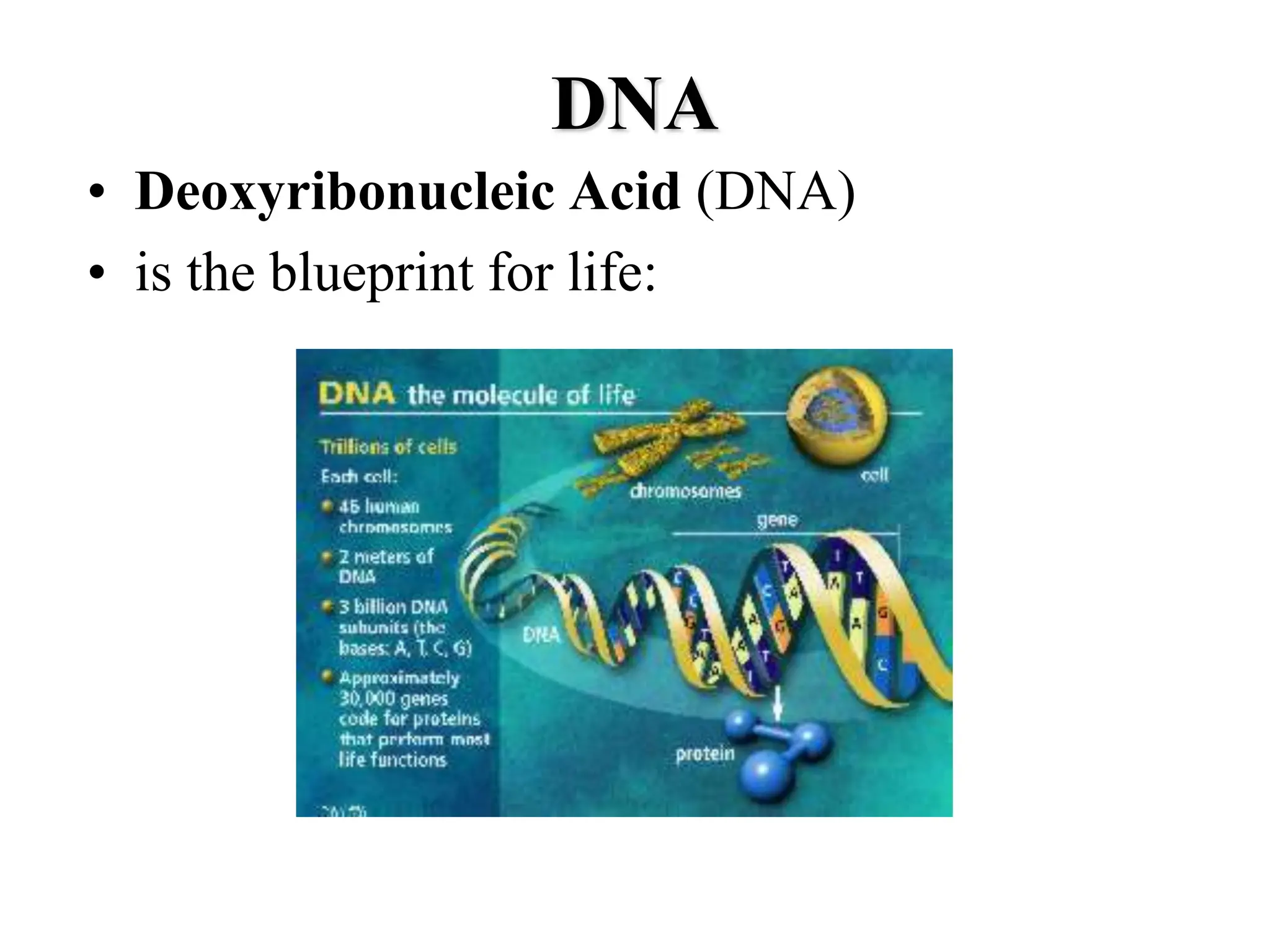
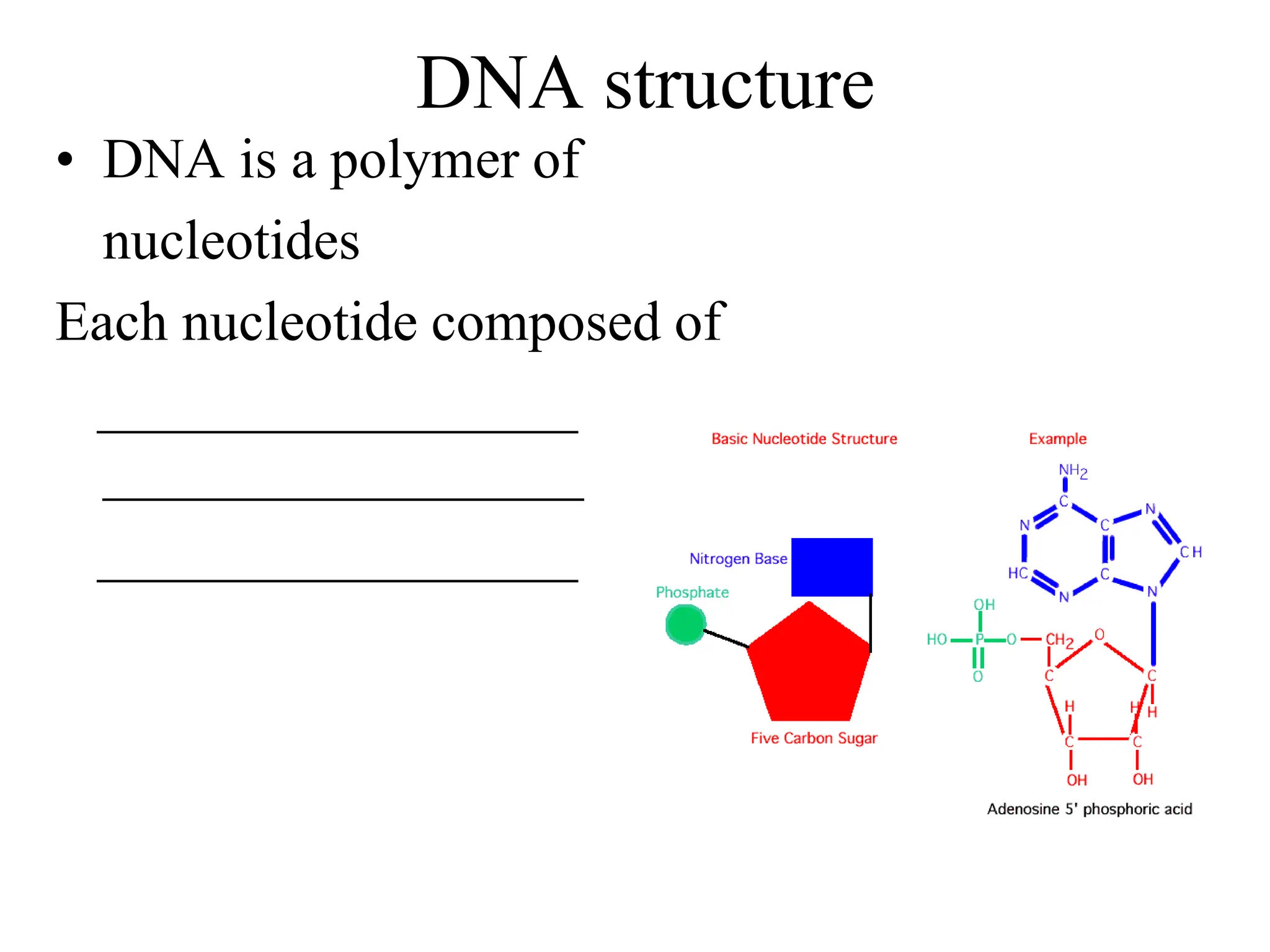
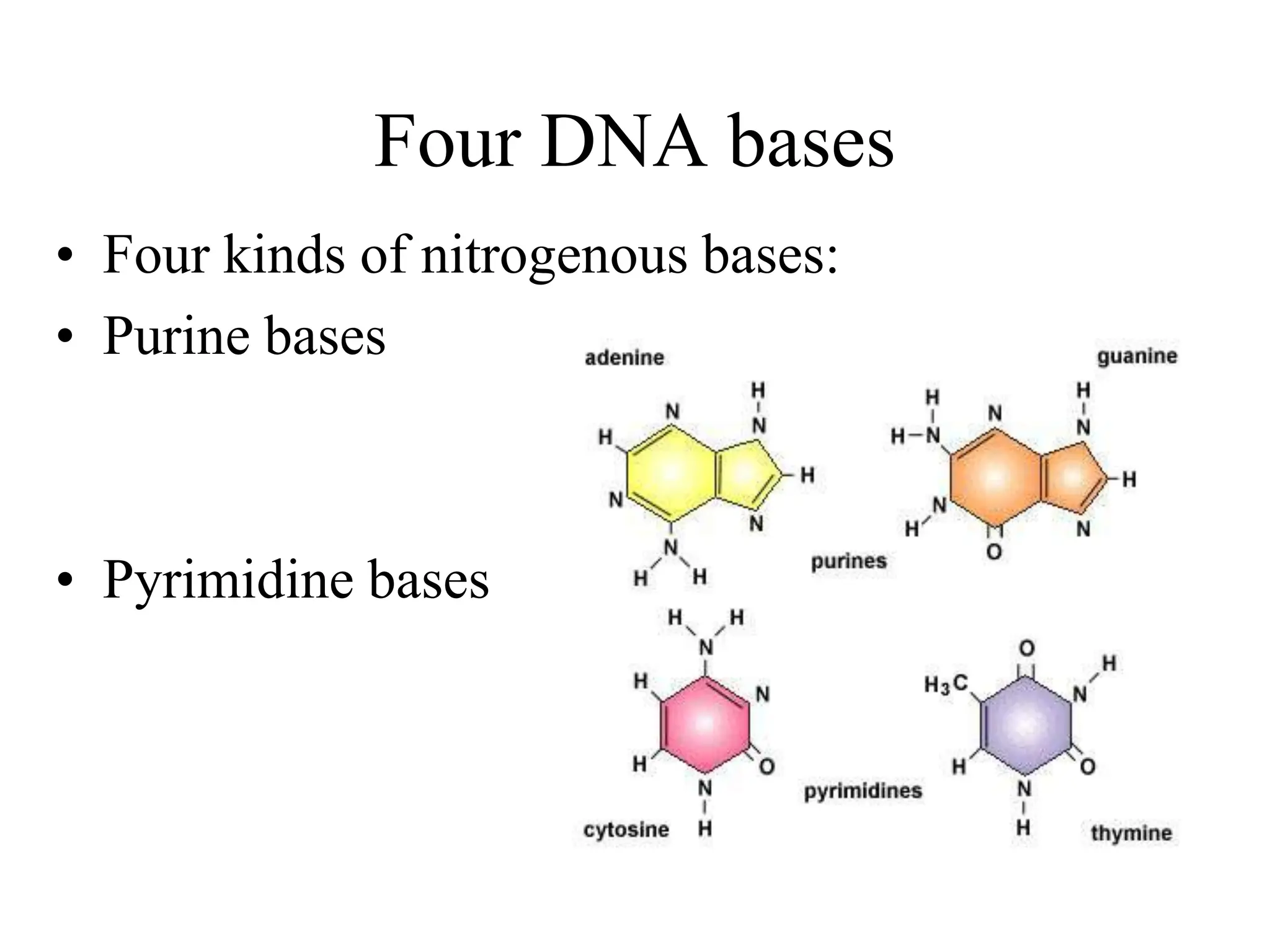
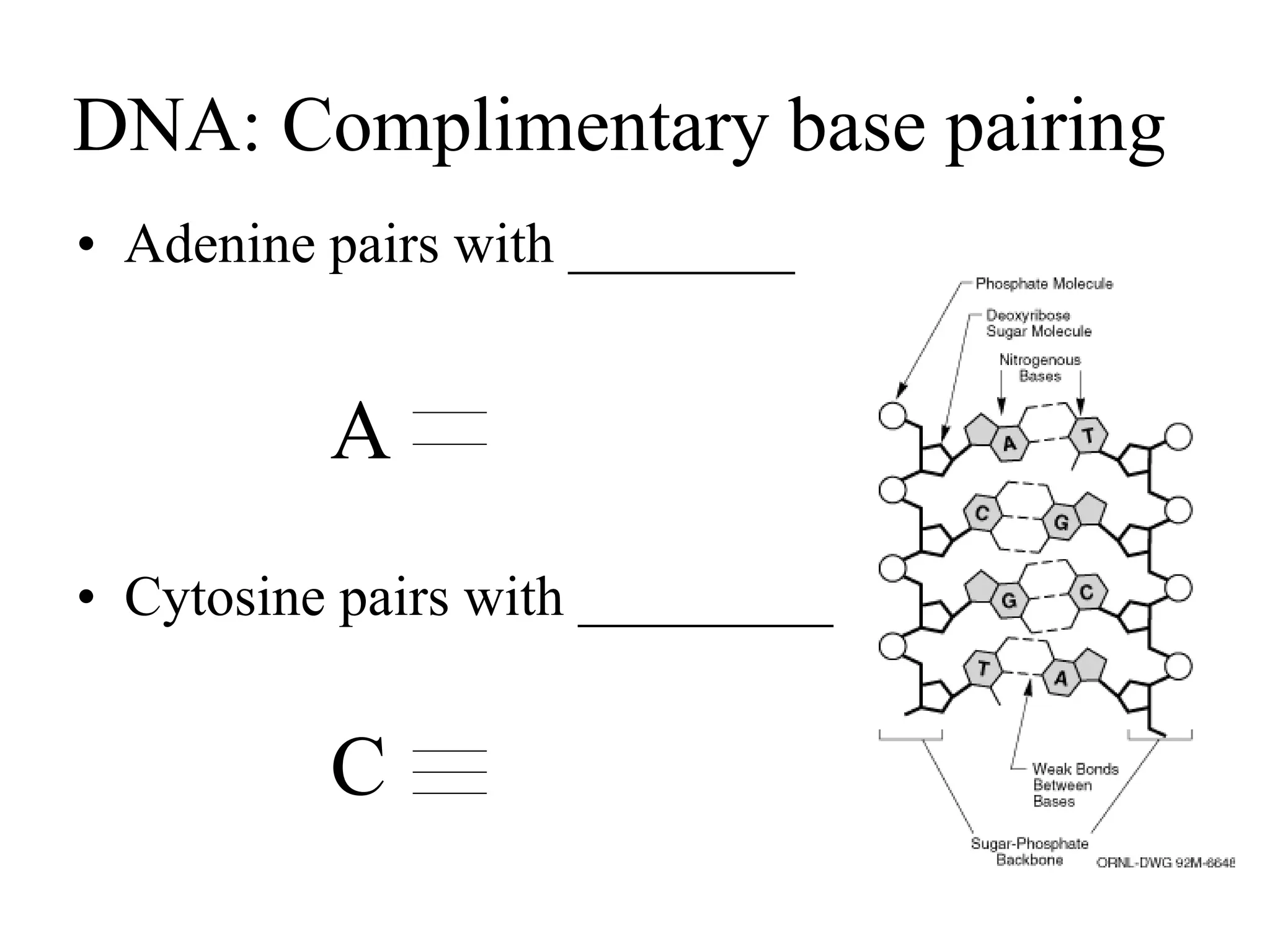
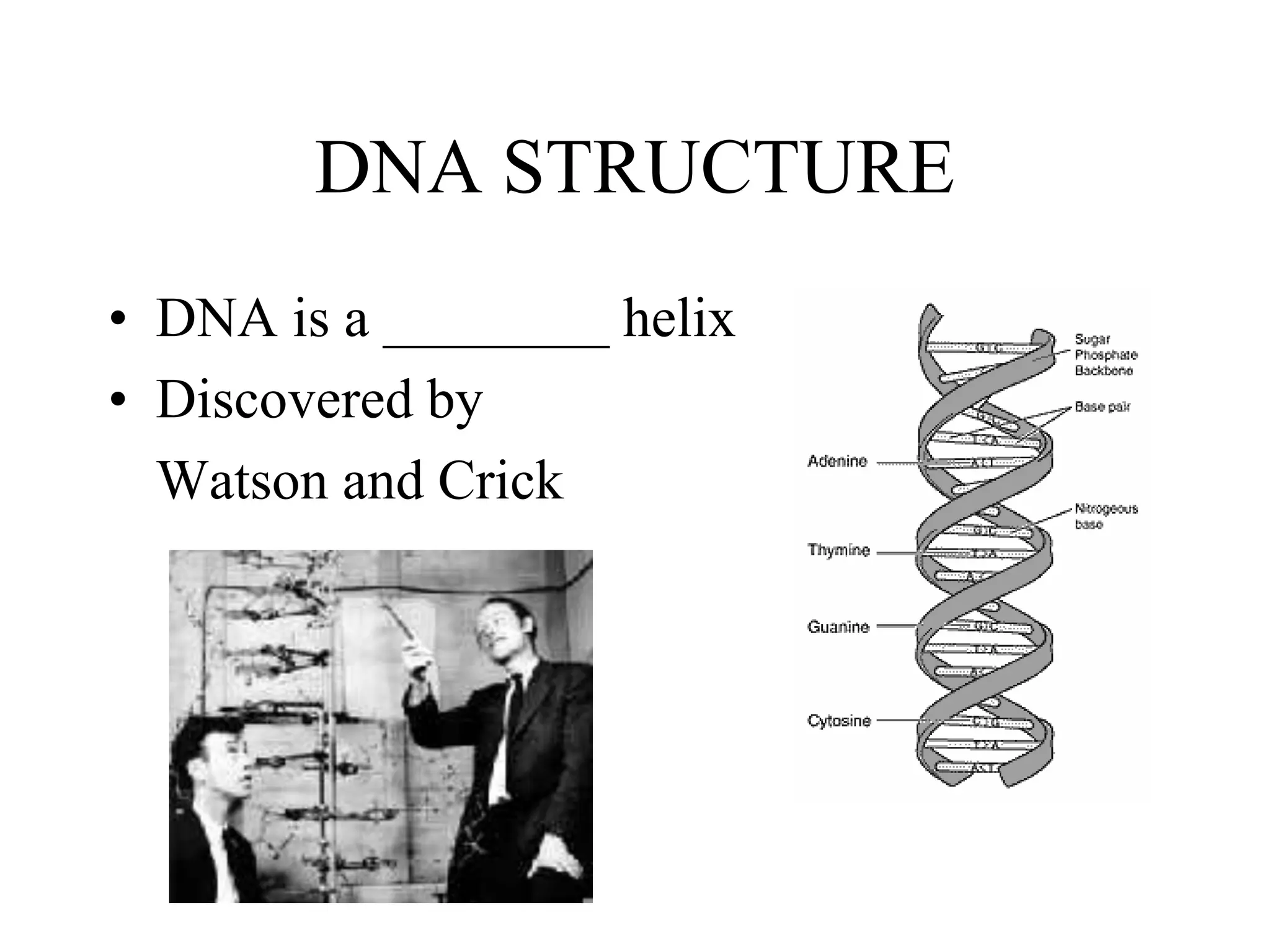
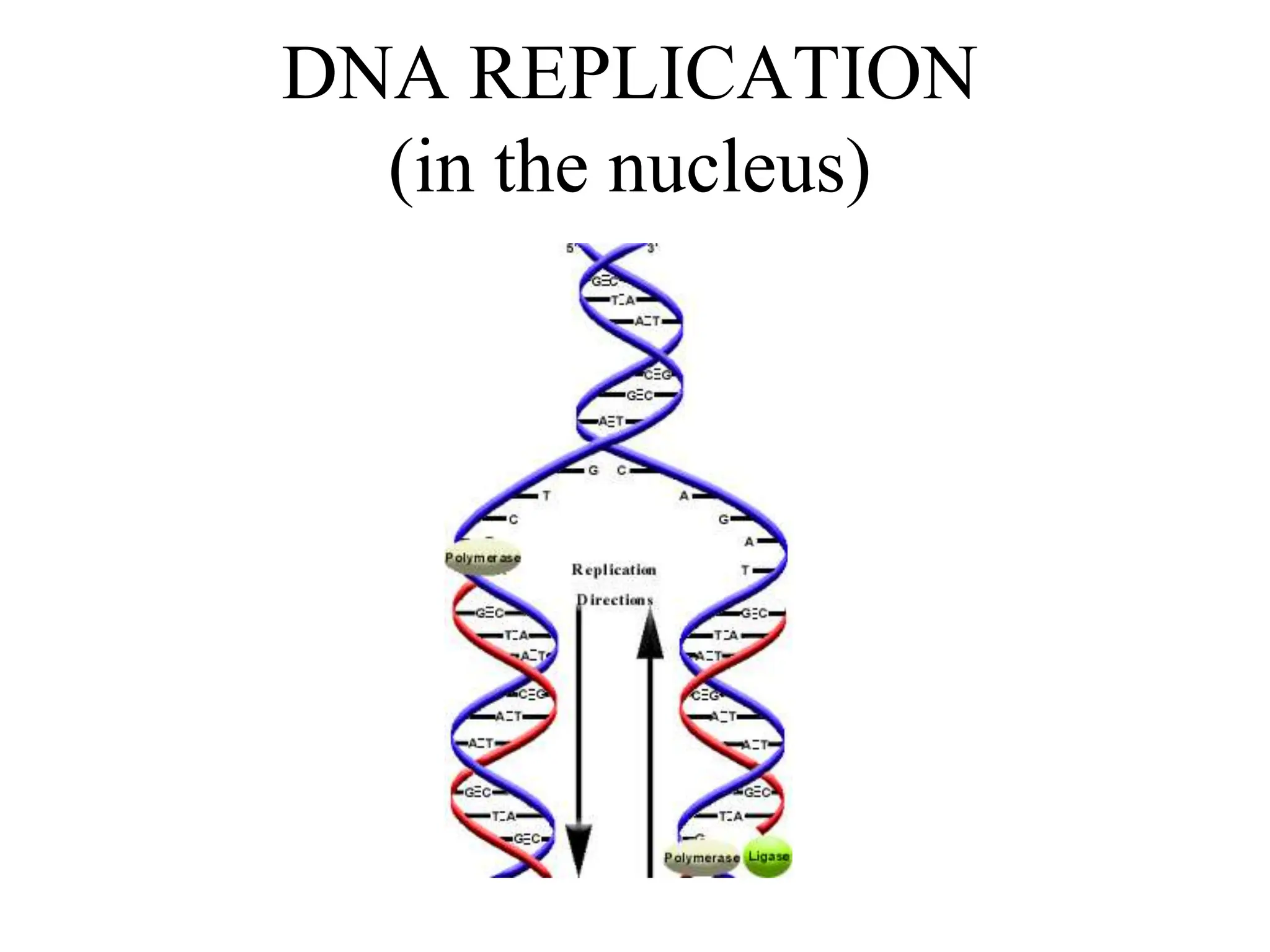
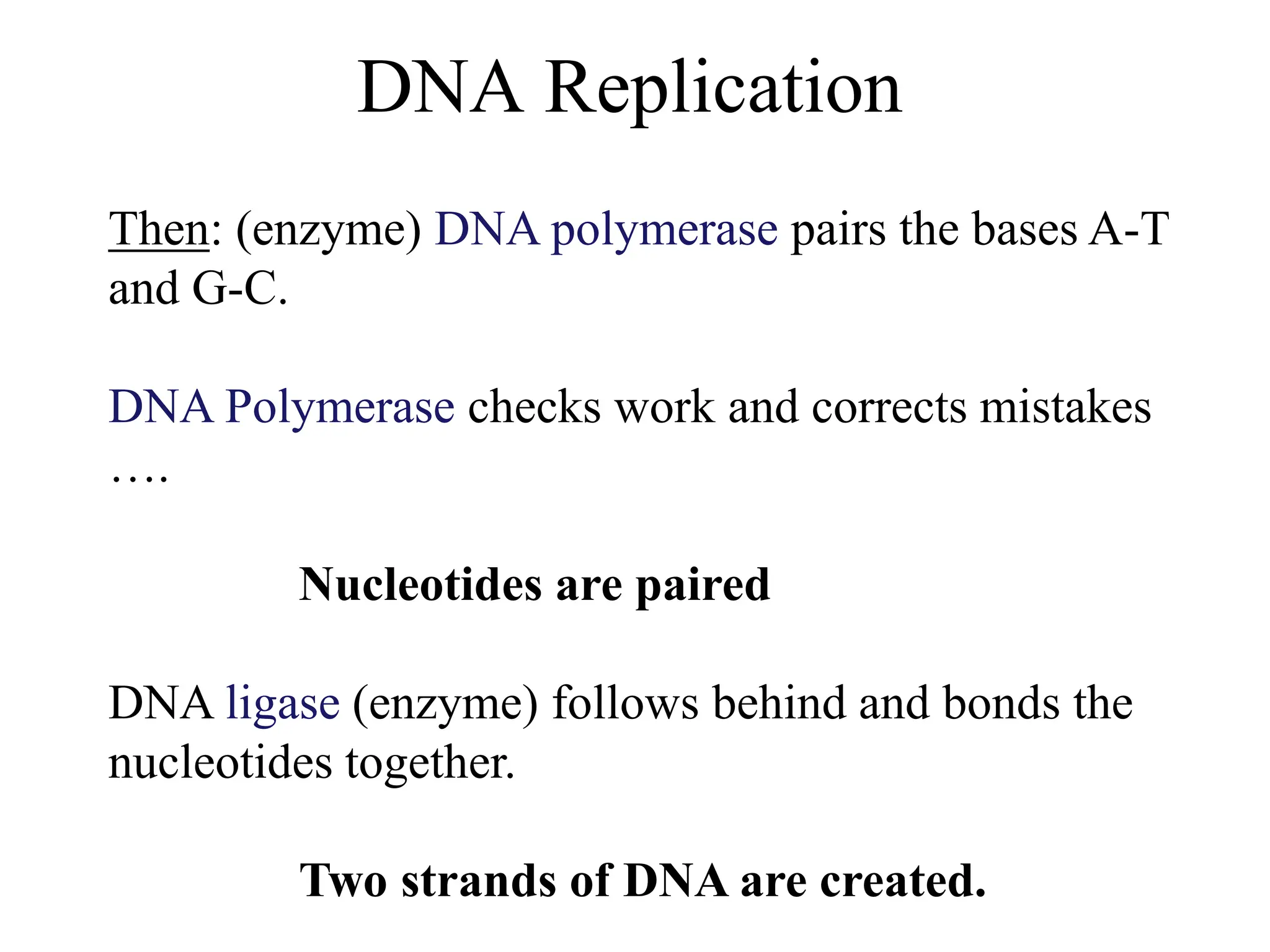
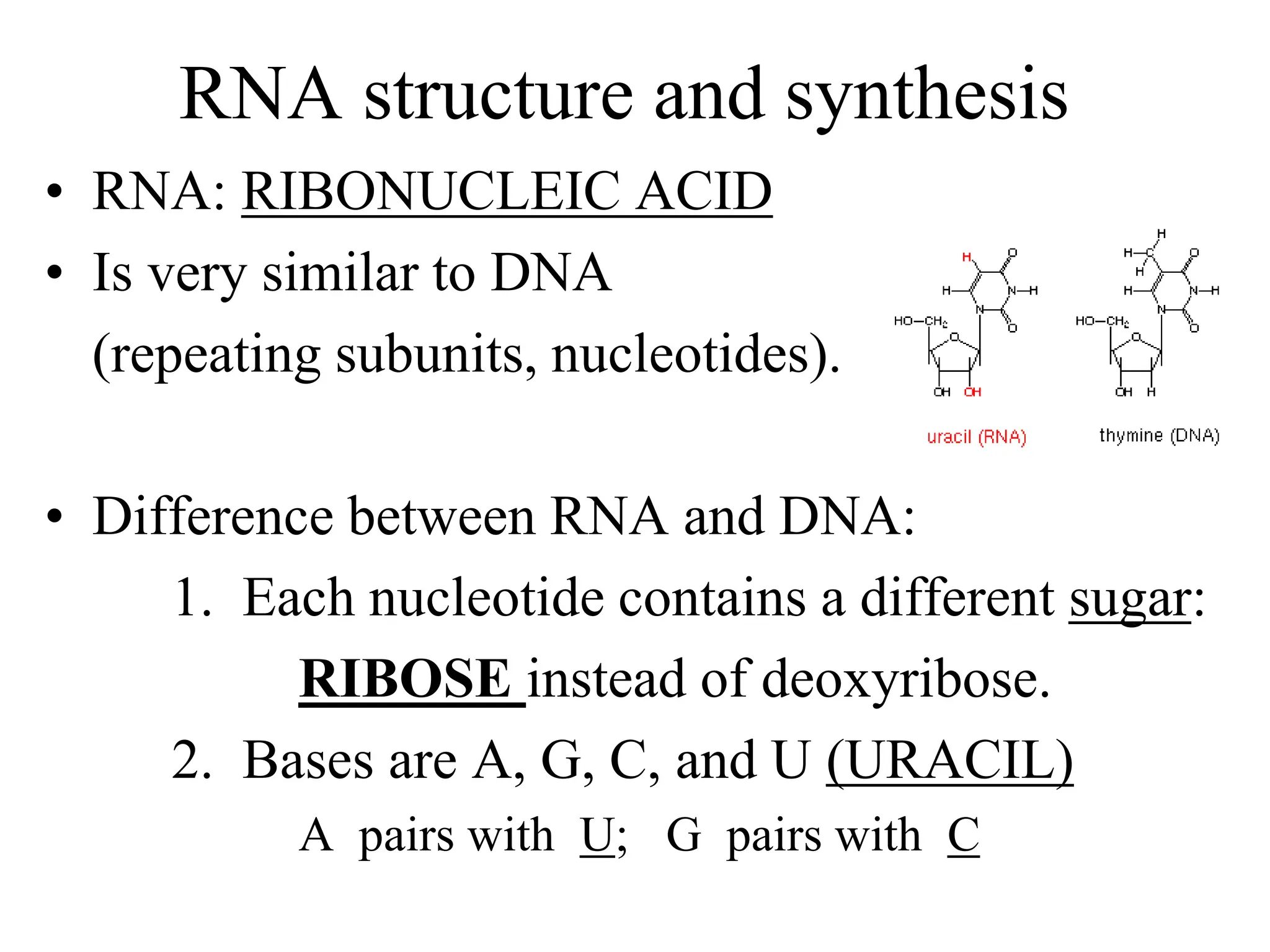
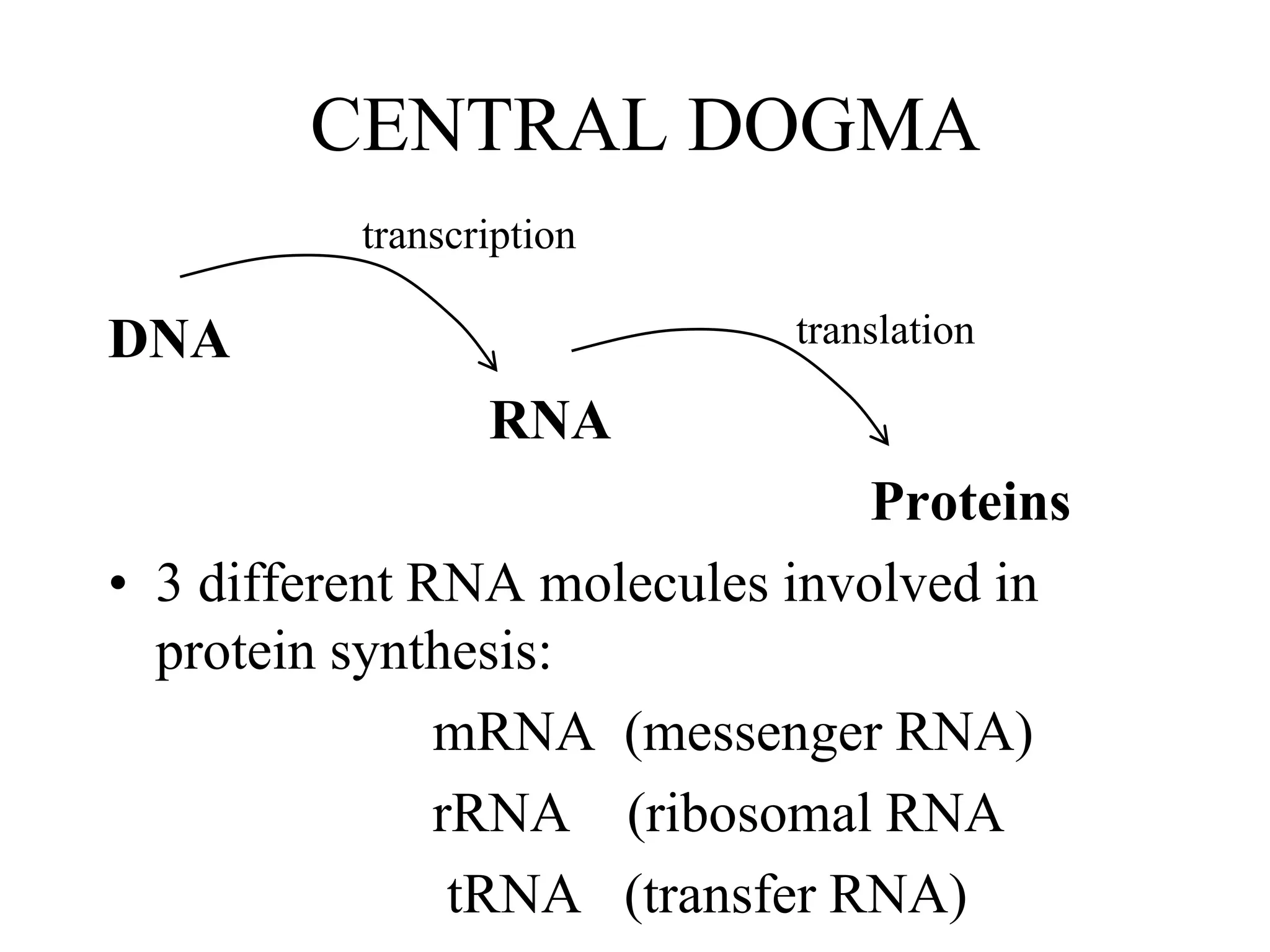
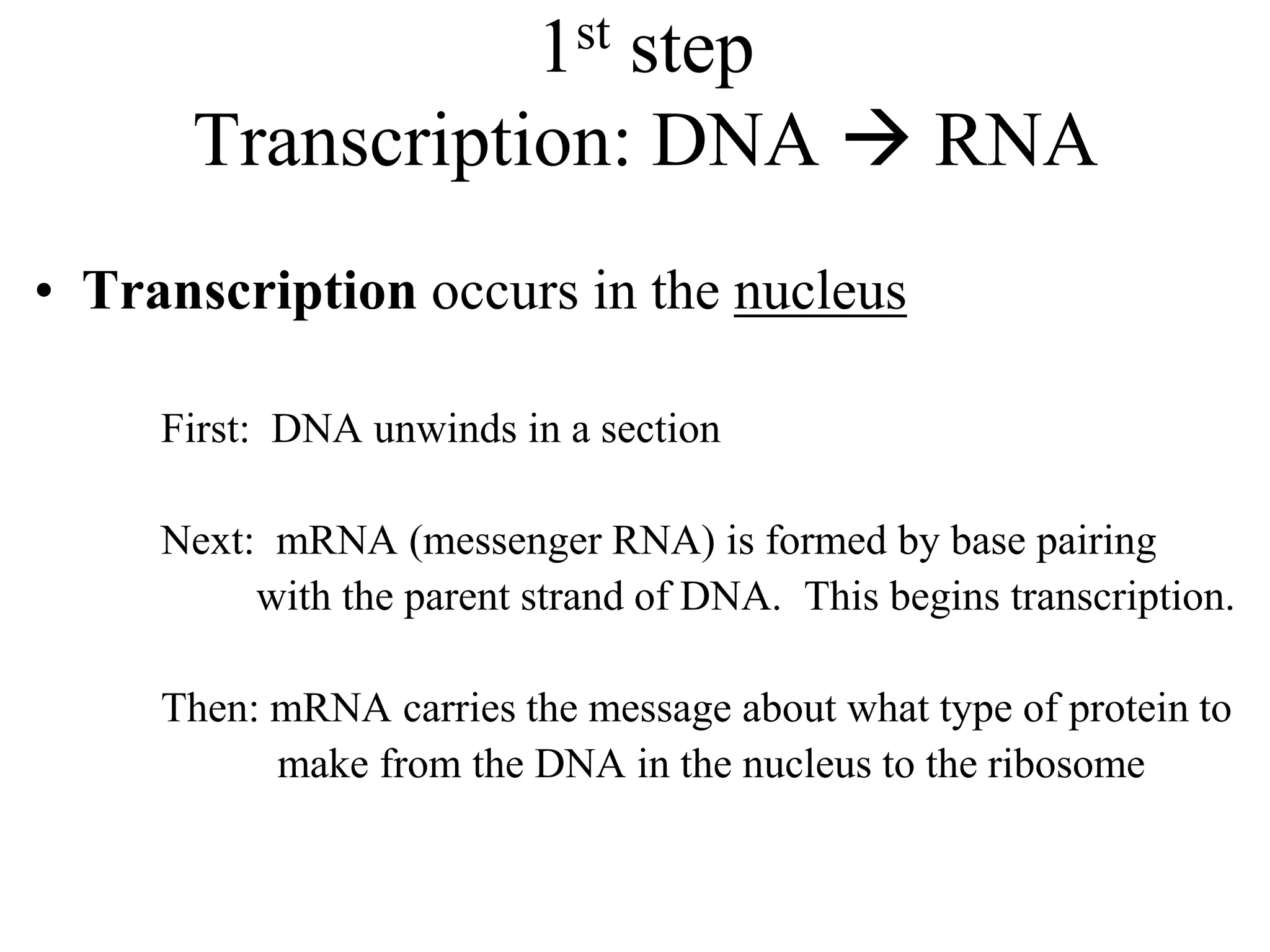
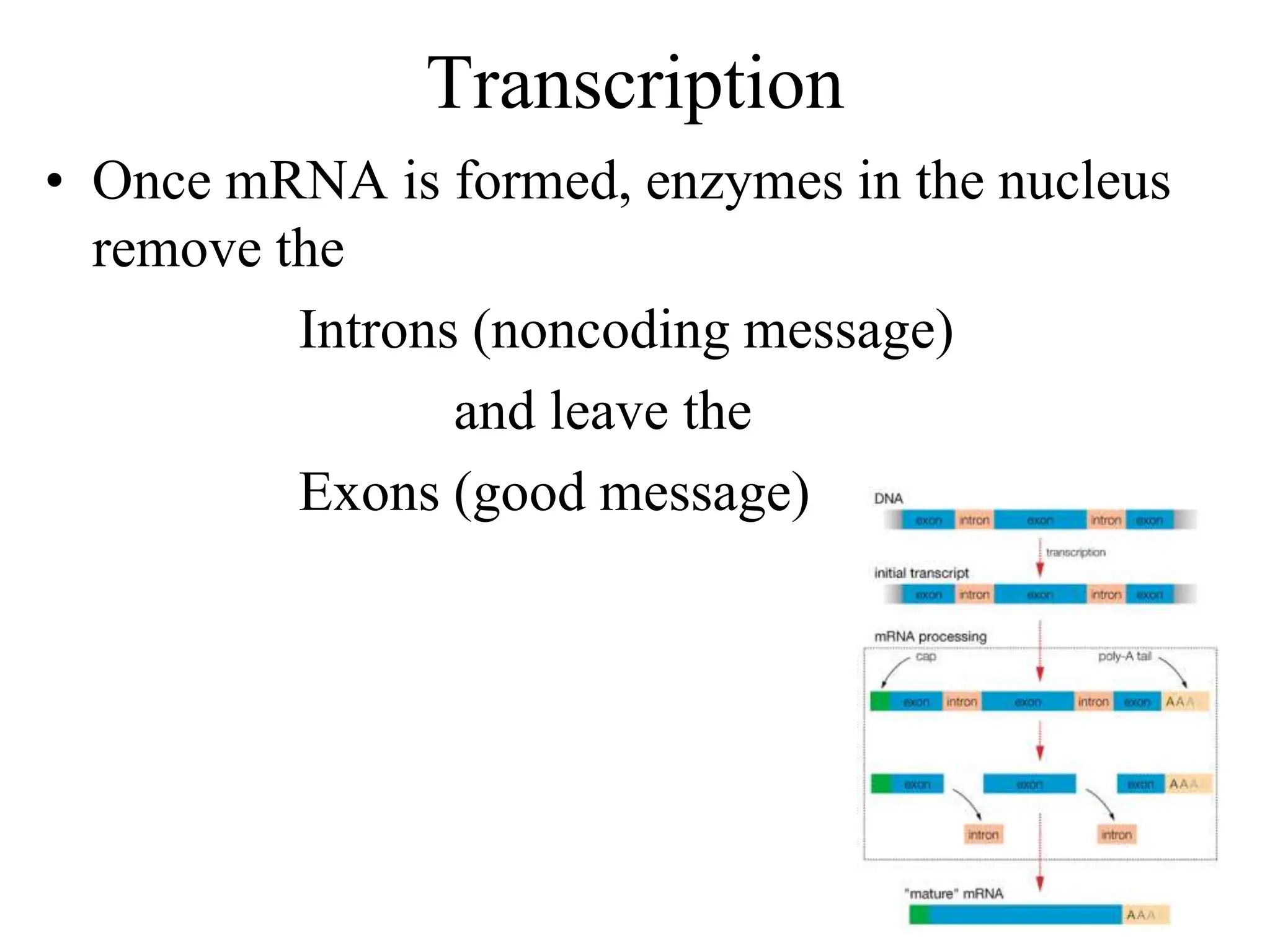
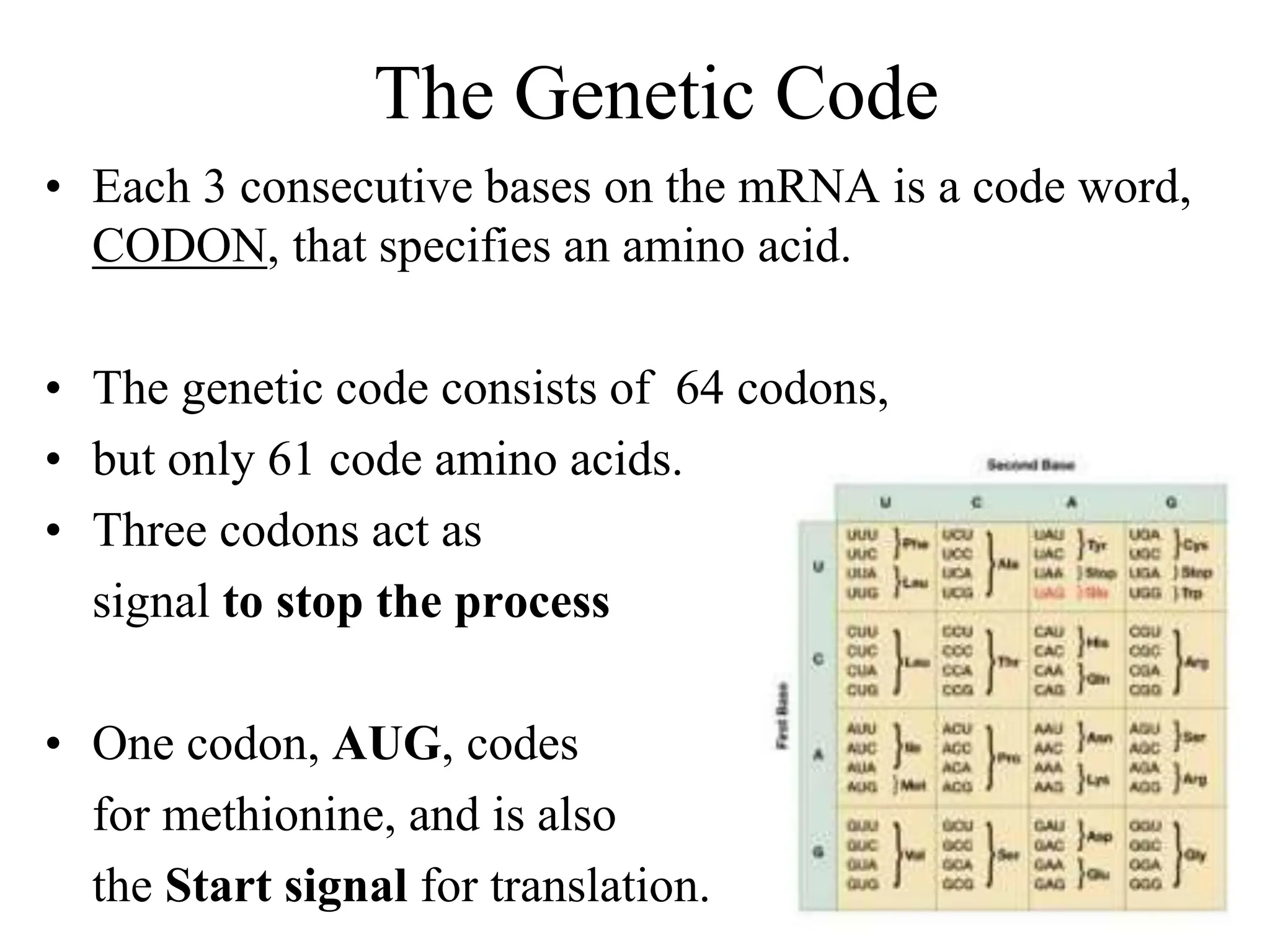
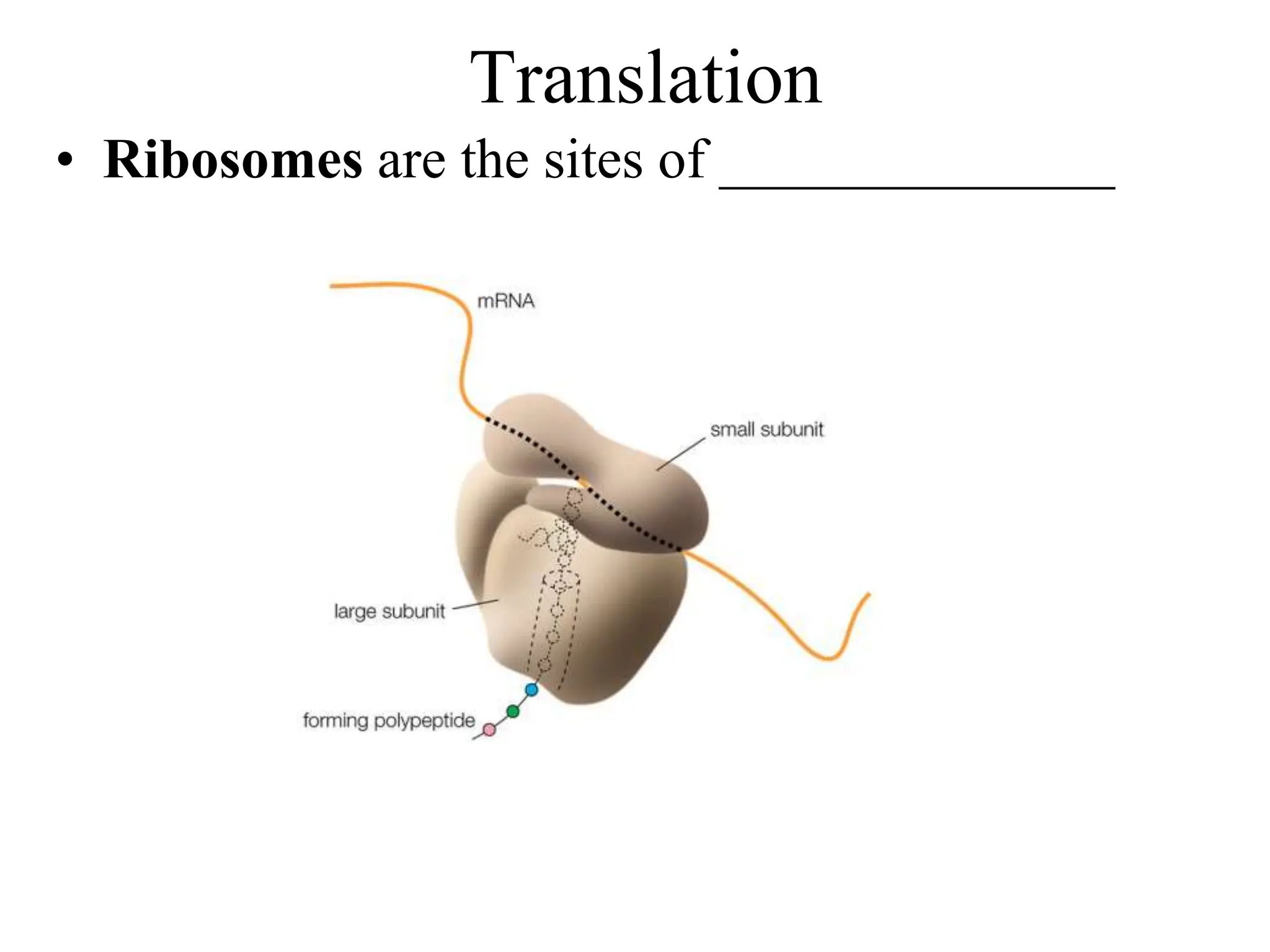
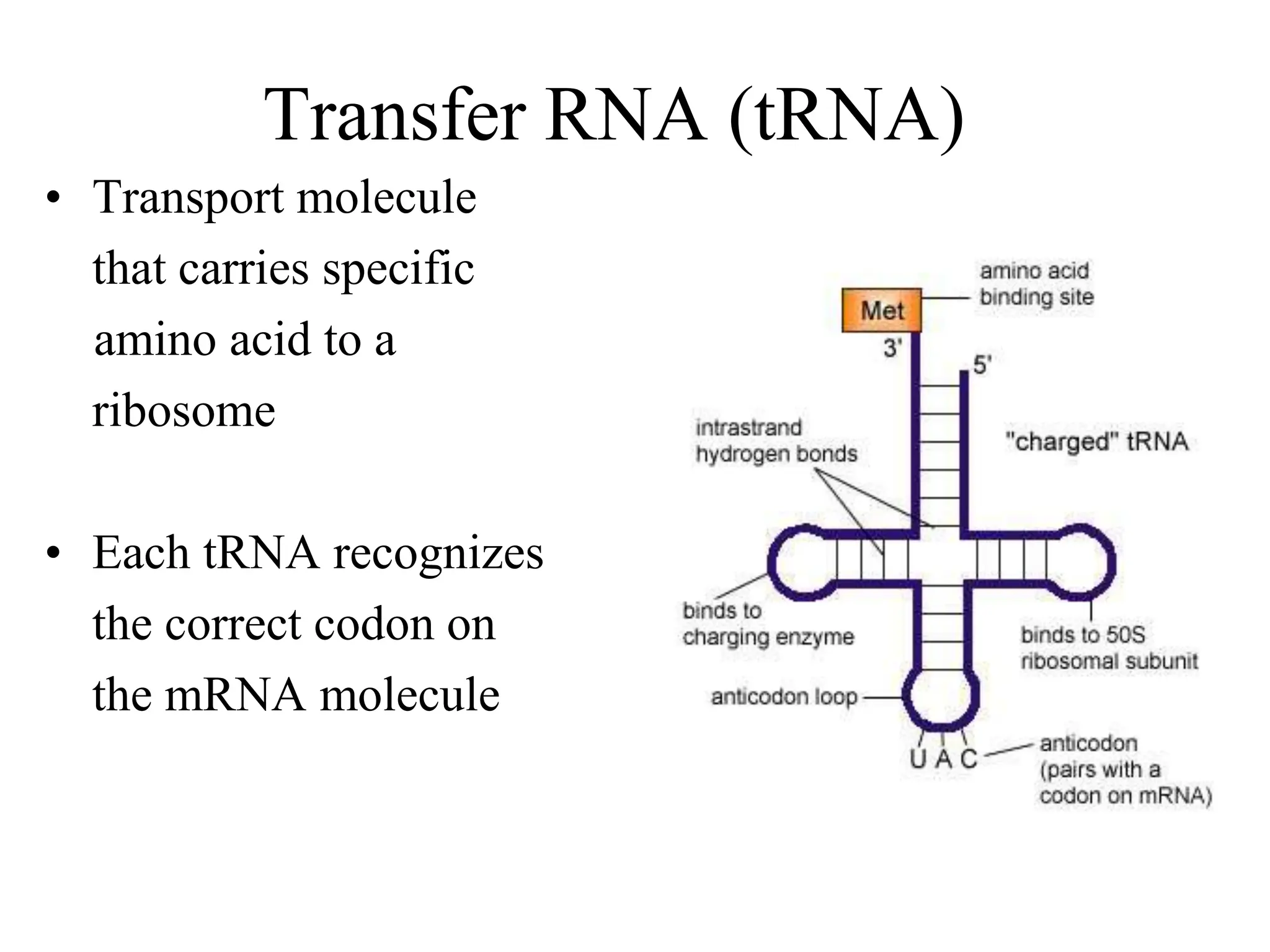
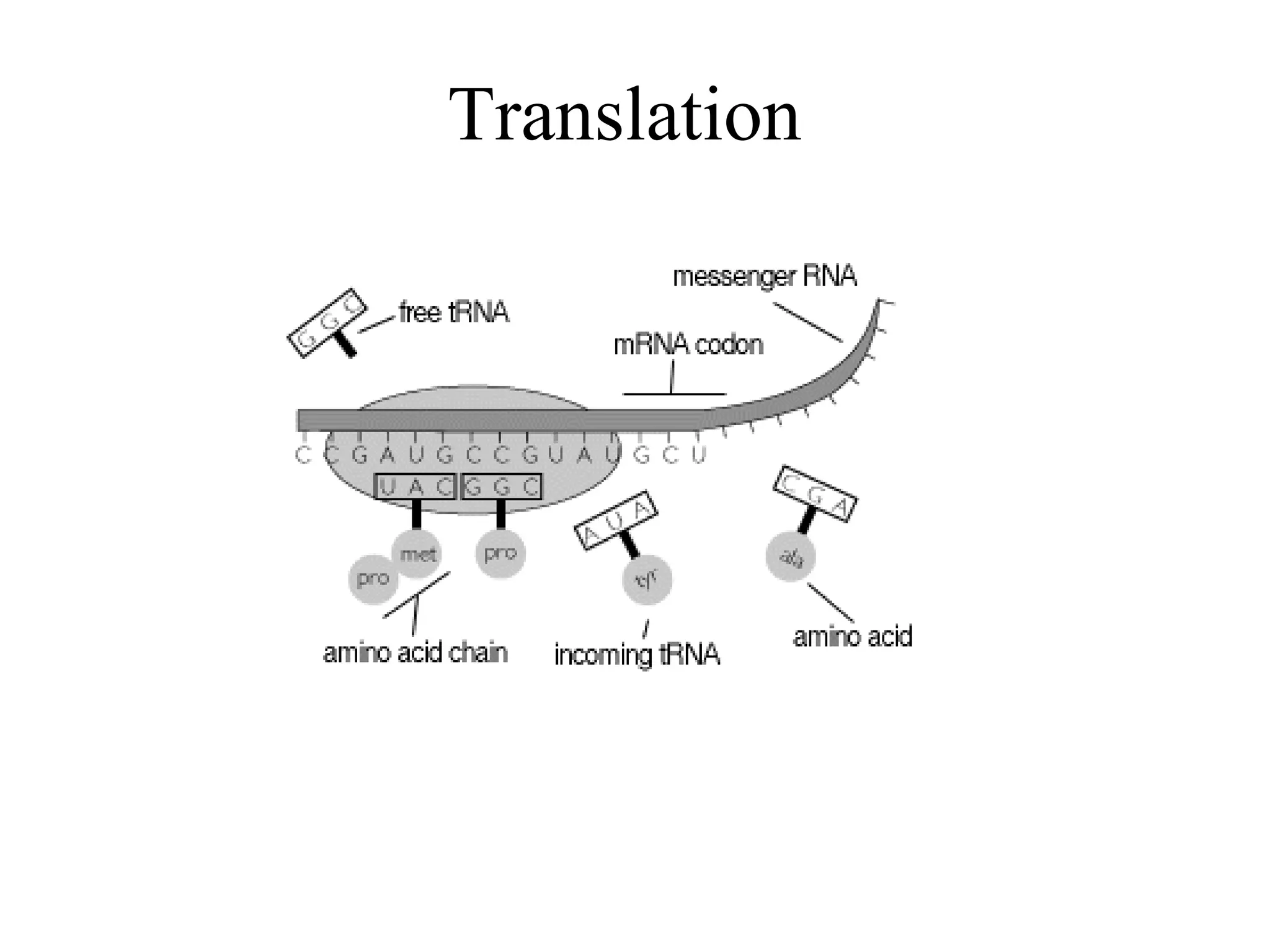
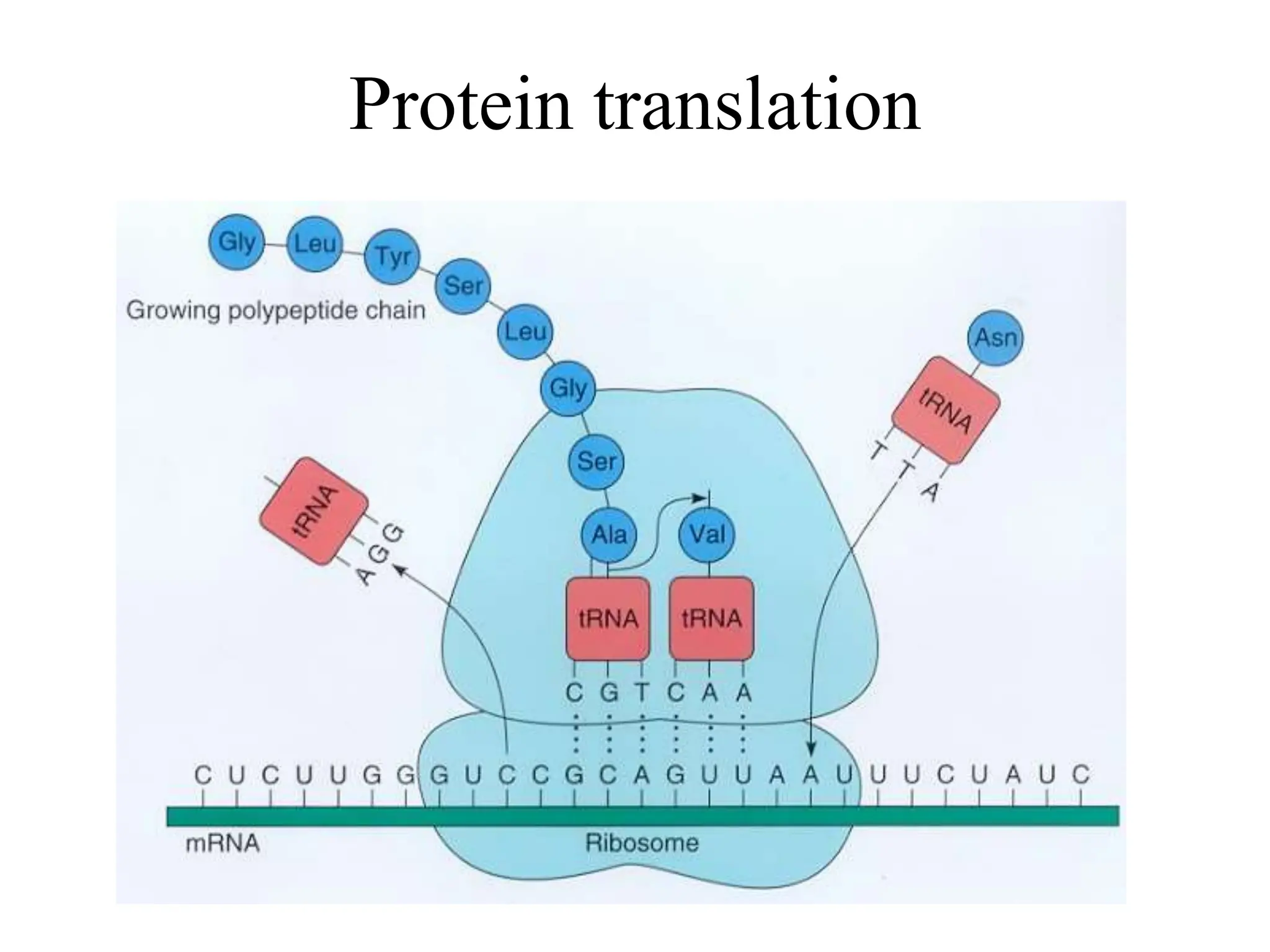
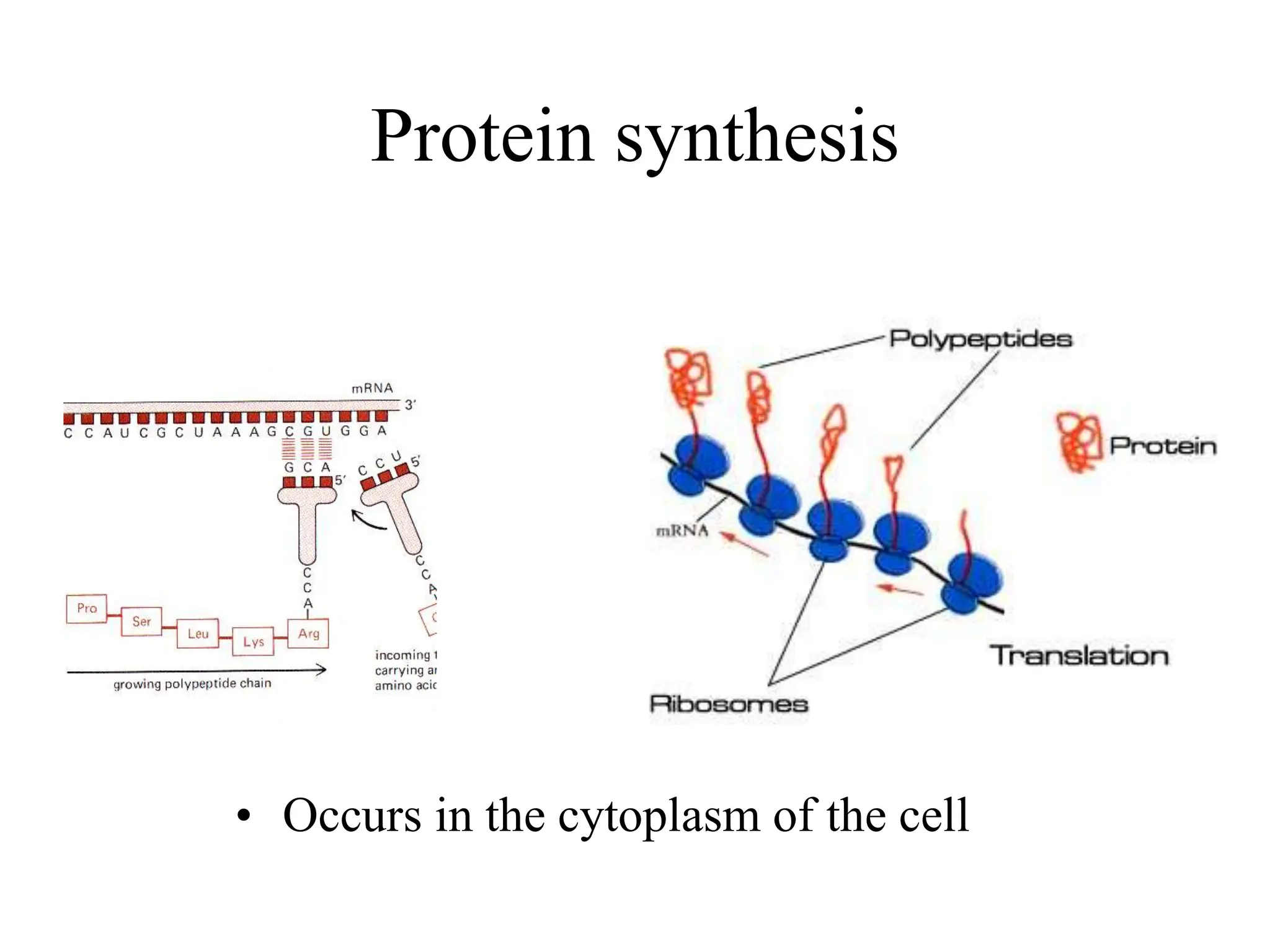
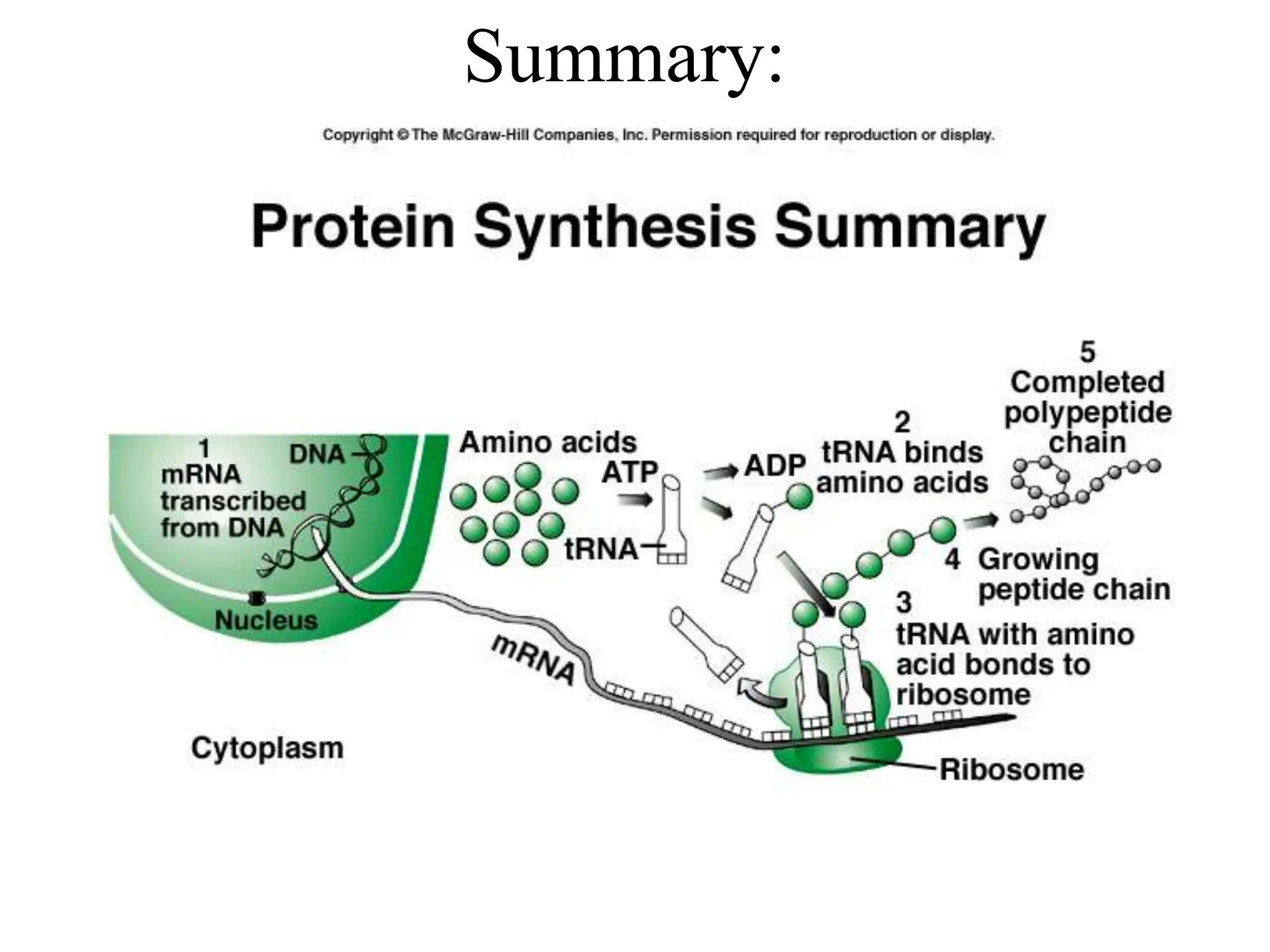
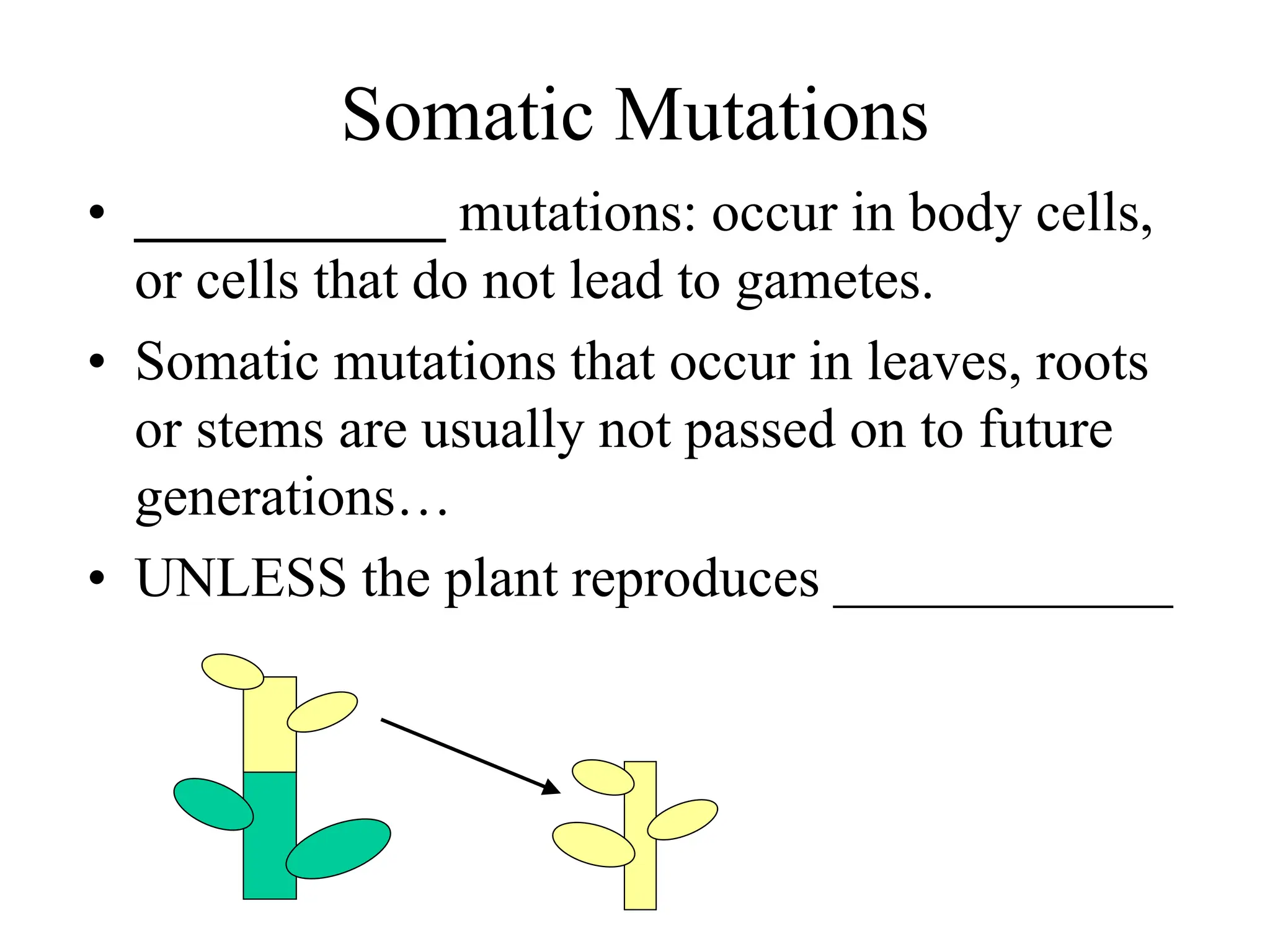
DNA contains the genetic blueprint and is made up of nucleotides. It takes the shape of a double helix and replicates before cell division. During transcription, a complementary mRNA copy is made from DNA in the nucleus. The mRNA then transports the genetic message to the cytoplasm for translation by ribosomes into proteins. Transfer RNA molecules ferry amino acids to the ribosome according to mRNA codons to produce a polypeptide chain. Mutations in DNA can cause changes to the genetic code and result in hereditary or somatic effects.