1. Pressing is the process of applying heat, pressure and moisture to shape garments. It flattens wrinkles, creates creases, and prepares garments for further assembly or finishing.
2. There are two main types of pressing: under pressing during construction, and top pressing after assembly. Garments require varying levels of pressing depending on style and construction.
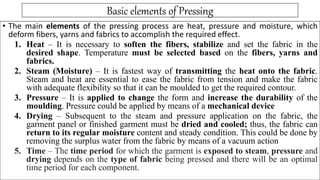
3. Basic pressing elements are heat, steam or moisture, and pressure. Heat softens fibers while steam transmits heat and moisture helps shape fabric. Pressure further sets the shape and durability.