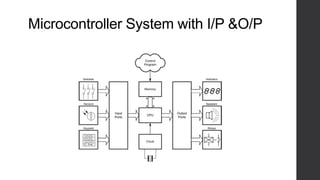
The document discusses microprocessors and their components. It describes how a microprocessor takes in numbers, performs arithmetic or logical operations according to a stored program, and produces results. The key components of a microprocessor system are the central processing unit (CPU), memory (RAM and ROM), and input/output interfaces. The CPU contains registers, an arithmetic logic unit, and a control unit. Clocks synchronize data movement and memory is addressed using address lines. Instructions are fetched and executed in machine cycles. Registers temporarily store data and addresses during operations.