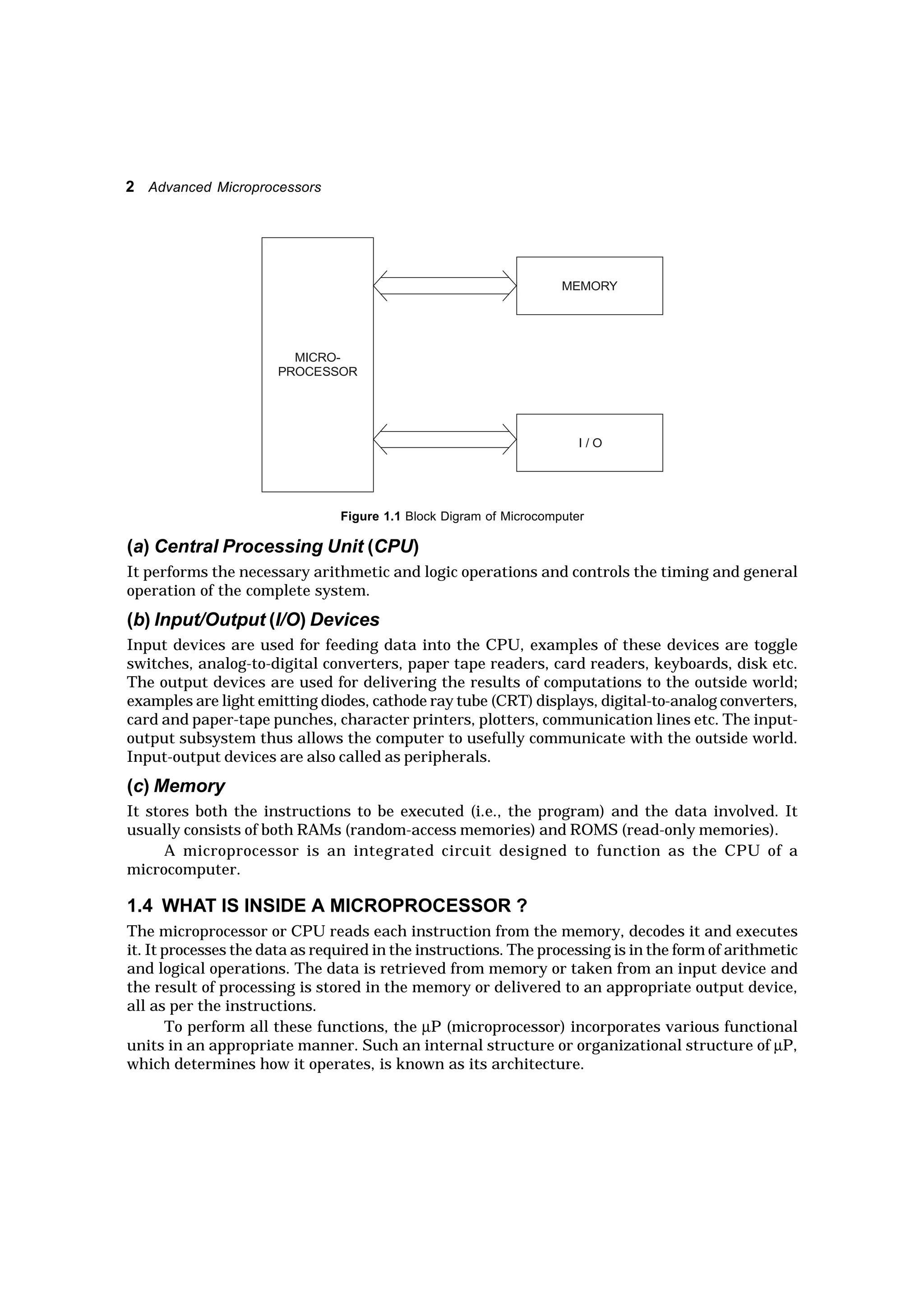
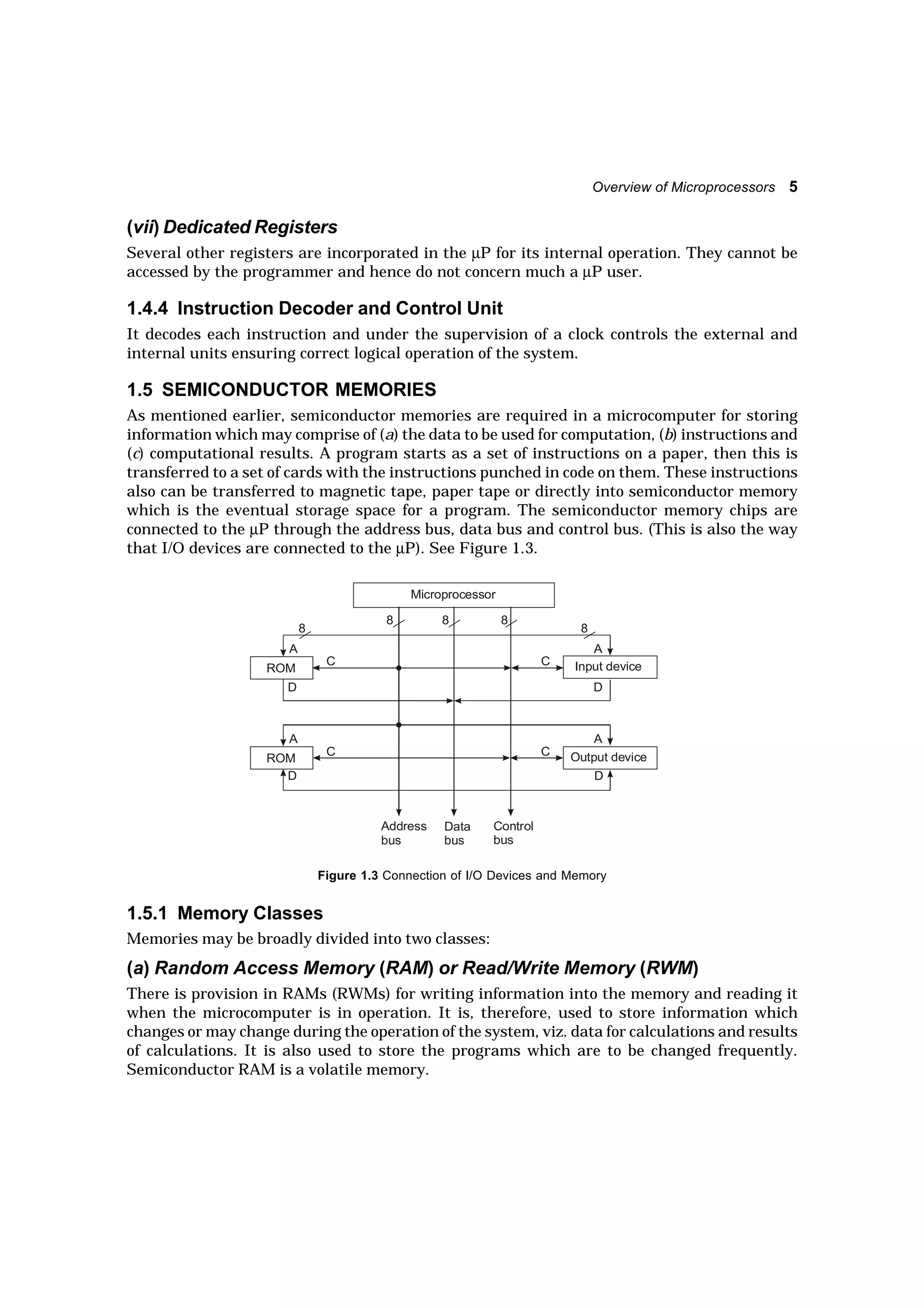
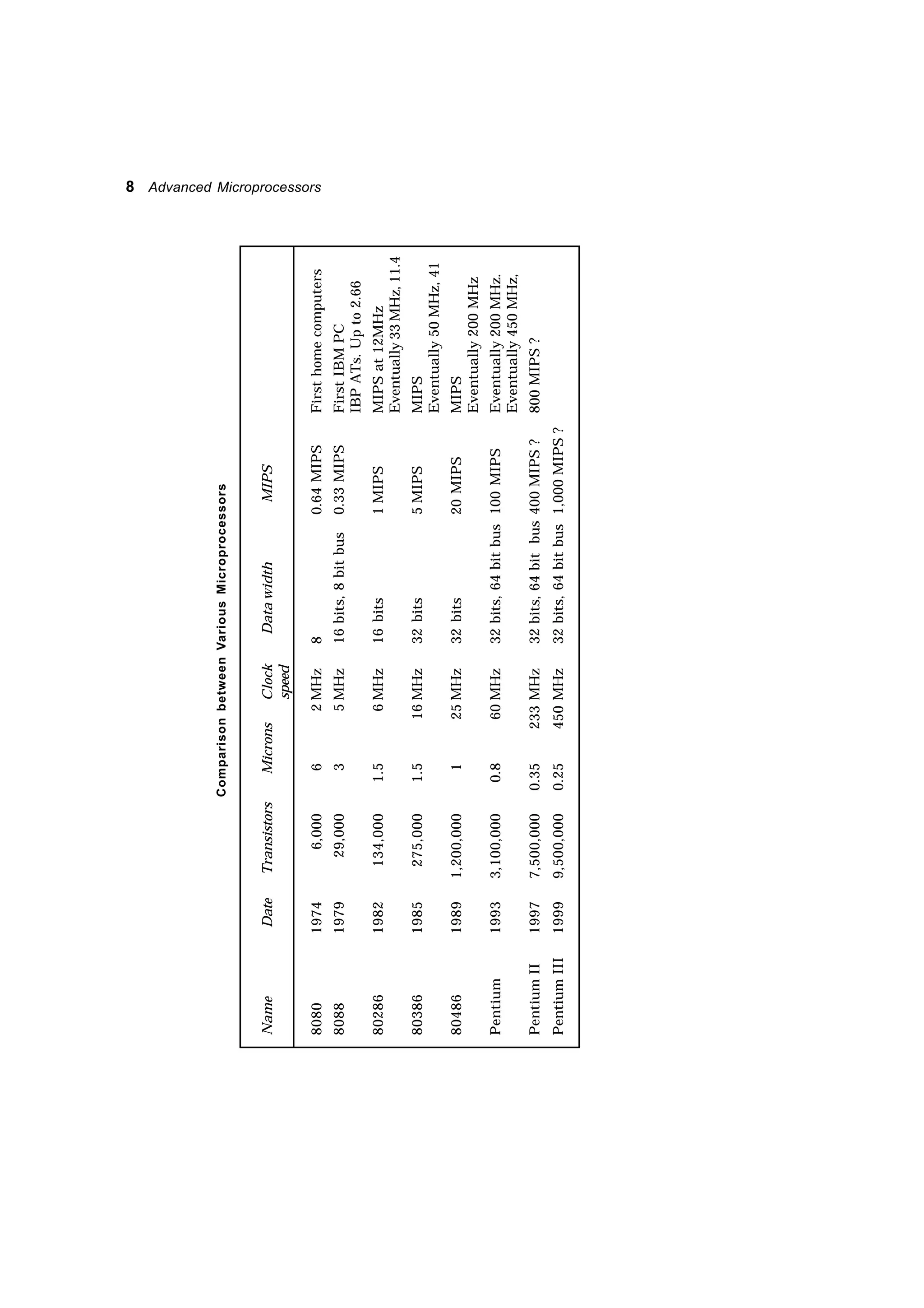
A microprocessor is an integrated circuit designed to function as the CPU of a microcomputer. It reads instructions from memory, decodes and executes them, and processes data as required. The microprocessor incorporates various functional units like an ALU, registers, instruction decoder, and control unit. It communicates with external memory and I/O devices via address, data, and control buses. Memory is used to store both instructions and data, and comes in RAM and ROM varieties. Interfaces are needed to connect peripherals to the microprocessor and handle functions like buffering, addressing decoding, and timing/control of data transfers. Software for microprocessors includes machine language programs and programs written in assembly/high-level languages which are