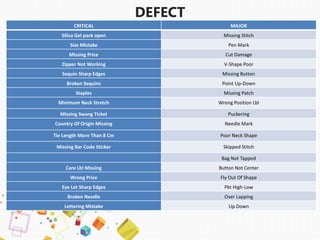
This presentation provides an overview of Khaled MD Ridwan's industrial training at Palmal Group, one of the largest apparel manufacturers in Bangladesh. The presentation covers Palmal's history and awards, its 21 factories and manufacturing units, key departments like merchandising, quality control, and compliance. It summarizes the production process from sample making to finishing, washing, embroidery, and final inspection before shipment.