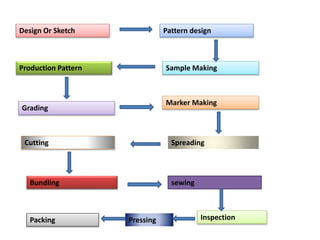
Garment manufacturing involves several key steps:
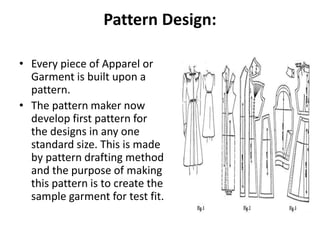
1. Design and pattern development where sketches are turned into patterns for specific sizes.
2. Sample making where the first patterns are sewn into prototypes to check fit and design.
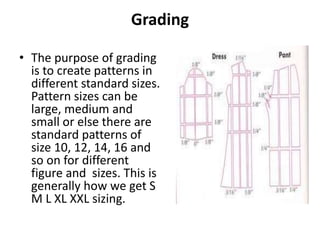
3. Grading to create patterns in different standard sizes.
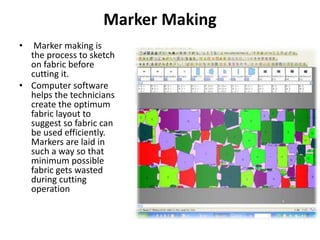
4. Cutting of fabric according to the graded patterns which is then bundled for sewing.