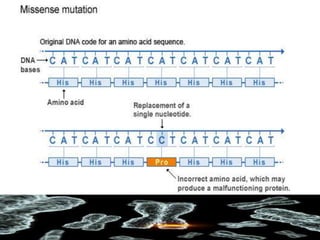
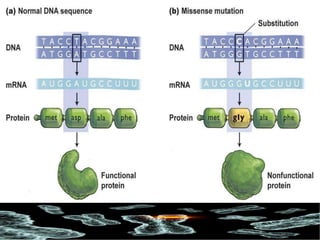
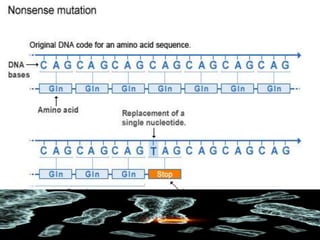
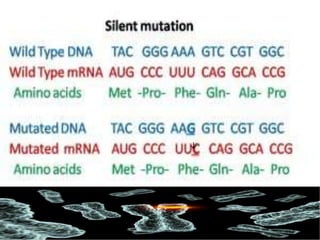
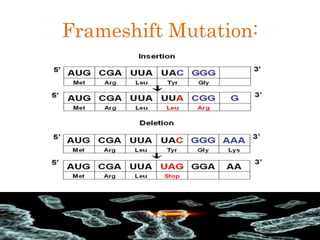
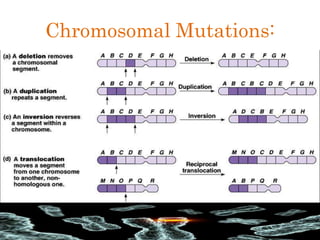
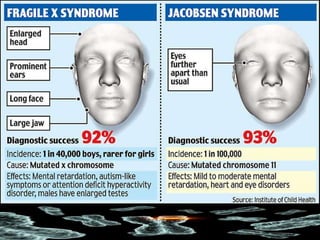
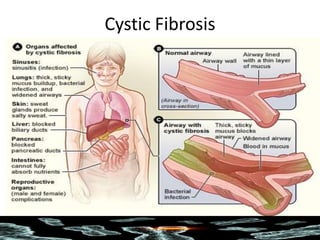
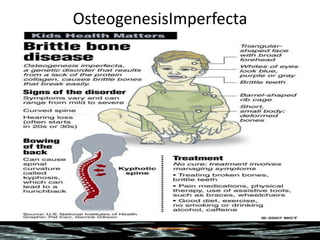
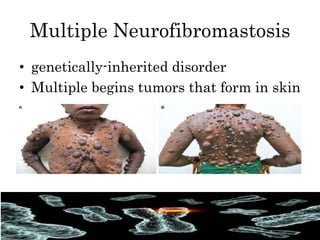
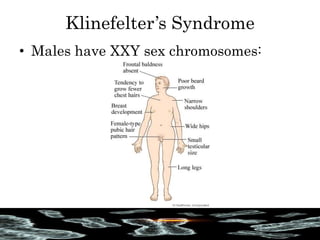
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can be caused by mistakes during DNA replication or by environmental factors like radiation. There are several types of mutations including point mutations, frameshift mutations, and chromosomal mutations. Point mutations involve a single DNA building block and can be missense, nonsense, or silent. Frameshift mutations are insertions or deletions that affect all subsequent amino acids. Chromosomal mutations involve changes in chromosome structure like translocations or deletions. Genetic mutations can cause disorders like cystic fibrosis, fragile X syndrome, and Klinefelter's syndrome.