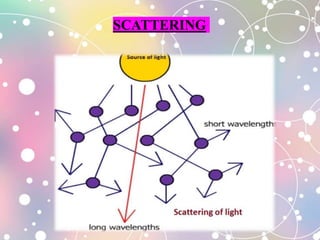
The document discusses microscopy, including the properties of light, components of the light microscope, and different types of microscopy. It describes the parts of the microscope like the eyepiece, objective lens, body tube, and stage. It explains concepts such as magnification, resolution, numerical aperture, reflection, refraction, and dispersion. The document also classifies microscopy techniques including phase contrast and fluorescence microscopy.