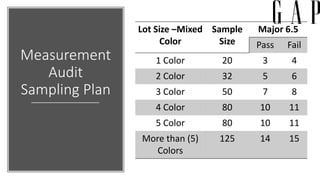
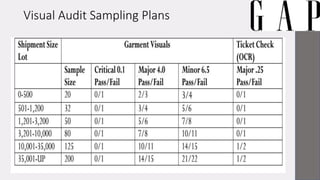
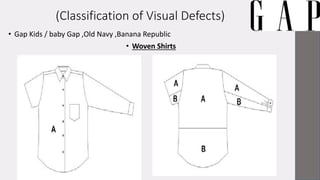
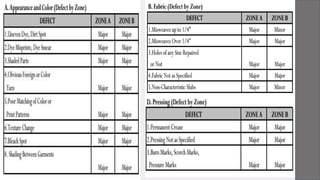
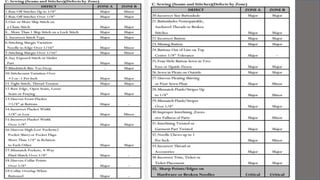
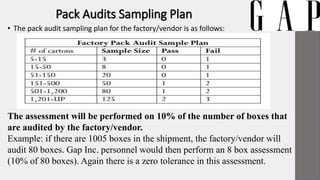
Gap Inc. is a leading global apparel retailer founded in 1969 in San Francisco. It operates brands like Gap, Banana Republic, Old Navy, and Athleta. The document outlines Gap Inc.'s quality assurance policies and procedures for vendors, including standards for defects, inspection methods for materials, production processes, and final products. Vendors must meet Gap's requirements for safety, measurements, visual quality, and packaging to ship orders.