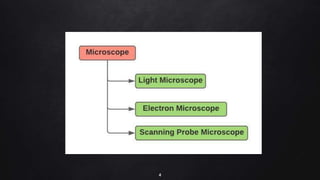
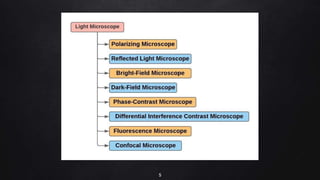
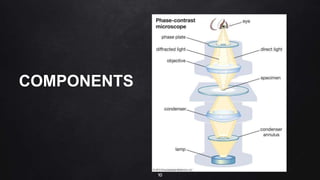
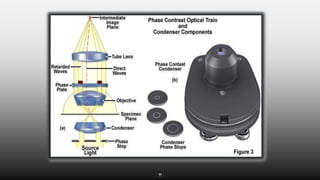
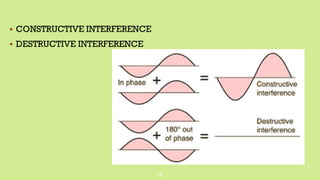
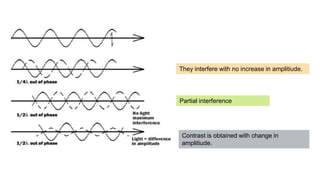
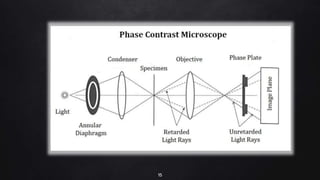
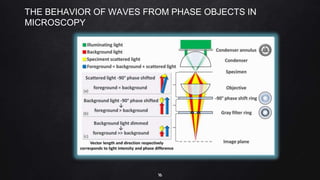
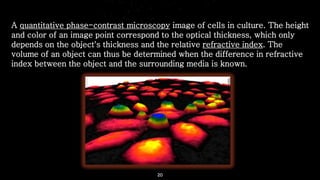
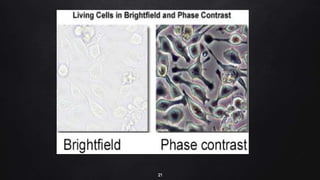
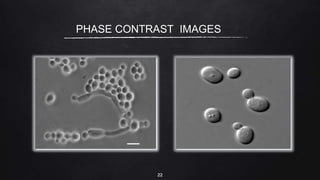
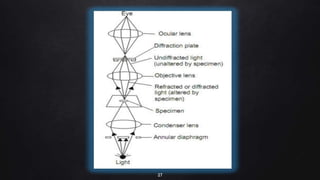
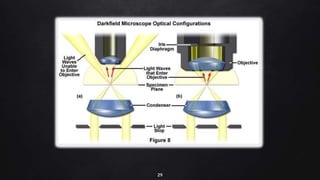
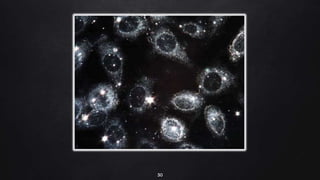
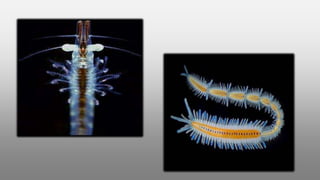
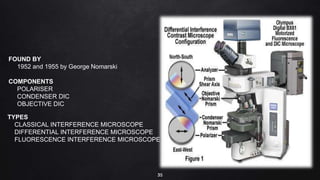
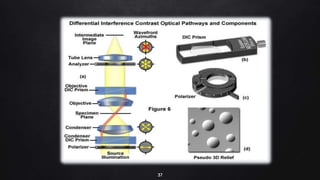
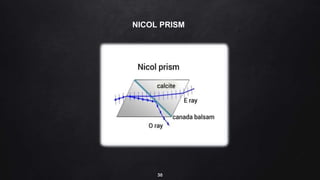
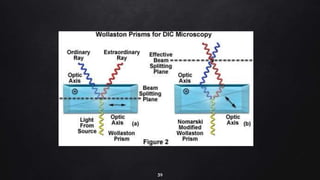
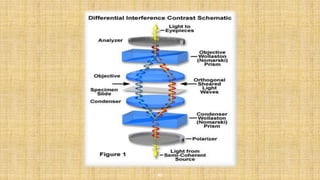
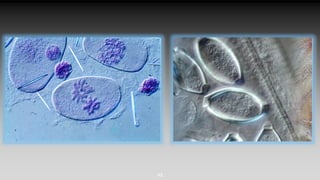
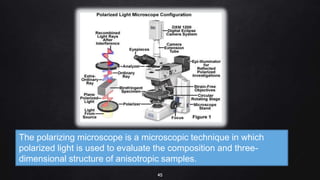
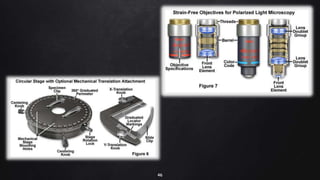
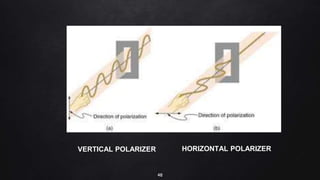
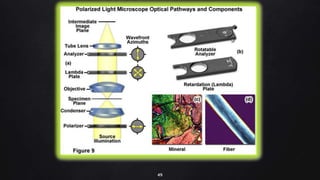
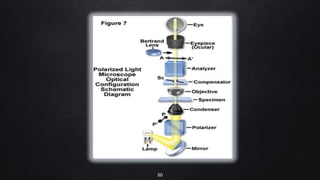
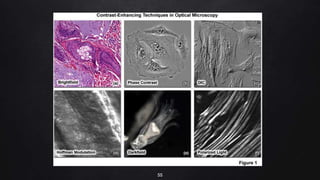
This document provides an overview of different microscopy techniques including phase contrast microscopy, dark field microscopy, interference microscopy, and polarized microscopy. It discusses the principle, components, working, uses, advantages, and limitations of each technique. Phase contrast microscopy produces high-contrast images of transparent samples by translating refractive index variations into changes in image amplitude. Dark field microscopy uses a condenser to create a hollow cone of light, allowing objects to appear bright against a dark background. Interference microscopy generates interfering beams to produce contrast based on refractive index differences. Polarized microscopy uses polarized light to evaluate anisotropic samples and identify structures like fibers and crystals.