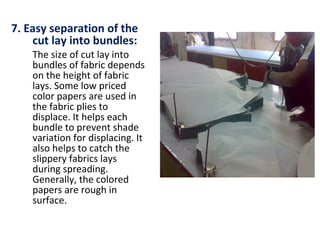
This document discusses the requirements for fabric spreading in garment manufacturing. It begins by introducing the author and their background. The document then covers 10 key requirements for proper fabric spreading: 1) the fabric must be flat, 2) have correct ply tension, 3) ply alignment, 4) correct ply direction and stability, 5) elimination of static electricity, 6) elimination of fabric flaws, 7) easy separation of cut layers, 8) avoidance of ply fusion during cutting, 9) avoidance of spread distortion, and 10) matching of checks and stripes. It also briefly discusses pattern making, marker making, and cutting methods. The author provides links to related textile technology Facebook pages and their blog.